目录
学的黑马Java基础教程,全面解析Java-IO流,一套通关
学的黑马Java基础教程,全面解析Java-IO流,一套通关
1.IO流的概述
IO流:存储和读取数据的解决方案
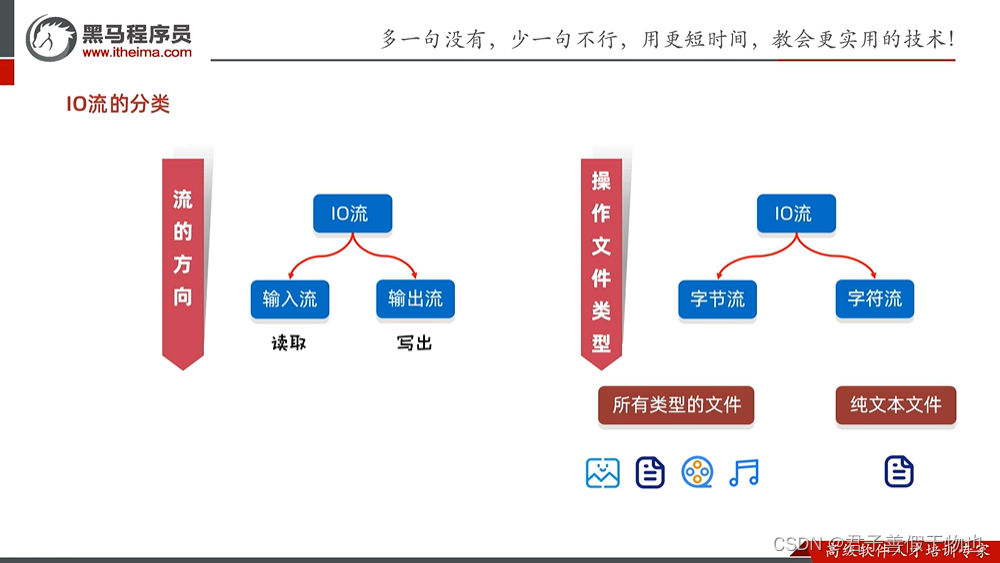
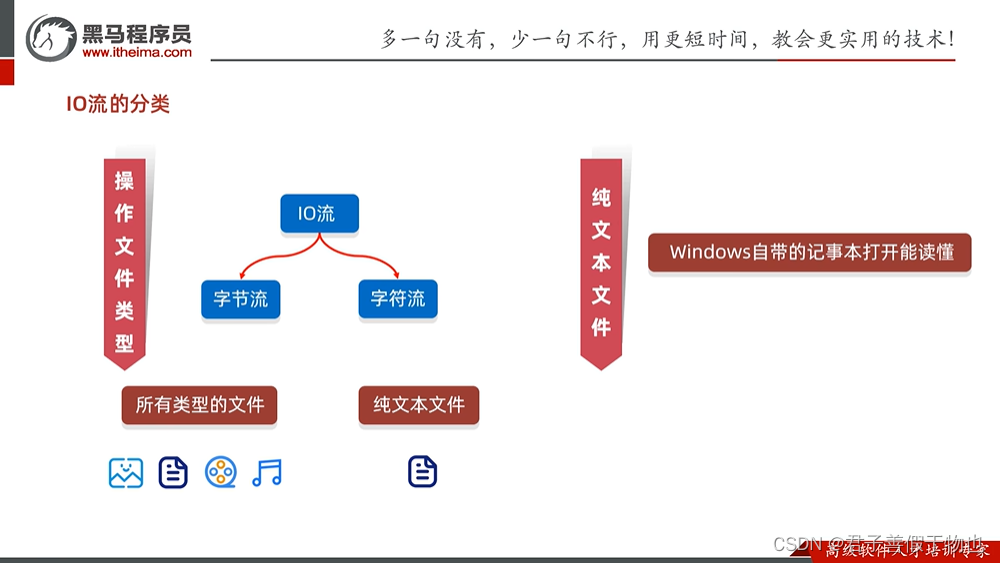

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.IO流的体系和字节流输出的基本用法
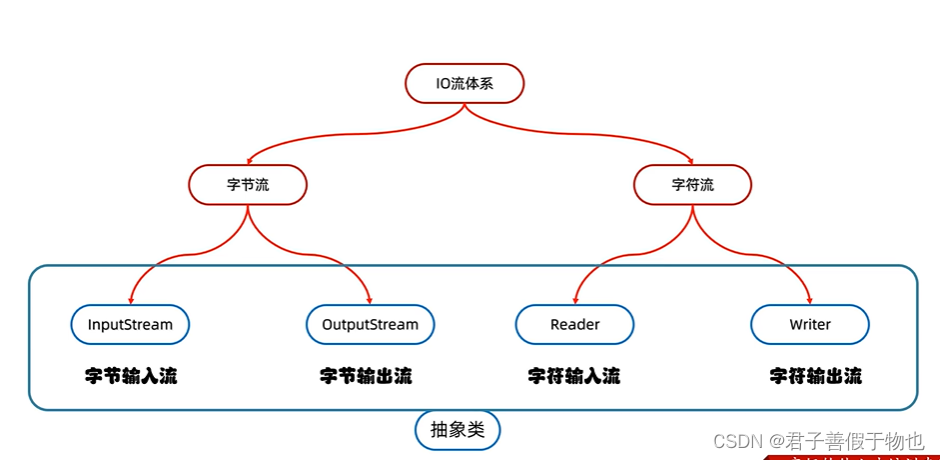
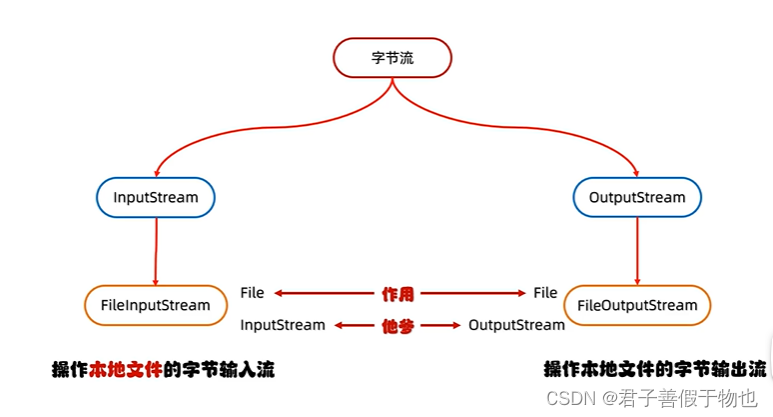
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 演示:字节输出流FileoutputStream
*
* 实现需求:写出一段文字体地文件中。《暂时不写中文)
* 实现步骤:
* 创建对象
* 写出数据
* 释放资源
*/
//1.创建对象
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/hhh.txt");
//2.写出数据
fileOutputStream.write(97);
//3.释放资源
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3.字节输出流的输出细节

---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4.字节输出流的三种写出数据方式
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建对象
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/hhh.txt");
//2.写出数据
//一次写一个字节数据 void write(int b)
//fileOutputStream.write(97);
//一次写一个字节数组数据
/*byte[] bytes={97,98,99,100};
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);*/
//一次写一个字节数组的部分数据
byte[] bytes={97,98,99,100};
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,1,2);//1是索引,2是个数
//3.释放资源
fileOutputStream.close();
}--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5.字节输出流换行写和续写
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 换行写:
* 再次写一个换行符就可以了
* Windows: \r\n
* Linux: \n
* Mac: \r
* 细节:
* 在Windows系统中,java对回车换行进行了优化
* 写一个\r 或者\n,但是建议写全
*
* 续写:
* 如果想要续写,打开续写开关就可以了
* 开关位置:创建对象的第二个参数
* 默认false:表示关闭续写。此时创建对象会清空文件
* 手动传递true:表示打开续写,此时创建对象不会清空文件
* //1.创建对象
* FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/hhh.txt",true);
*/
//1.创建对象
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/hhh.txt",true);
//2.写出数据
String str="djajjasjjacjkcnjsnc";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
//再次写一个换行符
String wrp = "\r\n";
byte[] bytes2 = wrp.getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes2);
String str2="6666";
byte[] bytes1 = str2.getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes1);
//3.释放资源
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6.字节输入流的基本用法

public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
演示:字节输入流FileInputStream
实现需求:读取文件中的数据。《管时不写中文》
实现步骤:
1. 创建对象
2. 读取数据
3. 释放资源
*/
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/hhh.txt");
//2.读取数据
//读取一个数据,想要全部读取出来,就是循环调用read
int b1=fileInputStream.read();
System.out.println(b1);
int b2=fileInputStream.read();
//读取的文件是英文,读取出来会素ASCII码
//我们转换char就不是数字了
System.out.println((char)b2);
//3.释放资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7.字节输入流循环读取
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
演示:字节输入流循环读取
实现步骤:
1. 创建对象
2. 读取数据
3. 释放资源
read :表示读取数据-而且是读联一个数据就移动一次指针
*/
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/hhh.txt");
//2.(循环)读取数据
//读取到-1,就表示已经读取完了的
int b;
while ((b=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) b);
}
//3.释放资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
}---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8.文件拷贝的基本代码
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
练习:
文件拷贝
把D:\itheima\movie.mp4拷贝到当前模块下。
注意;
选择一个比较小的文件。不要太大。大文件拷贝我们下一个视频会说。
*/
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\itheima\\movie.mp4");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\movie");
//2.拷贝
//核心思想:边读边写
int b;
while ((b=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(b);
}
//释放资源
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
9.文件拷贝的弊端和解决方案
FilelnputStream读取的问题:
IO流:如果拷贝的文件过大,那么速度会不会有影响?非常的慢,因为FilelnputStream一次读写一个字节。
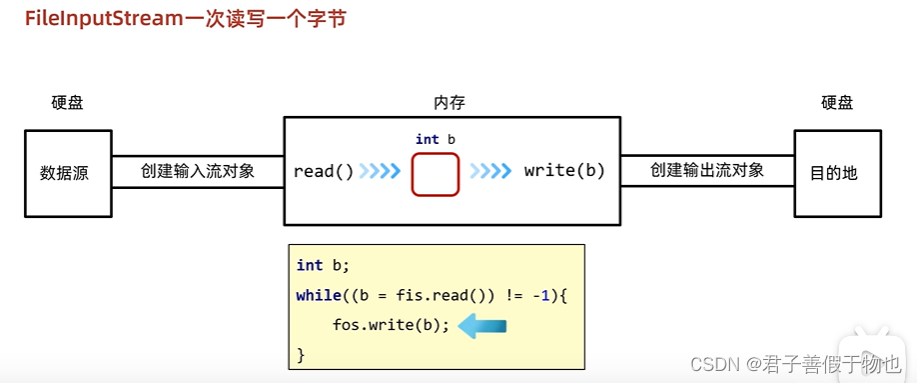
一次读多个字节

数组的长度一般写出1024的整数倍
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\hhh.txt");
//2.拷贝
//编写一次读两个字节
//2.1创建数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[2];
int len1=fileInputStream.read(bytes);
System.out.println("字节长度:"+len1);
String str1=new String(bytes,0,len1);
System.out.println("内容:"+str1);
//释放资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10.文件拷贝改写
package com.itheima.reggie.stream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author lpc
* @Date 2024 03 30 09 51
**/
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
练习:
文件拷贝
把D:\itheima\movie.mp4拷贝到当前模块下。
*/
//记录花费多少时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//1.创建对象
//数据来源
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\hhh.txt");
//数据输出地址
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\hhh2.txt");
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];//5兆
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//有多少数据我们就写多少
fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
//释放资源
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//输出拷贝花费的时间
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11.IO流中不同JDK版本捕获异常的方式
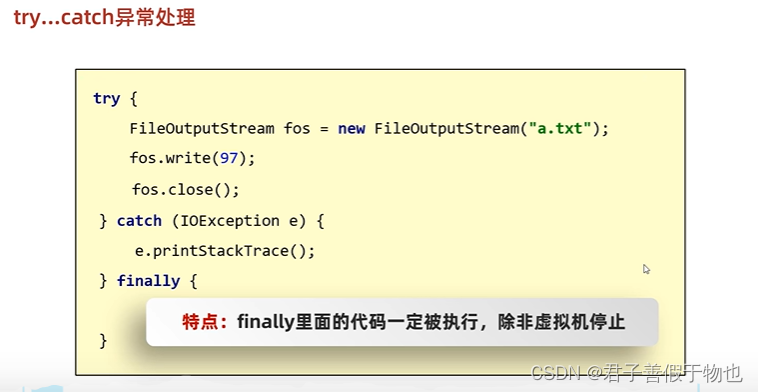
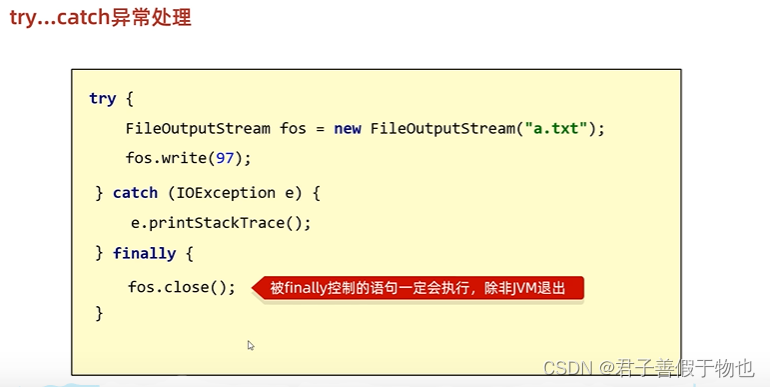
基本代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
利用try. ..catch. . .finally捕获拷贝文件中代码出现的异常
*/
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\hhh.txt");
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\hhh2.txt");
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];//5兆
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//有多少数据我们就写多少
fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//释放资源
if (fileInputStream!=null){
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (fileOutputStream!=null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
jdk7方案:
package com.itheima.reggie.stream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author lpc
* @Date 2024 04 10 14 59
**/
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 了解代码就可以了
* JDK7:IO流中捕获异露的写法
* try后面的小括号中写创建对象的代码,
* 注意:只有实现了AutoCloseable接口的类,才能在小括号中创建对象。
* try(){
* }catch(){
*
*
* }
*
*/
try(FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\hhh.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\hhh2.txt");)
{
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];//5兆
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//有多少数据我们就写多少
fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
jdk9方案:
package com.itheima.reggie.stream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author lpc
* @Date 2024 04 10 14 59
**/
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
/**
* JDK9:IO流中捕获异露的写法
*/
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\hhh.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\hhh2.txt");
try(fileInputStream;fileOutputStream)
{
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];//5兆
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//有多少数据我们就写多少
fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
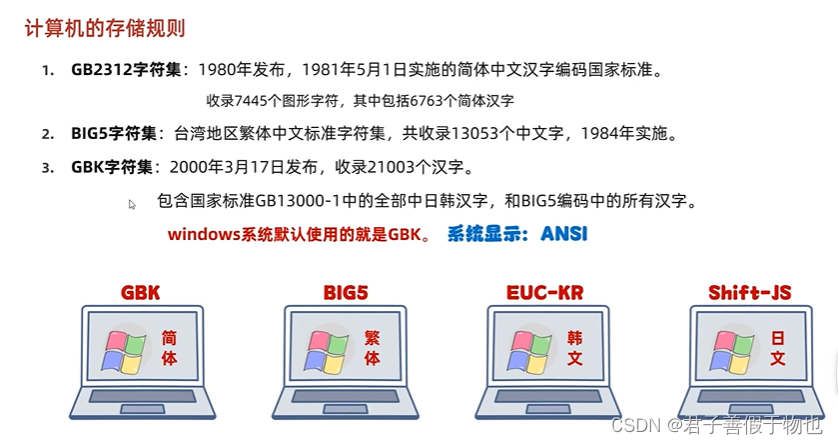
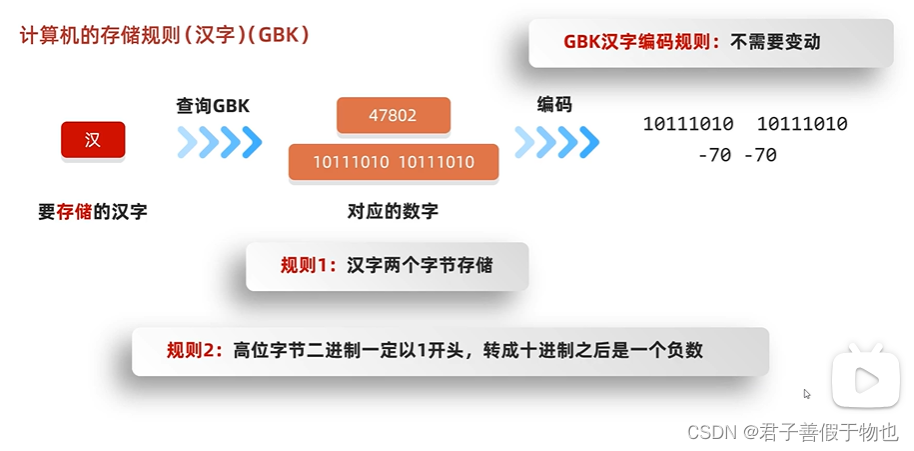
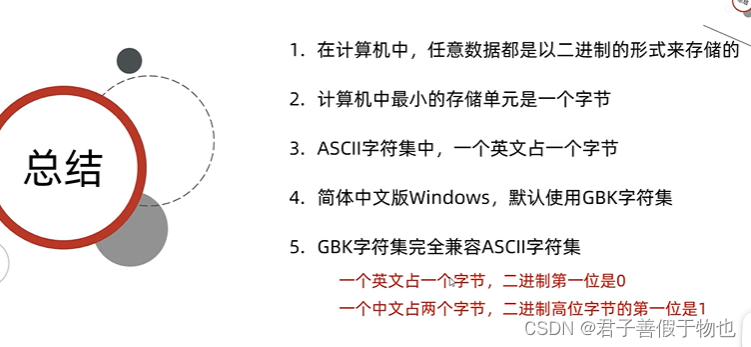
12.字符集详解(ASCII,GBK)
字节流读取中文会出现乱码问题
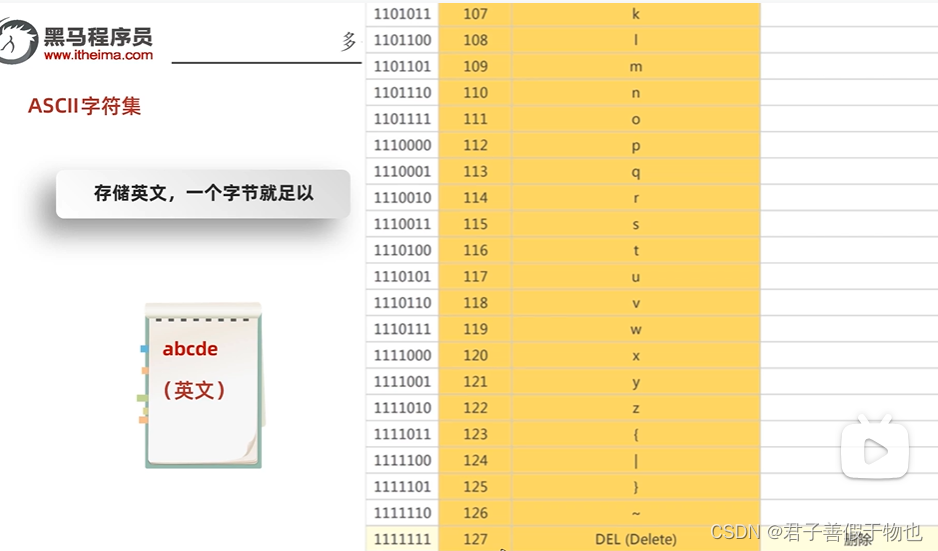



13.字符集(Unicode)

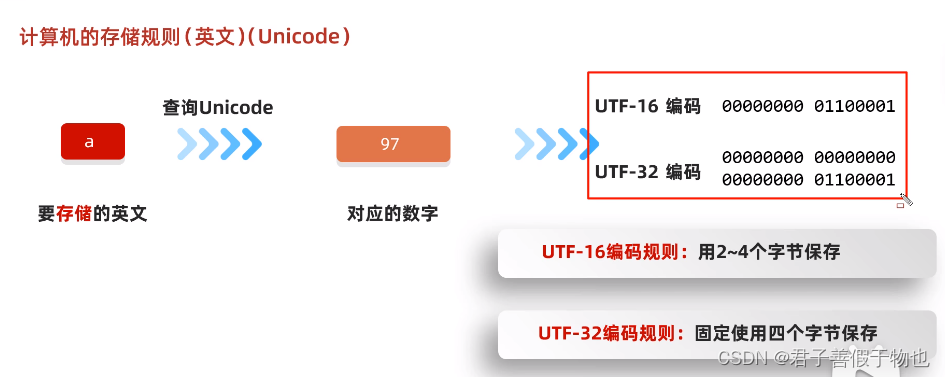


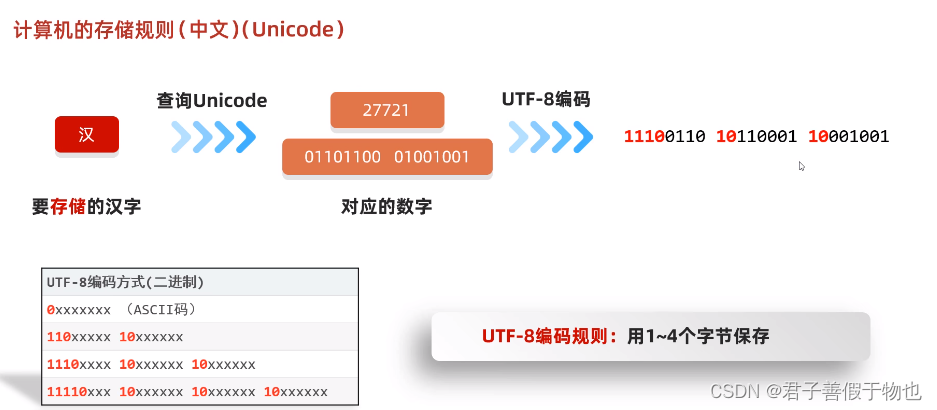
练习题1:
UTF-8是字符集吗?不是,它是Unicode字符集的一种编码方式


14.为什么会有乱码?

因为字节流一次读取一个字节,所有当读取汉字的三个字节,就会出错
2.解码的方式不用同一个导致
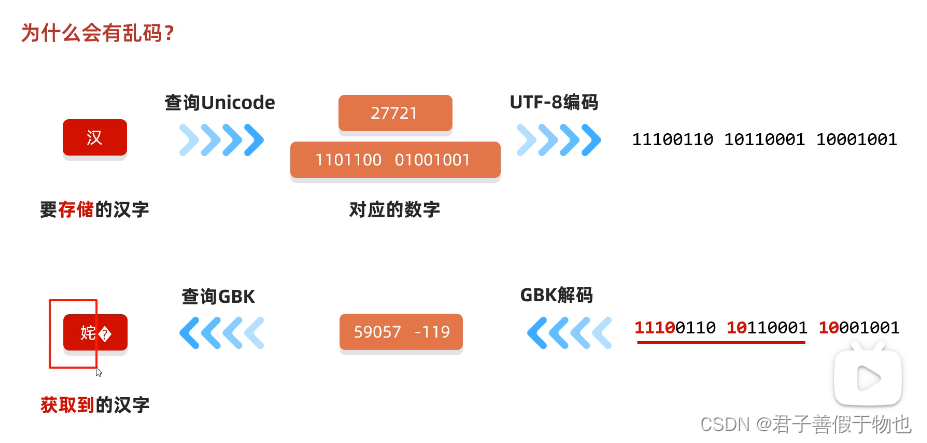
如何不产生乱码?
1,不要用字节流读取文本文件
2,编码解码时使用同一个码表,同一个编码方式






















 360
360











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








