掌握STL算法for_each、sort、find、 find_if、count、count_if、copy_if、swap的基本使用方法和函数对象概念、lambda表达式使用。
1.练习使用for_each、find、 find_if、copy_if、函数对象概念、lambda表达式
题目:编写程序,建立整型向量容器,从键盘上输入若干正整数,添加在向量容器尾部,输出向量容器内所有元素,再将向量容器内所有素数拷贝至整型双端队列容器内,再输出整型双端队列内所有元素,要求使用lambda函数。(其它功能是我自己加的,练习嘛)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<iterator>
#include<algorithm>//流迭代器,定义在<iterator>头文件中
#include<deque>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
//重载()运算符,使用函数对象
class IsSushu{
public:
bool operator() (int x) const{//x是参数
if(x==1) return 0;
int tmp = sqrt(x);//sqrt对应头文件<cmath>
for(int i=2;i<=tmp;i++){
if(x%i==0){
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
};
int main(){
vector<int> V;//建立整型向量容器
deque<int> D;//建立整型双端队列
/*以前我们是这么输入若干正整数的
int x;
while(cin>>x){
V.push_back(x);
cout<<x<<" ";
}*/
//现在我们使用流迭代器+copy算法+back_inserter()函数在容器V中插入元素
copy(istream_iterator<int>(cin),istream_iterator<int>(),back_inserter(V));
copy(V.begin(),V.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));//用输出流迭代器输出
cout<<endl;
//法一:使用函数对象,输出向量容器中所有素数
//cout<<"使用函数对象:"<<endl;
//copy_if(V.begin(),V.end(),back_inserter(D),IsSushu());
//法二:使用lambda表达式
auto f = [](int x){
if(x==1) return 0;
int tmp = sqrt(x);//sqrt对应头文件<cmath>
for(int i=2;i<=tmp;i++){
if(x%i==0){
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
};
//将向量容器内所有素数拷贝至整型双端队列容器内并输出
copy_if(V.begin(),V.end(),back_inserter(D),f);
copy(D.begin(),D.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
cout<<endl;
//for_each针对容器D内的每个元素作平方运算并输出
for_each(D.begin(),D.end(),[](int &x){x=x*x;});
copy(D.begin(),D.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
cout<<endl;
//find,eg:要找出向量容器V中所有等于5的元素并输出
//循环调用find算法可以找出所有符合要求的元素
auto it = begin(V);
while(true){
it = find(it,end(V),5);
if(it==end(V)){
break;
}
cout<<*it<<" ";
++it;
}
cout<<endl;
//find_if,eg:要找出所有偶数并输出
it = begin(V);
while(true){
it = find_if(it,end(V),[](int x){ return x%2==0;});
if(it==end(V)){
break;
}
cout<<*it<<" ";
++it;
}
return 0;
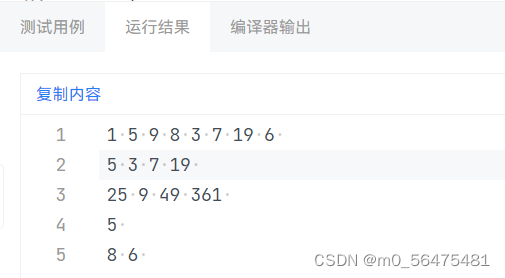
}运行结果:
2.对STL标准模板库中count_if、sort的考察
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool evenNum(int n)
{
return !(n%2);//偶数时返回true
}
int main( )
{
int arr[6]={2,10,9,7,20,12,};
vector<int> vec(arr,arr+6);//将arr数组的0-5元素(也就是前六个元素)赋值给vec向量
vector<int>::iterator it;
for(it=vec.begin(); it!=vec.end(); it++)
{
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//count_if在vec中满足evenNum函数要求(是偶数)的元素的个数
int num=count_if(vec.begin(),vec.end(),evenNum);
cout<<"even numbers: "<<num<<endl;
//sort对vec中元素排序,默认从小到大
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
cout<<"从小到大:"<<endl;;
for(it=vec.begin(); it!=vec.end(); it++)
{
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"也可以从大到小:"<<endl;
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),greater<int>());
for(it=vec.begin(); it!=vec.end(); it++)
{
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
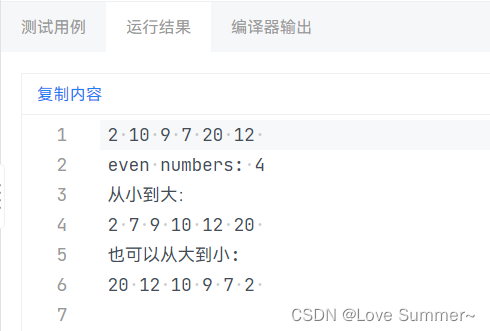
运行结果:
小练习:下面程序用STL的条件计数算法和自定义的函数对象对一个存放在整数向量类对象中的学生成绩进行统计及格人数并显示结果。请在下面程序的横线处填上适当字句,以使程序完整。
注:"//"后面的代码是需要填的空
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
//重载了()运算符的类对象可以作为函数对象
class Pass
{
public:
//bool operator()(int x)
//一元谓词,判断成绩是否大于60分
{
return x>=60;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> a;
int count;
a.push_back(78);
a.push_back(92);
a.push_back(52);
//函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
//count = count_if(a.begin(),a.end(),Pass());
cout<<"count="<<count<<endl;
}
运行结果:
count=2关于Amazing sort:






















 1872
1872











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








