引言
在现代游戏和应用程序中,实时人脸识别技术已成为增强用户交互和提升用户体验的重要工具。本文将介绍如何在 Unity 中使用 Barracuda 深度学习框架加载 version-RFB-320.onnx 模型来实现人脸识别,并通过 Compute Shader 处理输入输出数据以优化性能。
1. Unity Barracuda 简介
Unity Barracuda 是一个为 Unity 开发的跨平台深度学习推理库,支持 ONNX(开放神经网络交换格式)。它使得在游戏和应用中集成和运行深度学习模型变得简单快捷。
2. 分析ONNX 模型
首先,需要在 Unity 项目中导入 Barracuda 包和 version-RFB-320.onnx 模型。这个模型是一个已经训练好的人脸识别模型,能够在输入图像中检测人脸位置。导入模型后可以知道模型的输入输出值:

由图可知该模型的输入值是一个形状为(1,240,320,3)的张量(张量可以理解成多维数组),即一张高240,宽320,三通道(rgb)的一张图片;
输出值有两个, scores :float32[1,4420,2];boxes : float32[1,4420,4];如何理解这两个输出张量:
Scores (float32[1,4420,2])
-
维度说明:
1:批次大小,表示这一批处理的图像数量,这里为1表示一次处理一张图像。4420:这个维度代表了检测框的数量,即模型在图像中预测出4420个潜在的对象位置。2:对于每个对象,通常有两个分数,一般是非脸得分和是脸的得分。
-
功能:
- 这个张量提供了每个预测框是否包含对象的置信度。一般来说,第二个数值表示模型对该区域是感兴趣对象的置信度(如人脸),而第一个数值可能表示是背景的置信度。
Boxes (float32[1,4420,4])
-
维度说明:
1:同样代表批次大小。4420:与scores张量中的4420相对应,表示为每个预测生成一个边界框。4:代表每个边界框的四个坐标,通常是[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]。
-
功能:
- 这个张量具体描述了每个检测到的对象在图像中的位置。坐标通常是相对于输入图像的尺寸进行标准化的,表示相对位置。
知道了模型的输入输出值就好办了,把图片处理好传入模型,拿到输出值就知道人脸的位置了。
3.加载onnx模型
public NNModel modelAsset;
public Model model;
private IWorker worker;
void InitModel()
{
model = ModelLoader.Load(modelAsset);
worker = model.CreateWorker();
}4.处理输入图片
传入的图片需要特殊处理将颜色值从 [0, 1] 范围映射到 [-1, 1],高为240,宽为320:
#pragma kernel Preprocess
// Input
sampler2D Input; //输入图片
uint2 ImageSize; //输出的图片大小
// Output
RWStructuredBuffer<float> Output;
[numthreads(8, 8, 1)]
void Preprocess(uint2 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
//在图形处理中,纹理坐标通常是以纹理的左上角为原点(0,0)定义的。
float2 uv = float2(0.5 + id.x, ImageSize.y - 0.5 - id.y) / ImageSize;
float2 duv_dx = float2(1.0 / ImageSize.x, 0);
float2 duv_dy = float2(0, -1.0 / ImageSize.y);
float3 rgb = tex2Dgrad(Input, uv, duv_dx, duv_dy).rgb * 2 - 1;
uint offs = (id.y * ImageSize.x + id.x) * 3;
Output[offs + 0] = rgb.r;
Output[offs + 1] = rgb.g;
Output[offs + 2] = rgb.b;
}
preprocess.SetInts("ImageSize", inputTexWidth,inputTexHeight);
preprocess.SetTexture(0, "Input", source);
preprocess.SetBuffer(0, "Output", preprocessBuffer);
preprocess.Dispatch(0, inputTexWidth/8 ,inputTexHeight/8, 1);5.运行模型
将处理过后的数据传入模型,运行过后就可以获取输出值(score,boxes):
using (var t = new Tensor(new TensorShape(1, inputTexHeight, inputTexWidth, 3), preprocessBuffer))
worker.Execute(t);
using (var scoreOutput = worker.PeekOutput("scores"))
{
var scoreOutputTemp = scoreOutput.Reshape(new TensorShape(1, scores.height, scores.width, 2));
scoreOutputTemp.ToRenderTexture(scores);
scoreOutputTemp.Dispose();
}
using ( var boxesOutput = worker.PeekOutput("boxes"))
{
var boxesOutputTemp = boxesOutput.Reshape(new TensorShape(1, boxes.height, boxes.width, 4));
boxesOutputTemp.ToRenderTexture(boxes);
boxesOutputTemp.Dispose();
}6.筛选数据
拿到分数和预测框就可以筛选出得分大于阈值的预测框:
#pragma kernel Postprocess1
#include "Common.hlsl"
// Input
Texture2D<float2> Scores;
Texture2D<float4> Boxes;
uint2 InputSize;
float Threshold;
// Output
RWStructuredBuffer<Detection> Output;
RWStructuredBuffer<uint> OutputCount;
[numthreads(16, 4, 1)]
void Postprocess1(uint2 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
if (!all(id < InputSize)) return;
float score = Scores[uint2(id.x, id.y)].y;
float4 box = Boxes[uint2(id.x, id.y)];
if (score < Threshold) return;
Detection data;
data.x1 = box.x;
data.y1 = box.y;
data.x2 = box.z;
data.y2 = box.w;
data.score = score;
data.pad = 0;
//自动更新count
uint count = OutputCount.IncrementCounter();
if (count < MAX_DETECTION) Output[count] = data;
}
光筛选出分数大于阈值的预测框还不够,因为预测框会发生重叠,还要进一步筛选:
#pragma kernel Postprocess2
#include "Common.hlsl"
// Input
StructuredBuffer<Detection> Input;
RWStructuredBuffer<uint> InputCount; // Only used as a counter
float Threshold;
// Output
AppendStructuredBuffer<Detection> Output;
// Local arrays for data cache
groupshared Detection _entries[MAX_DETECTION];
groupshared bool _flags[MAX_DETECTION];
[numthreads(1, 1, 1)]
void Postprocess2(uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// Initialize data cache arrays
uint entry_count = min(MAX_DETECTION, InputCount.IncrementCounter());
if (entry_count == 0) return;
for (uint i = 0; i < entry_count; i++)
{
_entries[i] = Input[i];
_flags[i] = true;
}
// Overlap test permutation
for (i = 0; i < entry_count - 1; i++)
{
if (!_flags[i]) continue;
for (uint j = i + 1; j < entry_count; j++)
{
if (!_flags[j]) continue;
// Overlap test
if (CalculateIOU(_entries[i], _entries[j]) < Threshold) continue;
// Score comparison
if (_entries[i].score < _entries[j].score)
{
_flags[i] = false;
// The box in the outer loop is removed. Break the inner loop.
break;
}
else
_flags[j] = false;
}
}
// Output aggregation
for (i = 0; i < entry_count; i++)
if (_flags[i]) Output.Append(_entries[i]);
}
post2.SetCounterValue(0);
counter.SetCounterValue(0);
postprocess1.SetTexture(0, "Scores", scores);
postprocess1.SetTexture(0, "Boxes", boxes);
postprocess1.SetInts("InputSize", boxes.width,boxes.height);
postprocess1.SetFloat("Threshold", threshold);
postprocess1.SetBuffer(0, "Output", post1);
postprocess1.SetBuffer(0, "OutputCount", counter);
postprocess1.Dispatch (0, (boxes.width+15)/16,boxes.height/4,1);
postprocess2.SetFloat("Threshold", 0.5f);
postprocess2.SetBuffer(0, "Input", post1);
postprocess2.SetBuffer(0, "InputCount", counter);
postprocess2.SetBuffer(0, "Output", post2);
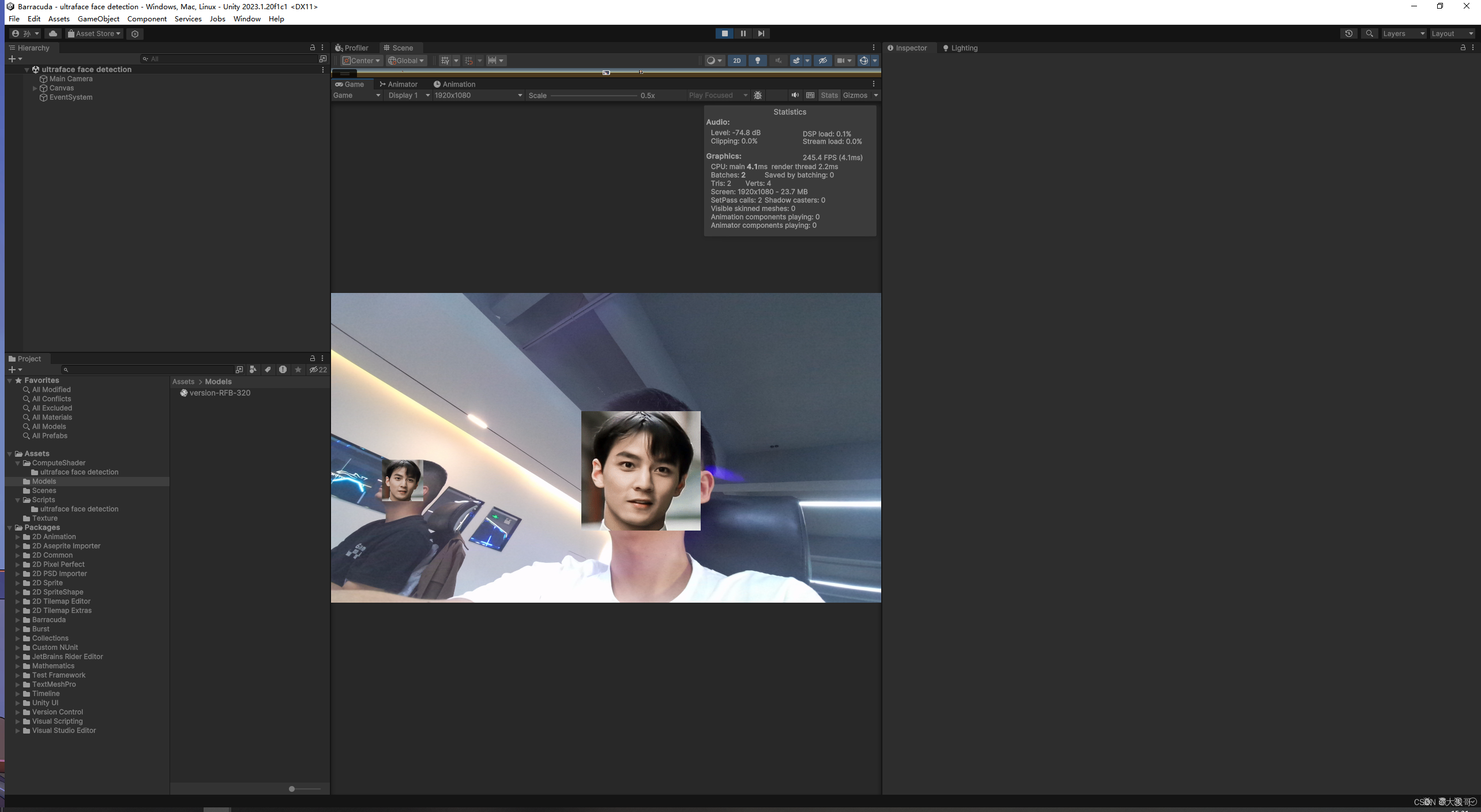
postprocess2.Dispatch(0, 1, 1, 1); 7.绘制彦祖
知道预测框的位置后就可以把彦祖的脸换上了。
完整代码:
using UnityEngine;
using Unity.Barracuda;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class Ultraface : MonoBehaviour
{
public NNModel modelAsset;
public Model model;
private IWorker worker;
private int inputTexWidth = 320, inputTexHeight = 240;
private int OutputCount = 4420;
public struct Detection
{
public float x1, y1, x2, y2;
public float score;
public float pad1, pad2, pad3;
public static int Size = 8 * sizeof(float);
}
[SerializeField]private WebCamTexture webTex;
public ComputeShader preprocess;
private ComputeBuffer preprocessBuffer;
public ComputeShader postprocess1;
private RenderTexture scores;
private RenderTexture boxes;
private ComputeBuffer post1;
public ComputeShader postprocess2;
private ComputeBuffer post2;
private ComputeBuffer counter;
[SerializeField] Shader _visualizer = null;
Material _material;
ComputeBuffer _drawArgs;
[SerializeField] private Texture2D _texture;
[SerializeField] RawImage _previewUI = null;
[SerializeField] private Texture2D dTexture;
public void SetIndirectDrawCount(ComputeBuffer drawArgs)
=> ComputeBuffer.CopyCount( post2, drawArgs, sizeof(uint));
private void Start()
{
InitWebCam();
InitModel();
InitBuffer();
_material = new Material(_visualizer);
_drawArgs = new ComputeBuffer(4, sizeof(uint),
ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments);
_drawArgs.SetData(new int [] {6, 0, 0, 0});
_previewUI.texture = webTex;
}
private void Update()
{
RunModel(webTex,0.2f);
}
void OnRenderObject()
{
SetIndirectDrawCount(_drawArgs);
_material.SetFloat("_Threshold", 0.2f);
_material.SetTexture("_Texture", _texture);
_material.SetBuffer("_Detections", post2);
_material.SetPass(_texture == null ? 0 : 1);
Graphics.DrawProceduralIndirectNow(MeshTopology.Triangles, _drawArgs, 0);
}
void InitWebCam()
{
webTex = new WebCamTexture(1920, 1080,30);
webTex.deviceName = WebCamTexture.devices[0].name;
webTex.Play();
}
void InitModel()
{
model = ModelLoader.Load(modelAsset);
worker = model.CreateWorker();
}
void InitBuffer()
{
preprocessBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(inputTexWidth * inputTexHeight * 3, sizeof(float));
scores = new RenderTexture(OutputCount / 20, 20, 0, RenderTextureFormat.RGFloat);
boxes = new RenderTexture(OutputCount / 20, 20, 0, RenderTextureFormat.ARGBFloat);
post1 = new ComputeBuffer(512, Detection.Size);
post2 = new ComputeBuffer(512, Detection.Size, ComputeBufferType.Append);
counter = new ComputeBuffer(1, sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.Counter);
}
void RunModel(Texture source, float threshold)
{
preprocess.SetInts("ImageSize", inputTexWidth,inputTexHeight);
preprocess.SetTexture(0, "Input", source);
preprocess.SetBuffer(0, "Output", preprocessBuffer);
preprocess.Dispatch(0, inputTexWidth/8 ,inputTexHeight/8, 1);
using (var t = new Tensor(new TensorShape(1, inputTexHeight, inputTexWidth, 3), preprocessBuffer))
worker.Execute(t);
using (var scoreOutput = worker.PeekOutput("scores"))
{
var scoreOutputTemp = scoreOutput.Reshape(new TensorShape(1, scores.height, scores.width, 2));
scoreOutputTemp.ToRenderTexture(scores);
scoreOutputTemp.Dispose();
}
using ( var boxesOutput = worker.PeekOutput("boxes"))
{
var boxesOutputTemp = boxesOutput.Reshape(new TensorShape(1, boxes.height, boxes.width, 4));
boxesOutputTemp.ToRenderTexture(boxes);
boxesOutputTemp.Dispose();
}
post2.SetCounterValue(0);
counter.SetCounterValue(0);
postprocess1.SetTexture(0, "Scores", scores);
postprocess1.SetTexture(0, "Boxes", boxes);
postprocess1.SetInts("InputSize", boxes.width,boxes.height);
postprocess1.SetFloat("Threshold", threshold);
postprocess1.SetBuffer(0, "Output", post1);
postprocess1.SetBuffer(0, "OutputCount", counter);
postprocess1.Dispatch (0, (boxes.width+15)/16,boxes.height/4,1);
postprocess2.SetFloat("Threshold", 0.5f);
postprocess2.SetBuffer(0, "Input", post1);
postprocess2.SetBuffer(0, "InputCount", counter);
postprocess2.SetBuffer(0, "Output", post2);
postprocess2.Dispatch(0, 1, 1, 1);
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
worker.Dispose();
preprocessBuffer.Dispose();
post1.Dispose();
post2.Dispose();
counter.Dispose();
_drawArgs.Dispose();
Destroy(webTex);
Destroy(scores);
Destroy(boxes);
Destroy(_material);
}
}





















 5012
5012











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








