3.1函数的默认参数
在C++中,函数的形参列表中的形参是可以有默认值的。
语法:返回值类型 函数名 (参数= 默认值){}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//如果是我们自己传入数据,就用自己的数据,如果没有,那么用默认值
//语法:返回值类型 函数名(形参=默认值){}
int func(int a, int b=20, int c=30)
{
return a + b + c;
}
//注意事项:
//1如果某个位置已经有了默认参数,那么从这个位置往后,从左到右都必须有默认值
//2.如果函数声明有默认参数,函数实现就不能有默认参数。如果函数实现有默认参数,函数声明就不能有默认参数
//声明和实现只能有一个有默认参数
int func2(int a=10, int b=10);//函数声明
int func2(int a,int b)//函数实现
{
return a + b;
}
int main()
{
cout<<func(10,30)<<endl;//70
cout << func2(10, 20) << endl;//30
system("pause");
return 0;
}3.2函数的占位参数
C++中函数的形参列表里可以有占位参数,用来做占位,调用函数时必须填补该位置
语法: 返回值类型 函数名 (数据类型){}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//占位参数
//返回值类型 函数名(数据类型){}
//目前阶段的占位参数,我们还用不到,后面课程会用到
void func(int a,int)
{
cout << "this is function" << endl;
}
//占位参数,还可以有默认参数
void func2(int a, int = 10)
{
cout << "this is function too" << endl;
}
int main()
{
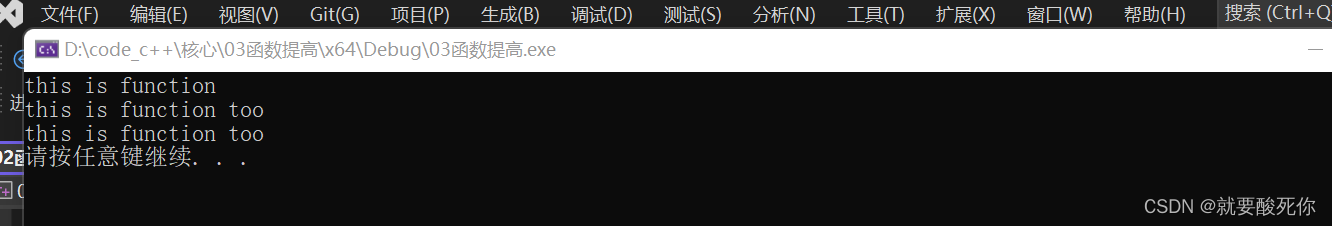
func(10, 10);
func2(10);
func2(10, 20);
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:
3.3函数重载
3.3.1函数重载的基本语法
作用:函数名可以相同,提高复用性
函数重载满足条件:
- 同一个作用域下
- 函数名称相同
- 函数参数类型不同 或者 个数不同 或者 顺序不同
注意: 函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数重载
//1.在同一个作用域下
//2.函数名称相同
//3.函数参数类型不同,或者个数不同,或者顺序不同
void func()
{
cout << "func的调用" << endl;
}
void func(int a)
{
cout << "func(int a)的调用" << endl;
}
void func(double a)
{
cout << "func(double a)的调用" << endl;
}
void func(int a, double b)
{
cout << "func(int a,double b)的调用" << endl;
}
void func(double a, int b)
{
cout << "func(double a,int b)的调用" << endl;
}
//注意事项:函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件
//int func(double a, int b)
//{
// cout << "func(double a,int b)的调用" << endl;
//}
int main()
{
func();
func(10);
func(3.14);
func(10, 3.14);
func(3.14, 10);
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果: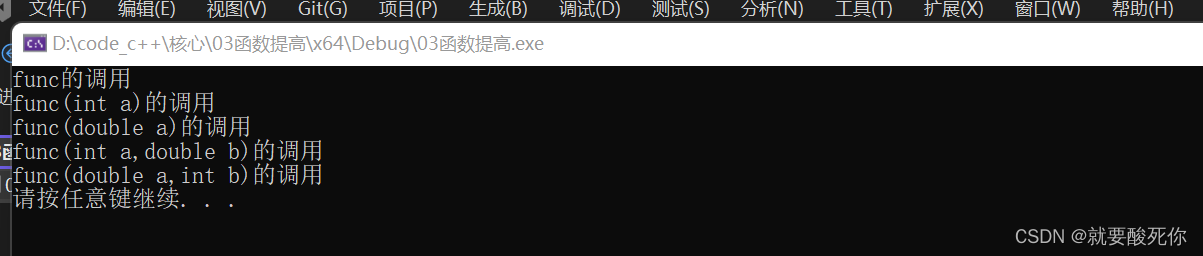
3.3.2函数重载的注意事项
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数重载的注意事项
//1.引用作为重载的条件
void function1(int& a)
{
cout << "func(int &a)的调用" << endl;
}
void function1(const int& a)//const int &a=20是合法的
{
cout << "func(const int &a)的调用" << endl;
}
//2.函数重载遇到默认参数
void function2(int a,int b=10)
{
cout << "func2(int a,intb)的调用" << endl;
}
void function2(int a)
{
cout << "func2(int a)的调用" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
function1(a);//调用无const
function1(20);//调用有const 不能调用上面那个函数,因为int &a=20是错误不合法的
//func2(30);//当函数重载遇到默认参数,出现二义性,报错,应该尽量避免这种情况
function2(30, 10);
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果: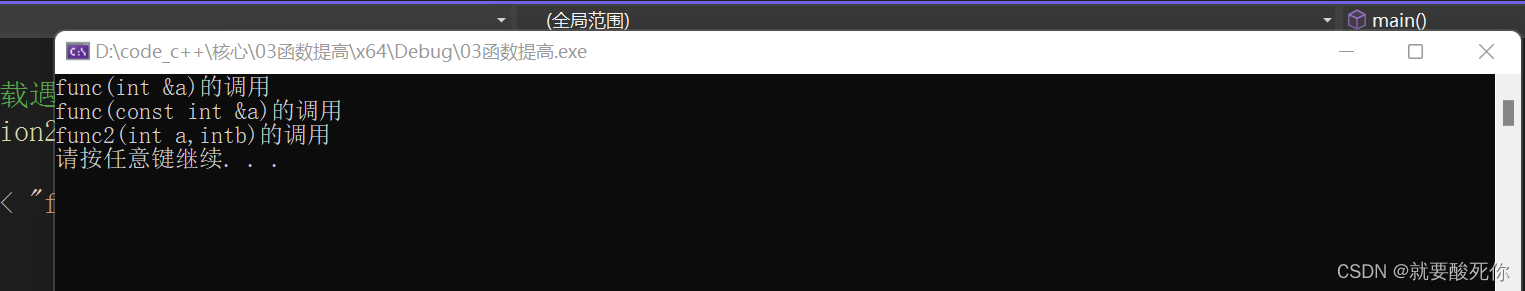






















 1542
1542











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








