✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
⛄ 内容介绍
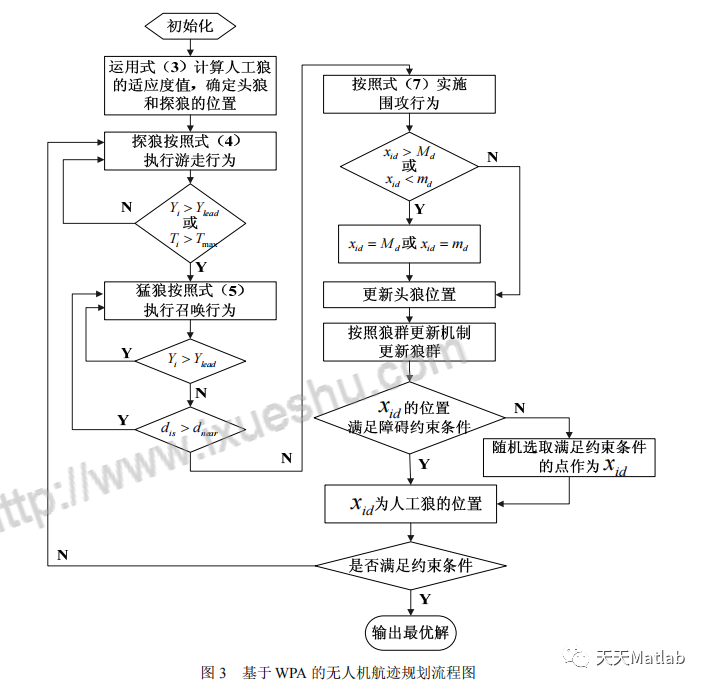
随着无人机可执行任务的多样化,航迹规划成为其顺利完成任务的基本前提。针对该问题,提出了基于狼群算法的无人机航迹规划方法。运用等效地形模拟方法,将作战区域中的敌方威胁、地形障碍等效为山峰,构建了无人机航迹规划的场景。以此为基础,采用抽象出游走、召唤和围攻3 种智能行为的狼群算法,对起始点和终点已知的无人机航迹进行规划,规划出的航迹安全地避开了威胁,长度较短,且平均耗时较小。仿真结果验证了该算法的有效性。
1.1 航迹规划问题的描述
无人机航迹规划问题的一般描述为:在给定的存在火力威胁和地形障碍等约束的作战环境中,为无人机从起始点到目标点求解一条可行航迹,该航迹不仅要避开障碍物,确保自身的安全,而且需要满足无人机自身的性能约束。此外,该航迹在某种性能指标的度量下需要达到最优,以保证所付出的代价最小。因此,从本质上讲,无人机航迹规划属于一种寻优问题。无人机航迹规划问题的约束条件可分为两类,一种是复杂作战环境约束,主要有:敌方火力威胁、地形障碍;另一种是无人机自身性能约束,主要有:最大水平转弯角、最大爬升/俯冲角、最小航迹段长度、最长飞行距离和最低飞行高度。该问题的目标函数为无人机的航迹长度达到最短。
1.2 航迹规划问题的模型构建
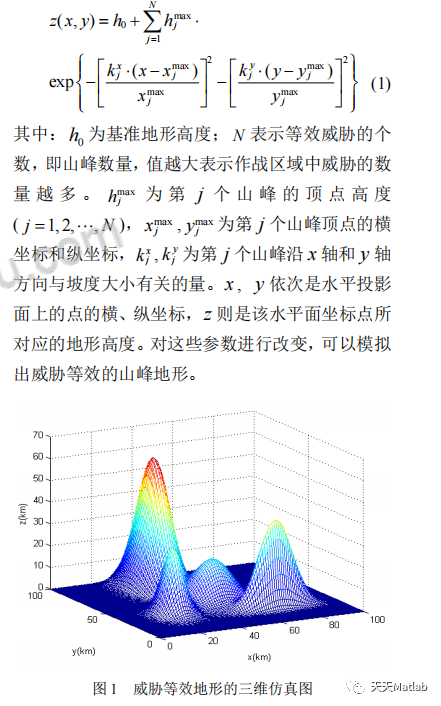
无人机在复杂作战环境中执行各种任务时,可能会面临敌方火力的威胁,如地空导弹、防空火炮等。目前雷达依然是对目标进行远距离探测、跟踪的主要设备,敌方的防空火力威胁几乎必须依靠雷达才能发挥其威力,故可将敌方的各种威胁简化为雷达威胁区域。无人机在作战区域中遇到的地形障碍,同样可以视为禁飞区域。威胁等效地形模拟方法,是将复杂环境中的威胁与障碍等效处理成山峰地形,已在多个文献中得到应用。它通过把敌方威胁处理成特殊的地形,其位置和作用范围叠加到数字地图上,威胁的作用就等同于抬高该作用范围的地形。经过这样处理后,无人机飞行区域内已知的地形障碍和敌方威胁融合成了综合的地形信息,而且把敌方威胁回避等效为地形回避进行处理,使航迹规划问题得到大大简化。根据该等效方法,本文对作战环境中的敌方威胁和地形障碍进行建模,可得威胁等效地形数学模型:
⛄ 部分代码
function varargout = major(varargin)
% MAJOR M-file for major.fig
% MAJOR, by itself, creates a new MAJOR or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = MAJOR returns the handle to a new MAJOR or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% MAJOR('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in MAJOR.M with the given input arguments.
%
% MAJOR('Property','Value',...) creates a new MAJOR or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before major_OpeningFunction gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to major_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Copyright 2002-2003 The MathWorks, Inc.
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help major
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 04-Jul-2010 13:06:09
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @major_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @major_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before major is made visible.
function major_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to major (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for major
handles.output = hObject;
global output sec_output thi_output for_output
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes major wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = major_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu1.
function popupmenu1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = get(hObject,'String') returns popupmenu1 contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from popupmenu1
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function popupmenu1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
set(hObject,'string',{'读者','管理员'});
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu2.
function popupmenu2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = get(hObject,'String') returns popupmenu2 contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from popupmenu2
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function popupmenu2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
set(hObject,'string',{' ','reader001','reader002','reader003','reader004','post001','post002'});
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
else
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'));
end
function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
else
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','xxxxxx');
end
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
popup1_index=get(handles.popupmenu1,'Value');
switch popup1_index
case 1
condition1=1;
case 2
condition1=0;
end
popup2_index=get(handles.popupmenu2,'Value');
switch popup2_index
case 1
condition2=2;
case 2
condition2=11;
case 3
condition2=12;
case 4
condition2=13;
case 5
condition2=21;
case 6
condition2=01;
case 7
condition2=02;
end
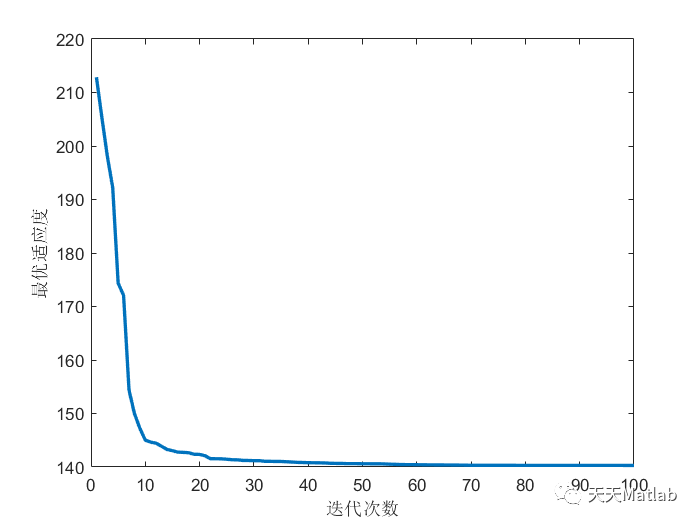
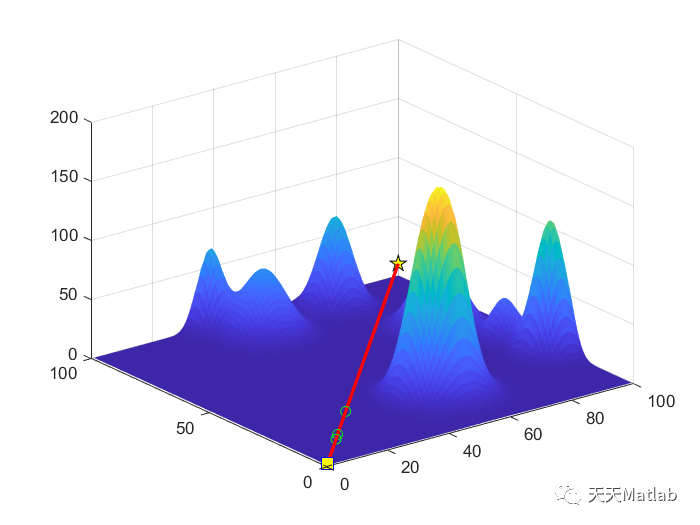
⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
[1] 胡观凯, 钟建华, 李永正,等. 基于IPSOGA算法的无人机三维路径规划[J]. 现代电子技术, 2023, 46(7):6.
[2] 陈洋, 张道辉, 赵新刚,等. 基于自主学习框架的无人机三维路径规划[C]// 中国自动化大会暨钱学森诞辰一百周年及中国自动化学会五十周年会庆. 中国自动化学会, 2011.
[3] 王宇, 王文浩, 徐凡,等. 基于改进蚁群算法的植保无人机路径规划方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020(011):051.
[4] 高明生, 徐楷文, 李建. 一种基于改进灰狼算法的无人机3D路径规划方法:, CN202211146728.6[P]. 2022.
[5] 贾鹤鸣, 饶洪华, 王琢,等. 基于改进蜜獾算法的无人机三维路径规划[J]. 龙岩学院学报, 2022(005):040.
[6] 赵志, 段炼, 路东林,等. 基于蚁群算法的无人机三维路径规划与冲突解脱[J]. 航空计算技术, 2022, 52(4):5.
⛳️ 代码获取关注我
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








