寒假摸鱼大赏
前言:大一上跑去摸deep learning的鱼去了,原本的算法学习耽搁了很久。前不久,本半吊子选手终于决定gap半年,从零开始,享受并拥抱做普通人的快乐。
数据结构篇
(数组模拟)
单调栈和单调队列
-
单调栈常用题型:给定一个序列,找到序列当中每一个数,它的左(右)边比它小(大)且离其最近的数。
e.给定一个长度为 N 的整数数列,输出每个数左边第一个比它小的数,如果不存在则输出 −1。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
int stk[N],tt;
int main()
{ int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
while(tt && stk[tt]>=x) tt--;
if(tt) printf("%d ",stk[tt]);
else printf("-1 ");
stk[++tt]=x;
}
return 0;
}
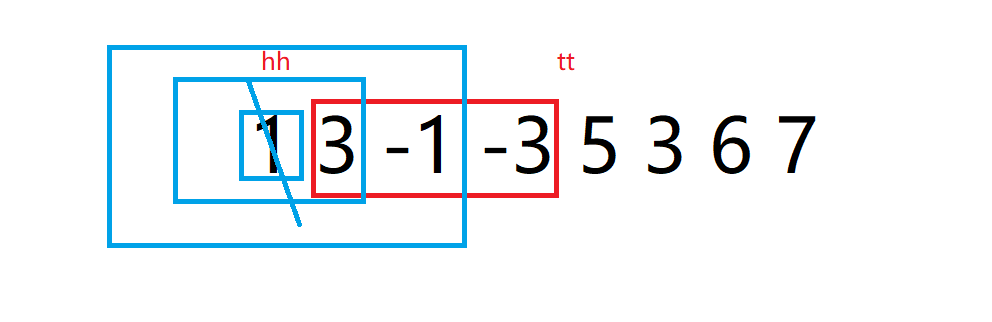
- 单调数列常用题型:滑动窗口
e.有一个长为 n n n的序列 a a a,以及一个大小为 k k k 的窗口。现在这个从左边开始向右滑动,每次滑动一个单位,求出每次滑动后窗口中的最大值和最小值。
最小值获取

for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//判断队头是否已经滑出滑动窗口
if(hh<=tt&&i-k+1>que[hh]) hh++;
while(hh<=tt&&a[que[tt]]>=a[i]) tt--;
que[++tt]=i;
if(i>=k-1) printf("%d",a[que[hh]]);
}
最大值获取同理
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//判断队头是否已经滑出滑动窗口
if(hh<=tt&&i-k+1>que[hh]) hh++;
while(hh<=tt&&a[que[tt]]<=a[i]) tt--;
que[++tt]=i;
if(i>=k-1) printf("%d",a[que[hh]]);
}
合并
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int h,t=-1;
const int N=1e6+10;
int a[N],q[N];
int main()
{
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(h<=t && i-q[h]+1>k) h++;
while(h<=t && a[q[t]]>=a[i]) t--;
q[++t]=i;
if(i+1>=k) cout<<a[q[h]]<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
h=0;t=-1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(h<=t && i-q[h]+1>k) h++;
while(h<=t && a[q[t]]<=a[i]) t--;
q[++t]=i;
if(i+1>=k) cout<<a[q[h]]<<' ';
}
return 0;
}
KMP
e.给定一个模式串
S
S
S,以及一个模板串
P
P
P,所有字符串中只包含大小写英文字母以及阿拉伯数字。模板串
P
P
P在模式串
S
S
S中多次作为子串出现。
求出模板串
P
P
P在模式串
S
S
S中所有出现的位置的起始下标。
参考:
浅析
数据结构KMP算法配图详解(超详细)


#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 1000010;
int n, m;
int ne[N];
char s[M], p[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> p + 1 >> m >> s + 1;
//求next[],通过模板串自己与自己进行匹配操作得出来
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
//匹配字符串
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if (j == n)
{
printf("%d ", i - n);
j = ne[j];
}
}
return 0;
}
Trie
高效的存储和查找字符串
eg.Trie字符串统计

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
int son[N][26],cnt[N],idx,n;
char str[N];
void insert(char *str)
{
int p=0;
for(int i=0;str[i];i++)
{
int u=str[i]-'a';
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx;
p=son[p][u];
}
cnt[p]++;
}
int query(char *str)
{
int p=0;
for(int i=0;str[i];i++)
{
int u=str[i]-'a';
if(!son[p][u]) return 0;
p=son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
char op[2];
scanf("%s %s",op,str);
if(*op=='I') insert(str);
else printf("%d\n",query(str));
}
return 0;
}
并查集
- 将两个集合合并
- 查询两个元素是否在同一集合之中
每个集合都用一棵树表示,树根的编号就是整个集合的编号。每个节点储存他的父节点,P[X]是X的父节点
问题:
- 如何判断树根:
if(p[x]==x) - 如何求x的集合编号:
while(p[x]!=x) x=p[x] - 如何合并两个集合: p x p_x px是 x x x的集合编号, p y p_y py是 y y y的集合编号。 p [ x ] = y p[x]=y p[x]=y即使两集合合并.
优化方法:路径压缩
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
int p[N],n,m;
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x) p[x]=find(p[x]); //压缩路径
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) p[i]=i;
while(m--)
{
char op[2];
int a,b;
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&a,&b);
if(*op=='M') p[find(a)]=find(b);
else
{ if(find(a)==find(b)) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
acwing 837
路径压缩

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int p[N], cnt[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
cnt[i] = 1;
}
while (m -- )
{
string op;
int a, b;
cin >> op;
if (op == "C")
{
cin >> a >> b;
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if (a != b)
{
p[a] = b;
cnt[b] += cnt[a];
}
}
else if (op == "Q1")
{
cin >> a >> b;
if (find(a) == find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
else
{
cin >> a;
cout << cnt[find(a)] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
堆
- 插入一个数:
head[++size]=x;up(x) - 求集合中的最小值:
heap[1] - 删除最小值:
heap[1]=heap[size];size--;down(!) - 删改任意一个元素:
heap[k]=heap[size];size--;down(k);up(k) - 修改任意一个元素:
heap[k]=x;sown(k);up(k)
堆是完全二叉树






















 299
299











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








