简介:
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a secret (with the HMAC algorithm) or a public/private key pair using RSA or ECDSA.
是一种小巧的、自包含的JSON对象,用于两个端系统之间的安全传输,它是一种数字标签,它可以使用了一种严格的算法进行签名,或者使用公钥和私钥的形式进行签名
JWT的使用场景
Authorization: This is the most common scenario for using JWT. Once the user is logged in, each subsequent request will include the JWT, allowing the user to access routes, services, and resources that are permitted with that token. Single Sign On is a feature that widely uses JWT nowadays, because of its small overhead and its ability to be easily used across different domains.↳
Information Exchange: JSON Web Tokens are a good way of securely transmitting information between parties. Because JWTs can be signed—for example, using public/private key pairs—you can be sure the senders are who they say they are. Additionally, as the signature is calculated using the header and the payload, you can also verify that the content hasn't been tampered with.
1、授权: 比如在web应用当中我们通常需要使用到授权,来给授权用户进行访问相应的路由、服务和资源
2、信息的交换:因为JWT是被签名的,所以能够非常安全的在端系统之间传输消息,通过JWT你可以确认发送者和内容是否被篡改
JWT的结构
In its compact form, JSON Web Tokens consist of three parts separated by dots (
.), which are:↳
Header
Payload
Signature
Therefore, a JWT typically looks like the following.
xxxxx.yyyyy.zzzzzHeader
The header typically consists of two parts: the type of the token, which is JWT, and the signing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA.↳
For example:
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" }Then, this JSON is Base64Url encoded to form the first part of the JWT.
Payload
The second part of the token is the payload, which contains the claims. Claims are statements about an entity (typically, the user) and additional data. There are three types of claims: registered, public, and private claims.↳
Registered claims: These are a set of predefined claims which are not mandatory but recommended, to provide a set of useful, interoperable claims. Some of them are: iss (issuer), exp (expiration time), sub (subject), aud (audience), and others.
Public claims: These can be defined at will by those using JWTs. But to avoid collisions they should be defined in the IANA JSON Web Token Registry or be defined as a URI that contains a collision resistant namespace.
Private claims: These are the custom claims created to share information between parties that agree on using them and are neither registered or public claims.
An example payload could be:↳
{ "sub": "1234567890", "name": "John Doe", "admin": true }The payload is then Base64Url encoded to form the second part of the JSON Web Token.
Signature
To create the signature part you have to take the encoded header, the encoded payload, a secret, the algorithm specified in the header, and sign that.↳
For example if you want to use the HMAC SHA256 algorithm, the signature will be created in the following way:
HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload), secret)The signature is used to verify the message wasn't changed along the way, and, in the case of tokens signed with a private key, it can also verify that the sender of the JWT is who it says it is.
Putting all together
The output is three Base64-URL strings separated by dots that can be easily passed in HTML and HTTP environments, while being more compact when compared to XML-based standards such as SAML.
The following shows a JWT that has the previous header and payload encoded, and it is signed with a secret.
JWT是如何工作的
In authentication, when the user successfully logs in using their credentials, a JSON Web Token will be returned. Since tokens are credentials, great care must be taken to prevent security issues. In general, you should not keep tokens longer than required.
一般就是用户成功获取到资格后,服务器需要返回一个JWT,用户进行保存,当时注意JWT的保存时间,需要在特定时间进行删除,若用户需要再次获取,经过上一个步骤
Whenever the user wants to access a protected route or resource, the user agent should send the JWT, typically in the Authorization header using the Bearer schema. The content of the header should look like the following:↳
Authorization: Bearer <token>
当我们请求受保护的路由和资源的时候需要再请求中携带JWT,典型的就是在请求头中设置Authorization字段,如上
This can be, in certain cases, a stateless authorization mechanism. The server's protected routes will check for a valid JWT in the
Authorizationheader, and if it's present, the user will be allowed to access protected resources. If the JWT contains the necessary data, the need to query the database for certain operations may be reduced, though this may not always be the case.Note that if you send JWT tokens through HTTP headers, you should try to prevent them from getting too big. Some servers don't accept more than 8 KB in headers. If you are trying to embed too much information in a JWT token, like by including all the user's permissions, you may need an alternative solution, like Auth0 Fine-Grained Authorization.
如果你携带了JWT,服务器的保护路由将会检查你头部的Authorization是否携带了一个真确的JWT,如果有就会放行,如果你JWT包括了一些必要的数据,比如userid 或者 username 对于某些操作,你就可以不需要去进行数据库的查询了,当是不能够让Http请求的头部较大,大部分的服务器接收的请求头不能操作8KB
If the token is sent in the
Authorizationheader, Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) won't be an issue as it doesn't use cookies.
此处它指出,JWT并不需要使用cookies,所以能解决跨域问题,更适用于前后端分离的项目当中
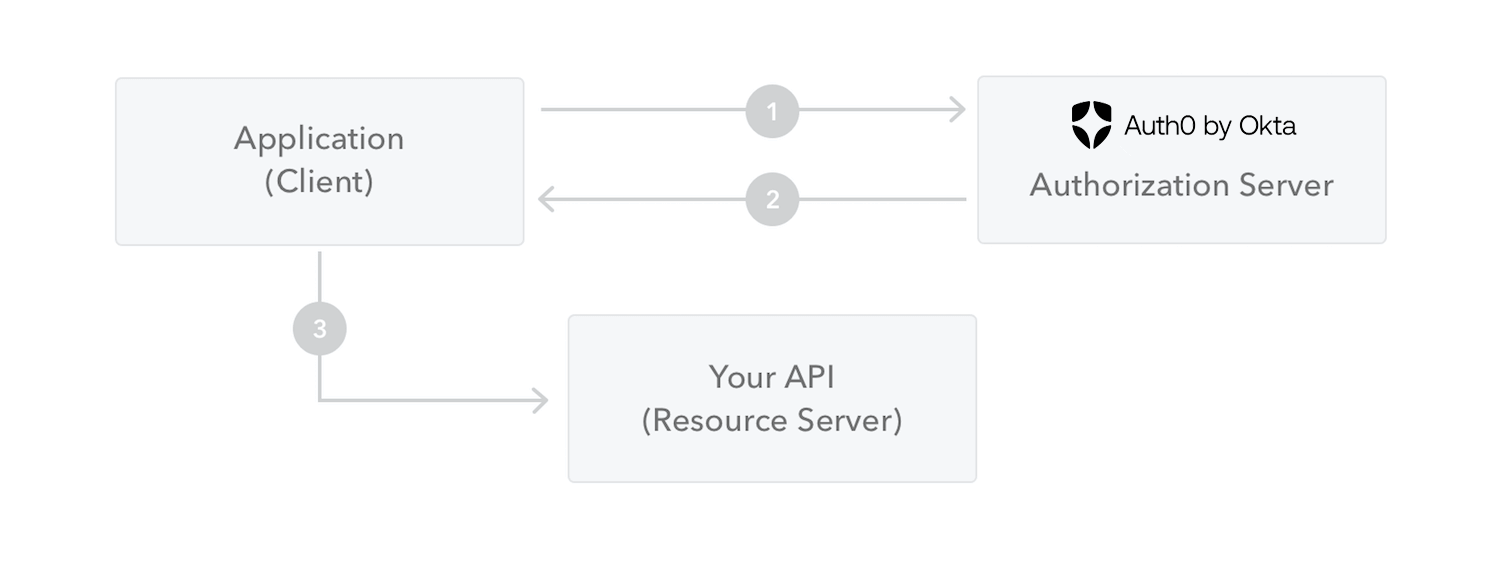
The following diagram shows how a JWT is obtained and used to access APIs or resources:
The application or client requests authorization to the authorization server. This is performed through one of the different authorization flows. For example, a typical OpenID Connect compliant web application will go through the
/oauth/authorizeendpoint using the authorization code flow.When the authorization is granted, the authorization server returns an access token to the application.
The application uses the access token to access a protected resource (like an API).
Do note that with signed tokens, all the information contained within the token is exposed to users or other parties, even though they are unable to change it. This means you should not put secret information within the token.
我之前使用Node.js去实现过,后续会将实现代码进行一个补充







 本文详细介绍了JSONWebToken(JWT)的概念、使用场景,包括授权和信息交换,以及JWT的结构(包括Header、Payload和Signature),并讨论了如何创建和验证JWT,以及在处理时需注意的安全问题。
本文详细介绍了JSONWebToken(JWT)的概念、使用场景,包括授权和信息交换,以及JWT的结构(包括Header、Payload和Signature),并讨论了如何创建和验证JWT,以及在处理时需注意的安全问题。















 701
701











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








