目录
一:自带算法
链表list自带算法,是按照地址排序的,示例如下
CStaff.h:
#ifndef CSTAFF_H
#define CSTAFF_H
#define ADMIN 1
#define MANAGER 2
#define WAITER 3
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Staff
{
public:
Staff();
Staff(int id,string name,string pwd,int prole);
~Staff();
int getId();
string getName();
string getPwd();
int getRole();
// bool operator < (Staff &user);//隐式传参 this
private:
int ID;
string name;
string pwd;
int role;
};
#endifCStaff.cpp:
#include"CStaff.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
Staff::Staff()
{
}
Staff::Staff(int id,string name,string pwd,int prole)
{
this->ID = id;
this->name = name;
this->pwd = pwd;
this->role = prole;
}
int Staff::getId()
{
return this->ID;
}
string Staff::getName()
{
return this->name;
}
string Staff::getPwd()
{
return this->pwd;
}
int Staff::getRole()
{
return this->role;
}
Staff::~Staff()
{
}
/*
bool Staff::operator <(Staff &user)//函数排序
{
if(this->ID<user.ID) //从小到大
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
*/main.cpp:
#pragma warning (disable :4786)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<list>
#include"CStaff.h"
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
void demo_list();
int main()
{
demo_list();
return 0;
}
void demo_list()
{
list<Staff*> staffV;
staffV.push_back(new Staff(1001,"admin","123",ADMIN));
staffV.push_back(new Staff(1003,"lily","123",ADMIN));
staffV.insert(staffV.begin(),new Staff(1002,"admin","123",ADMIN));
//1002 1001 1003
list<Staff*>::iterator it;
for(it=staffV.begin();it!=staffV.end();it++)
{
cout<<(*it)<<"---"<<(*it)->getId()<<endl;
}
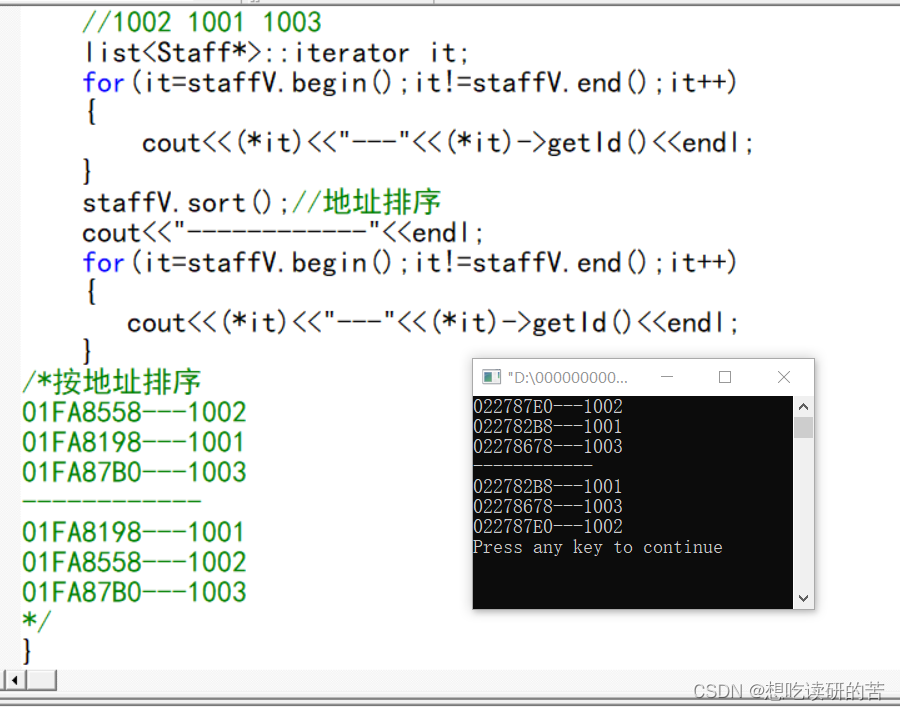
staffV.sort();//地址排序
cout<<"------------"<<endl;
for(it=staffV.begin();it!=staffV.end();it++)
{
cout<<(*it)<<"---"<<(*it)->getId()<<endl;
}
/*按地址排序
01FA8558---1002
01FA8198---1001
01FA87B0---1003
------------
01FA8198---1001
01FA8558---1002
01FA87B0---1003
*/
}
二:自定义算法
1. 自定义按照Id排序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include"CStaff.h"
#include<functional>//函数对象
#include<algorithm> //算法
bool sortByName(Staff staff1,Staff staff2) //自定义姓名排序
{
if(staff1.getName()<staff2.getName())
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool sortById(Staff staff1,Staff staff2) //自定义Id排序
{
if(staff1.getId()<staff2.getId())
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void demo_vector()
{
vector<Staff> staffV;
staffV.push_back(Staff(1001,"admin","123",ADMIN));
staffV.push_back(Staff(1003,"lily","123",ADMIN));
staffV.push_back(Staff(1002,"banana","123",ADMIN));
staffV.push_back(Staff(1004,"candy","123",ADMIN));
vector<Staff>::iterator it;
for(it=staffV.begin();it!=staffV.end();it++)
{
cout<<(*it).getId()<<endl;
}
sort(staffV.begin(),staffV.end(),sortById);
cout<<"----------"<<endl;
for(it=staffV.begin();it!=staffV.end();it++)
{
cout<<(*it).getId()<<endl;
}
}
/*
1001
1003
1002
1004
----------
1001
1002
1003
1004
*/
int main()
{
demo_vector();
return 0;
}

2. 自定义按照姓名排序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include"CStaff.h"
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
bool sortByName(Staff staff1,Staff staff2)
{
if(staff1.getName()<staff2.getName())
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void demo_vector()
{
vector<Staff> staffV;
staffV.push_back(Staff(1001,"admin","123",ADMIN));
staffV.push_back(Staff(1003,"lily","123",ADMIN));
staffV.push_back(Staff(1002,"banana","123",ADMIN));
staffV.push_back(Staff(1004,"candy","123",ADMIN));
vector<Staff>::iterator it;
for(it=staffV.begin();it!=staffV.end();it++)
{
cout<<(*it).getId()<<":"<<(*it).getName().c_str()<<endl;
}
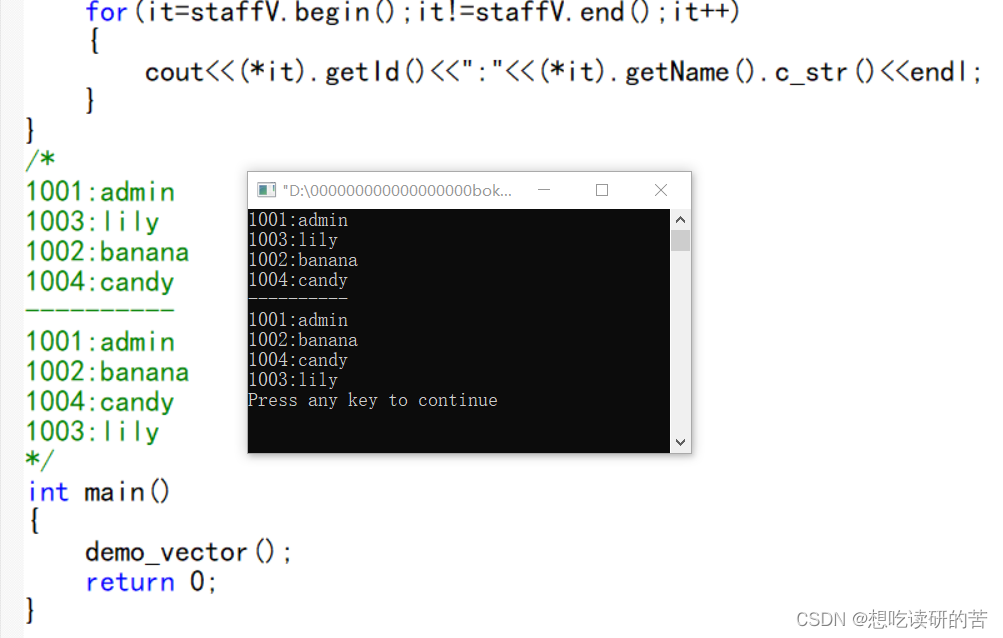
sort(staffV.begin(),staffV.end(),sortByName);
cout<<"----------"<<endl;
for(it=staffV.begin();it!=staffV.end();it++)
{
cout<<(*it).getId()<<":"<<(*it).getName().c_str()<<endl;
}
}
/*
1001:admin
1003:lily
1002:banana
1004:candy
----------
1001:admin
1002:banana
1004:candy
1003:lily
*/
int main()
{
demo_vector();
return 0;
}
三:函数对象
1. 任何普通的函数和任何重载了调用运算符operator()的类的对象都满足函数对象的特征
2. STL中也定义了一些标准的函数对象,如果以功能划分,可以分为算术运算、关系运算、
逻辑运算三大类;为了调用这些标准函数对象,需要包含头文件<functional>
四:标准C++库中的算法
1.算法本身是一种函数模板
2.不可变序列算法(non-mutating algorithms)
不直接修改所操作的容器内容的算法
3.可变序列算法(mutating algorithms)
可以修改它们所操作的容器的元素。
4.算法部分主要由头文件<algorithm>,<numeric>和<functional>组成
五:STL算法的头文件
1. <algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,它是由一大堆模版函数组成的,可以认为每个函数在很大程度上都是独立的,其中常用到的功能范围涉及到比较、交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改、移除、反转、排序、合并等等
2. <numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数,包括加法和乘法在序列上的一些操作
3. <functional>中则定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象
























 26
26











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










