目录
习题课
一、比较两个数值的大小
要求:使用单分支,双分支,三目运算符三种方式
1.单分支
int main()
{
int a, b;
int max;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
max = a;
if (max < b)
{
max = b;
}
printf("%d", max);
}2.双分支
int main()
{
int a, b;
int max;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
if (a > b)
{
max = a;
}
else
{
max = b;
}
printf("%d", max);
}3.三目运算符
int main()
{
int a, b;
int max;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
max = a > b ? a : b;
printf("%d", max);
}二、比较三个数值的大小
要求:使用单分支,双分支,三目运算符三种方式
1.单分支
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
int max;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
max = a;
if (max < b)
{
max = b;
}
if (max < c)
{
max = c;
}
printf("max = %d", max);
}2.双分支
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
int max;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a > b)
{
if (a > c)
{
max = c;
}
else
{
max = a;
}
}
else
{
if (b > c)
{
max = b;
}
else
{
max = c;
}
}
printf("%d", max);
}3.三目运算符
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
int max;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
max = a > b ? a : b;
max = max > c ? max : c;
printf("%d", max);
}三、构造函数求最大数
1.两个数求最大数
有多种求两值最大值的方式,这里列举一种:
int MaxInt(int a, int b)
{
int max;
if (a > b)
{
max = a;
}
else
{
max = b;
}
return max;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
int maxval = MaxInt(a, b);
printf("%d", maxval);
}2.三个数求最大数
有多种求两值最大值的方式,这里列举一种:
int MaxInt(int a, int b, int c)
{
int max;
max = a > b ? a : b;
max = max > c ? max : c;
return max;
}
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
int max;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
max = MaxInt(a, b, c);
printf("%d", max);
}四、三个数排序
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
int temp;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a > b)
{
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
if (b > c)
{
temp = b;
b = c;
c = temp;
}
if (a > b)
{
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
printf("%d %d %d", a, b, c);
}Q: 单独设置及一个交换的函数,在主函数中每次调用,可以得出正确结果吗?
void Swap(int x, int y)
{
int temp;
temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a > b)
{
Swap(a, b);
}
if (b > c)
{
Swap(b, c);
}
if (a > b)
{
Swap(a, b);
}
printf("%d %d %d", a, b, c);
}A:不可以,你可以这样想,你调用函数的时候,将a的值给x,将b的值给y,所以在进行操作的时候,仅仅是在交换数值,对于你a,b,c本身的值是没有改变的。
修改方法:
void Swap(int *x, int *y)
{
int temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a > b)
{
Swap(&a, &b);
}
if (b > c)
{
Swap(&b, &c);
}
if (a > b)
{
Swap(&a,&b);
}
printf("%d %d %d", a, b, c);
}五、作业
1.统计键盘输入字符个数
统计输入字符串中大写英文字符的个数,小写英文字符的个数,数字字符的个数以及其他字符的个数。要求使用四种方法:getchar(),charbuffer[100],scanf("%c",&ch),ctype.h
scanf("%c")
int main()
{
char ch;
int upper_letter = 0, lower_letter = 0, num = 0, others = 0;
while (1)
{
scanf("%c", &ch);
if (ch == '\n')
{
break;
}
if ('A' <= ch && ch <= 'Z')
{
upper_letter += 1;
}
else if ('a' <= ch && ch <= 'z')
{
lower_letter += 1;
}
else if ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9')
{
num += 1;
}
else
{
others += 1;
}
}
printf("big_letter=%d\nsmall_letter=%d\nnum=%d\nothers=%d\n", upper_letter, lower_letter, num, others);
}char buffer[100]
int main()
{
char str[100];
int big_letter = 0, small_letter = 0, num = 0, others = 0;
scanf("%s", str);
for (int i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; ++i)
{
if ('A' <= str[i] && str[i] <= 'Z')
{
big_letter += 1;
}
else if ('a' <= str[i] && str[i] <= 'z')
{
small_letter += 1;
}
else if ('0' <= str[i] && str[i] <= '9')
{
num += 1;
}
else
{
others += 1;
}
}
printf("big_letter=%d\nsmall_letter=%d\nnum=%d\nothers=%d\n", big_letter, small_letter, num, others);
}我很好奇为什么这里不能使用“\n”呀,使用“\n”就抛出异常。为什么scanf("%c",ch)就可以按照ch=='\n'来判断
1. scanf("%c",ch)的代码是一次输入一个字符,而不是整个字符串。
2. 每次输入一个字符之后,会立即判断是否为'\n'。
3. 一旦读到'\n',就结束输入循环。这样每次只读取一个字符,然后判断是否为换行符,在换行时结束循环,可以正确使用'\n'来表示输入结束。
但这个解决方法里面是一次性输入整个字符串,存储在str数组中。str作为字符串,不会包含'\n'。所以判断'\n'不会退出循环,造成错误。
综上,判断'\n'标记结束只适用于一次输入一个字符的情况。对于整个字符串的处理,还是需要使用'\0'来判断字符串结束。
所以两者的区别在于:
- 按字符逐个输入可以用'\n'判断结束
- 对整个字符串的处理需要'\0'判断结束
getchar()
int main()
{
char str;
int big_letter = 0;
int small_letter=0;
int num=0;
int others=0;
while ((str = getchar()) != '\n')
{
if ('A' <= str && str <= 'Z')
{
big_letter += 1;
}
else if ('a' <= str && str <= 'z')
{
small_letter += 1;
}
else if ('0' <= str && str <= '9')
{
num += 1;
}
else
{
others += 1;
}
}
printf("big_letter=%d\nsmall_letter=%d\nnum=%d\nothers=%d\n", big_letter, small_letter, num, others);
}ctype.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string>
#include<cctype>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[100];
int len;
scanf("%s", str);
len = strlen(str);
int lowerletter = 0;
int upperletter = 0;
int number = 0;
int other = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (isalnum(str[i]))
//是否是为数字字母
{
if (isalpha(str[i]))
//是否是字母
{
if (islower(str[i]))
//是否小写字母
{
lowerletter++;
}
else
{
upperletter++;
}
}
else
{
number++;
}
}
else
{
other++;
}
}
printf("upperletter=%d\nlowerletter=%d\nnumber=%d\nother=%d\n", upperletter, lowerletter, number, other);
}2.打印状态机状态
基本知识
这张图是操作系统进程状态及进程状态切换的示意图:
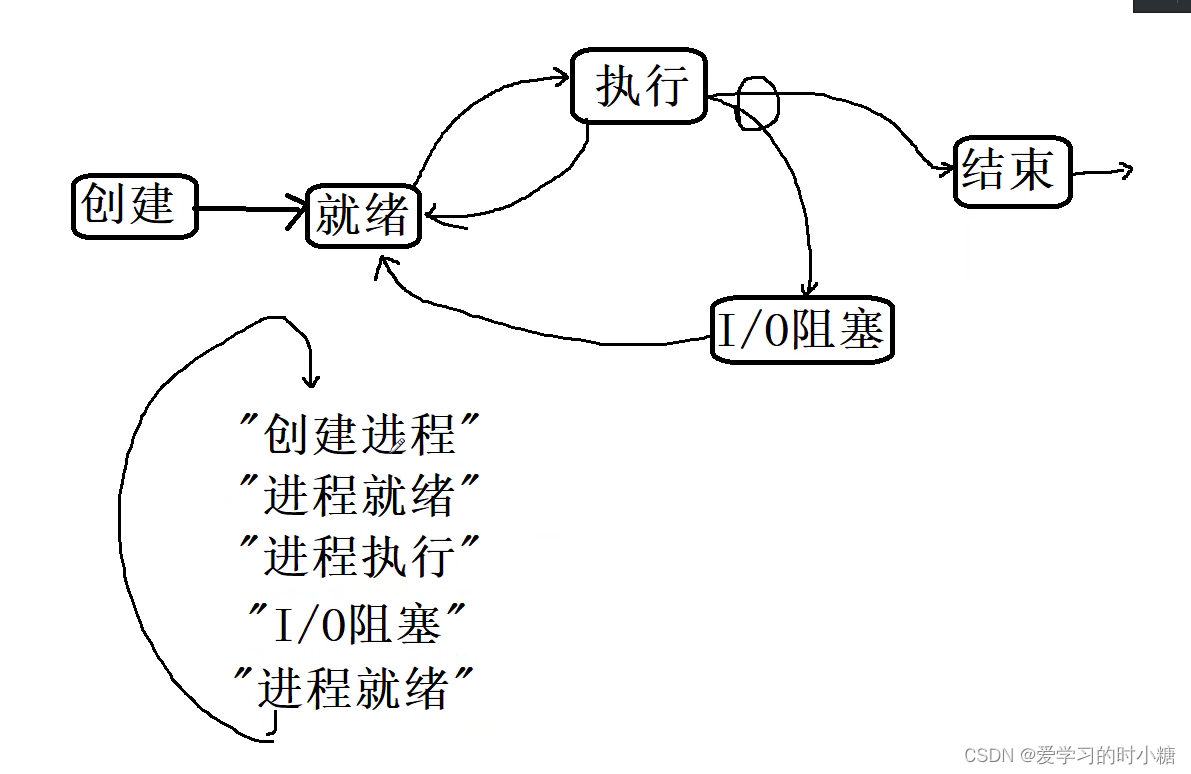
三条基本状态:
就绪——执行——结束
就绪——执行——就绪
就绪——执行——阻塞——就绪
详细介绍操作系统状态的链接如下:
操作系统之进程状态及进程状态切换 (六) --- 创建态、就绪态、运行态、阻塞态、终止态。_程序从执行态变为就绪态-CSDN博客
遇到的问题及解决方法
Q:执行操作结束之后可能出现的情况为:结束、阻塞、就绪,怎么表示出来呢?
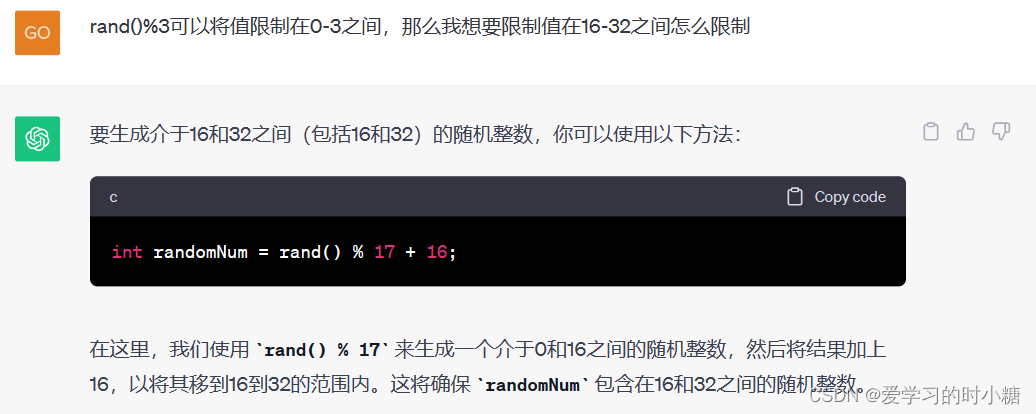
使用随机数表示,通过引入stdlib.h库,使用rand函数,rand函数可以生成随机数,使用rand()%3,A:取余运算,将值限制在0、1、2。
使用这个方法限制值,其他例子如下:
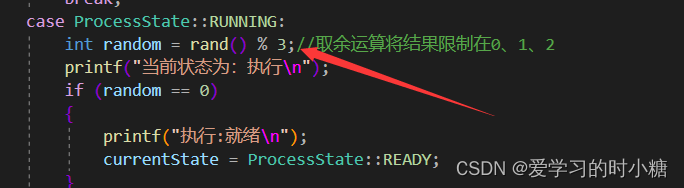
Q:在我将生成随机数的代码写在case ProcessState::RUNNING:代码后,程序报错,报错内容为“random”初始化被“case”标签跳过,报错代码:C2360。编译器错误 C2360 | Microsoft Learn
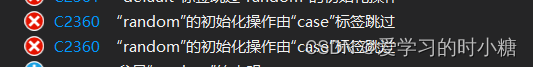
A: C语言的 switch 语句有一个特性,即不能在 case 标签中声明变量。为了解决这个问题,可以将 int random = rand() % 3; 的声明放在 case 之前的代码块中,然后在 case 中使用这个变量。
Q:此时编写的代码大致正确使用enum函数,编写的代码,但是有警告,警告代码C26812,它显示 首选“enum class”而不是“enum” (Enum.3)。
A:警告 C26812 | Microsoft Learn为了更加严谨,我将下面代码:
enum ProcessState {START,READY,RUNNING,BLOCKED,END}
修改成了如下:
enum class ProcessState {START,READY,RUNNING,BLOCKED,END};
相关的使用也从:
case START
修改成为了:
case ProcessState::START
最终完整代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
enum class ProcessState {START,READY,RUNNING,BLOCKED,END};
int main()
{
ProcessState currentState = ProcessState::START;
int Endflag = 1;
while (Endflag== 1)
{
int random = rand() % 3;//取余运算将结果限制在0、1、2
switch (currentState)
{
case ProcessState::START :
printf("当前状态为:创建\n");
printf("执行:就绪\n");
currentState = ProcessState::READY;
break;
case ProcessState::READY:
printf("当前状态为:就绪\n");
printf("执行:执行\n");
currentState = ProcessState::RUNNING;
break;
case ProcessState::RUNNING:
printf("当前状态为:执行\n");
if (random == 0)
{
printf("执行:就绪\n");
currentState = ProcessState::READY;
}
else if(random == 1)
{
printf("执行:阻塞\n");
currentState = ProcessState::BLOCKED;
}
else
{
printf("执行:结束\n");
currentState = ProcessState::END;
}
break;
case ProcessState::BLOCKED:
printf("当前状态为:阻塞\n");
printf("执行:就绪\n");
currentState = ProcessState::READY;
break;
case ProcessState::END:
printf("当前状态为:结束\n");
Endflag = 0;
break;
default:
printf("未知状态\n");
return 1; // 错误退出
}
}
return 0;
}运行结果如下:






















 390
390











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








