栈- 顺序栈的原理
定义:栈是限制在一端进行插入操作和删除操作的线性表(俗称堆栈)。允许进行操作的一端称为“栈顶" ,另一固定端称为“栈底”,当栈中没有元素时称为“空栈”。
特点:
后进先出(LIFO)。

栈 - 顺序栈的实现1
顺序栈
定义:他是顺序表的一种,具有顺序表同样的存储结构,由数组定义,配合用数组下标表示的栈顶指针top (相对指针)完成各种操作。
typedef int data_t; //定义栈中数据元素的数据类型
typedef struct
{
data_t *data; //用指针指向栈的存储空间
int maxlen; //当前栈的最大元素个数
int top; //只是栈顶位置(数组下标)的
}sqstack; //顺序栈类型定义顺序栈的创建
函数结构
sqstack * stack_create(int len);算法思路:栈结构体中包含三个成员 data_t *data; int maxlen; int top;
(1)需要申请一个栈空间存放三个成员,但空间不足以存入更多数据,
(2)所以还需要data申请空间去存储用户需要存放数据所需的空间,如图所示:

代码实现:
sqstack * stack_create(int len) {
sqstack * s;
//第一次空间申请
if ((s = (sqstack *)malloc(sizeof(sqstack))) == NULL) {
printf("malloc sqstack failed\n");
return NULL;
}
//第二次空间申请
if ((s->data = (data *)malloc(len * sizeof(data_t))) == NULL) {
printf("malloc data failed\n");
return NULL;
}
//赋初值
memset(s->data, 0, len*sizeof(data_t));
s->maxlen = len;
s->top = -1;
retirn s;栈 - 顺序栈的实现2
顺序栈入栈操作
函数结构
int stack_push(sqstack * s, data_t value) ;算法思路:
(1)检查栈是否已满;
(2)未满,进行存值,top++;
(3)data[top]存入
代码实现:
int stack_push(sqstack * s, data_t value) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
if (s->top == s->maxlen-1) {
printf("stack is full\n");
return -1;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = value;
return 0;
}检查栈是空或是满栈
函数结构
int stack_empty(sqstack *s); //是否为空函数
int tsack_full(sqstakk *s); //是否为满算法思路:检查栈是否为满栈就是比较s->top栈顶元素是否等于最后一个元素即s->maxlen-1;
代码实现:
//@ret 1-mept
int stack_empty(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL);
return -1;
}
//若s->top==-1成立则返回1否则返回0
return (s->top == -1 ? 1 :0);
}
//@ret 1-full
int stack_full(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("stack is full\n");
return -1;
}
return (s->top == s->maxlen-1 ? 1 : 0);
}
出栈操作
函数结构
data_t stack_pop(sqstack *s);算法思路:
(1)判断顺序栈是否为空;
(2)栈顶位置更新 top-- ;
(3)将要出栈的元素取出 data[top+1];
代码实现:
data_t stack_pop(sqstack *s) {
s->top--;
return (s->data[s->top+1]);
}这里函数原型的返回值就是要出站的值,所以逻辑结构要在main.c函数里实现即:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sqstack.h"
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
sqstack *s;
s = stack_create(100);
if (s == NULL)
return -1;
stack_push(s, 10);
stack_push(s, 20);
stack_push(s, 30);
stack_push(s, 40);
while(!stack_empty(s)) {
printf("pop: %d\n", stack_pop(s));
}
return 0;
}查看栈顶元素
函数原型
data_t stack_pop(stack *s);代码实现:
data_t stack_pop(sqstack *s) {
return (s->data[s->top]);
}栈元素清空操作
函数原型
int stack_clear(sqstack *s);功能:清空顺序栈中的元素
代码实现:
int stack_clear(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("stack is full\n");
return -1;
}
s->top = -1;
return 0;
}栈空间的释放操作
函数原型
int stack_free(sqstack *s);算法思路:
(1)空间释放free跟空间申请malloc要成对出现;
(2)释放空间时为防止数据丢失,与建立时过程相反,即先释放后申请的空间。
代码实现:
int stack_free(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("stack is full\n");
return -1;
}
if (s->data != NULL)
free(s->data);
free(s);
return 0;
}注意这里存在两种情况:
(1)在创建的时候会出现s->data空间创建失败返回NULL提示整个栈空间创建失败,其实这种情况下s空间是有可能创建成功的,所以要加上判断语句s->data != NULL;
(2)若是不加则需要在前面s->data创建空间失败时加上free(s)即:
if ((s->data = (data *)malloc(len * sizeof(data_t))) == NULL) {
printf("malloc data failed\n");
free(s);
return NULL;
----------------------------------------
int stack_free(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("stack is full\n");
return -1;
}
free(s->data);
free(s);
return 0;
}顺序栈完整代码
sqstack.h
typedef int data_t;
typedef struct {
data_t *data;
int maxlen;
int top;
}sqstack;
sqstack * stack_create(int len);
int stack_push(sqstack * s, data_t value);
int stack_empty(sqstack *s);
int stack_full(sqstack *s);
data_t stack_pop(sqstack *s);
data_t stack_top(sqstack *s);
int stack_clear(sqstack *s);
int stack_free(sqstack *s);
sqstack.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "sqstack.h"
sqstack * stack_create(int len) {
sqstack * s;
if ((s =(sqstack *)malloc(sizeof(sqstack))) == NULL) {
printf("malloc sqstack failed\n");
return NULL;
}
if ((s->data = (data_t *)malloc(len * sizeof(data_t)))==NULL) {
printf("malloc data failed\n");
free(s);
return NULL;
}
memset(s->data, 0, len*sizeof(data_t));
s->maxlen = len;
s->top = -1;
return s;
}
int stack_push(sqstack * s, data_t value) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
if (s->top == s->maxlen-1) {
printf("stack is full\n");
return -1;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = value;
return 0;
}
/*
*@ret 1-empty
* */
int stack_empty(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
return (s->top == -1 ? 1 : 0);
}
/*
* @ret 1-full
* */
int stack_full(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
return (s->top == s->maxlen-1 ? 1 : 0);
}
data_t stack_pop(sqstack *s) {
s->top--;
return (s->data[s->top+1]);
}
data_t stack_top(sqstack *s) {
return (s->data[s->top]);
}
int stack_clear(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
s->top = -1;
return 0;
}
int stack_free(sqstack *s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
if (s->data != NULL)
free(s->data);
free(s);
return 0;
}
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sqstack.h"
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
sqstack *s;
s = stack_create(100);
if (s == NULL)
return -1;
stack_push(s, 10);
stack_push(s, 20);
stack_push(s, 30);
stack_push(s, 40);
while (!stack_empty(s)) {
printf("pop: %d \n", stack_pop(s) );
}
stack_free(s);
return 0;
}
栈-链式栈原理及实现
链式栈
定义:插入操作和删除操作均在链表头部进行,链表尾部就是栈底,栈顶指针就是头指针。
链式栈结构体:
typedef int data_t; //定义栈中数据元素数据类型
typedef struct node{
data_t data; //数据域
struct node *next; //链接指针域
}listnode, *linktack; //链栈类型定义
链式栈的创建
函数原型:
linkstack stack_create();代码实现
linkstack stack_create() {
linkstack s;
s = (linkstack)malloc(sizeof(liatnode));
if (s == NULL) {
printf("malloc failed\n");
return NULL;
}
s->data = 0;
s->next = NULL;
return s;
}入栈操作
函数原型:
int stack_push(linkstack s, data_t value);算法思路:分两种情况,
(1)首次插入:s->next = p;
(2)多次插入:p->next = s->next; s->next = p;
如下图所示:
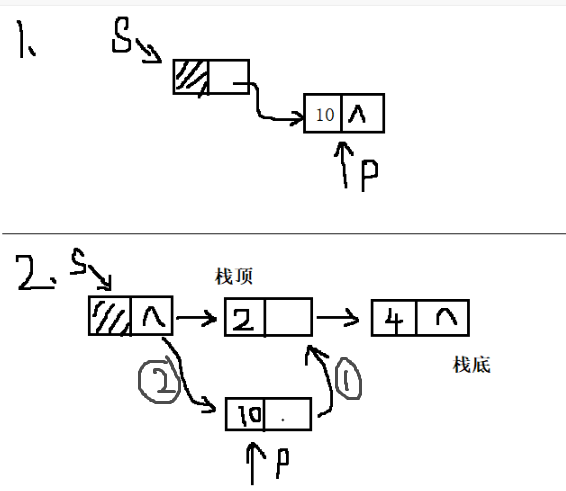
代码实现:
int stack_push(linkstack s, sdata_t value) {
linkstack p;
if (s == NULL) {
printf("stack is full\n");
return -1;
}
p = (linkstack)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
if (s == NULL) {
printf("malloc failed\n");
return -1;
}
p->data = value;
p->next = s->next;
s->next = p;
return 0;
}出栈操作
函数原型:
data_t stack_pop(linkstack s) ;算法思路:
(1)指针变量p指向待删除的变量 p = s->next;
(2)s->next = p->next;
(3)利用变量t接收出站元素;
(4)释放空间free。

代码实现:
data_t stack_pop(linkstak s) {
linkstack p;
data_t t;
p = s->next;
s->next = p->next;
t = p->next;
free(p);
p = NULL;
return t;
}栈是否为空栈
函数原型:
int stack_empty(linkstack s );代码实现:
int stack_empty(linkstack s {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
return (s->next == NULL ? 1 : 0);
}栈顶元素
函数原型:
data_t stack_top(linkstack s);代码实现:
data_t stack_top(linkstack s) {
return (s->next->data);
}栈空间释放
函数原型:
linkstack stack_free(linkstack s);算法思路:
代码实现:
linkstack stack_free(linkstack s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return NULL;
}
while(s != NULL) {
p = s;
s = s->next;
printf("free:%d\n", p->data);
free(p);
}
return NULL;
}























 1185
1185











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








