| 3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 4 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 5 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0 |
| 6 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0 |
| 7 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 8 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 9 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 0 |
| 10 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 11 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 12 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0 |
| 13 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0 |
| 14 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 15 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0 |
| 16 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0 |
| 17 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0 |
| 18 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0 |
| 19 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0 |
| 20 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 21 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0 |
| 22 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 23 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0 |
| 24 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 25 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 26 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 0 |
| 27 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 28 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 29 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0 |
| … | … | … | … |
| 120 | 5.7 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 121 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 2 |
| 122 | 6.7 | 2.0 | 2 |
| 123 | 4.9 | 1.8 | 2 |
| 124 | 5.7 | 2.1 | 2 |
| 125 | 6.0 | 1.8 | 2 |
| 126 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 2 |
| 127 | 4.9 | 1.8 | 2 |
| 128 | 5.6 | 2.1 | 2 |
| 129 | 5.8 | 1.6 | 2 |
| 130 | 6.1 | 1.9 | 2 |
| 131 | 6.4 | 2.0 | 2 |
| 132 | 5.6 | 2.2 | 2 |
| 133 | 5.1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 134 | 5.6 | 1.4 | 2 |
| 135 | 6.1 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 136 | 5.6 | 2.4 | 2 |
| 137 | 5.5 | 1.8 | 2 |
| 138 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 2 |
| 139 | 5.4 | 2.1 | 2 |
| 140 | 5.6 | 2.4 | 2 |
| 141 | 5.1 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 142 | 5.1 | 1.9 | 2 |
| 143 | 5.9 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 144 | 5.7 | 2.5 | 2 |
| 145 | 5.2 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 146 | 5.0 | 1.9 | 2 |
| 147 | 5.2 | 2.0 | 2 |
| 148 | 5.4 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 149 | 5.1 | 1.8 | 2 |
150 rows × 3 columns
【5】数据集的标准化(本数据集特征比较接近,实际处理过程中未标准化)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import pandas as pd
trans = StandardScaler()
_iris_simple = trans.fit_transform(iris_simple[["petal\_length", "petal\_width"]])
_iris_simple = pd.DataFrame(_iris_simple, columns = ["petal\_length", "petal\_width"])
_iris_simple.describe()
| petal_length | petal_width | |
|---|---|---|
| count | 1.500000e+02 | 1.500000e+02 |
| mean | -8.652338e-16 | -4.662937e-16 |
| std | 1.003350e+00 | 1.003350e+00 |
| min | -1.567576e+00 | -1.447076e+00 |
| 25% | -1.226552e+00 | -1.183812e+00 |
| 50% | 3.364776e-01 | 1.325097e-01 |
| 75% | 7.627583e-01 | 7.906707e-01 |
| max | 1.785832e+00 | 1.712096e+00 |
【6】构建训练集和测试集(本课暂不考虑验证集)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_set, test_set = train_test_split(iris_simple, test_size=0.2) # 20%的数据作为测试集
test_set.head()
| petal_length | petal_width | species | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 111 | 5.3 | 1.9 | 2 |
| 24 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 5 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0 |
| 92 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 1 |
iris_x_train = train_set[["petal\_length", "petal\_width"]]
iris_x_train.head()
| petal_length | petal_width | |
|---|---|---|
| 63 | 4.7 | 1.4 |
| 93 | 3.3 | 1.0 |
| 34 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| 35 | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| 126 | 4.8 | 1.8 |
iris_y_train = train_set["species"].copy()
iris_y_train.head()
63 1
93 1
34 0
35 0
126 2
Name: species, dtype: int32
iris_x_test = test_set[["petal\_length", "petal\_width"]]
iris_x_test.head()
| petal_length | petal_width | |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| 111 | 5.3 | 1.9 |
| 24 | 1.9 | 0.2 |
| 5 | 1.7 | 0.4 |
| 92 | 4.0 | 1.2 |
iris_y_test = test_set["species"].copy()
iris_y_test.head()
3 0
111 2
24 0
5 0
92 1
Name: species, dtype: int32
13.1 k近邻算法
【1】基本思想
与待预测点最近的训练数据集中的k个邻居
把k个近邻中最常见的类别预测为带预测点的类别
【2】sklearn实现
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
- 构建分类器对象
clf = KNeighborsClassifier()
clf
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30, metric='minkowski',
metric_params=None, n_jobs=None, n_neighbors=5, p=2,
weights='uniform')
- 训练
clf.fit(iris_x_train, iris_y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30, metric='minkowski',
metric_params=None, n_jobs=None, n_neighbors=5, p=2,
weights='uniform')
- 预测
res = clf.predict(iris_x_test)
print(res)
print(iris_y_test.values)
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
- 翻转
encoder.inverse_transform(res)
array(['setosa', 'virginica', 'setosa', 'setosa', 'versicolor',
'versicolor', 'setosa', 'virginica', 'versicolor', 'virginica',
'versicolor', 'virginica', 'virginica', 'virginica', 'versicolor',
'setosa', 'setosa', 'setosa', 'versicolor', 'setosa', 'virginica',
'setosa', 'virginica', 'versicolor', 'setosa', 'versicolor',
'setosa', 'setosa', 'versicolor', 'versicolor'], dtype=object)
- 评估
accuracy = clf.score(iris_x_test, iris_y_test)
print("预测正确率:{:.0%}".format(accuracy))
预测正确率:97%
- 存储数据
out = iris_x_test.copy()
out["y"] = iris_y_test
out["pre"] = res
out
| petal_length | petal_width | y | pre | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 111 | 5.3 | 1.9 | 2 | 2 |
| 24 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 |
| 92 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 1 | 1 |
| 57 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 112 | 5.5 | 2.1 | 2 | 2 |
| 106 | 4.5 | 1.7 | 2 | 1 |
| 136 | 5.6 | 2.4 | 2 | 2 |
| 80 | 3.8 | 1.1 | 1 | 1 |
| 131 | 6.4 | 2.0 | 2 | 2 |
| 147 | 5.2 | 2.0 | 2 | 2 |
| 113 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 2 | 2 |
| 84 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 1 | 1 |
| 39 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 40 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 17 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 56 | 4.7 | 1.6 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 100 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 2 | 2 |
| 42 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 144 | 5.7 | 2.5 | 2 | 2 |
| 79 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 19 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 75 | 4.4 | 1.4 | 1 | 1 |
| 44 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 |
| 37 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| 64 | 3.6 | 1.3 | 1 | 1 |
| 90 | 4.4 | 1.2 | 1 | 1 |
out.to_csv("iris\_predict.csv")
【3】可视化
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def draw(clf):
# 网格化
M, N = 500, 500
x1_min, x2_min = iris_simple[["petal\_length", "petal\_width"]].min(axis=0)
x1_max, x2_max = iris_simple[["petal\_length", "petal\_width"]].max(axis=0)
t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, M)
t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, N)
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2)
# 预测
x_show = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1)
y_predict = clf.predict(x_show)
# 配色
cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(["#A0FFA0", "#FFA0A0", "#A0A0FF"])
cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(["g", "r", "b"])
# 绘制预测区域图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.pcolormesh(t1, t2, y_predict.reshape(x1.shape), cmap=cm_light)
# 绘制原始数据点
plt.scatter(iris_simple["petal\_length"], iris_simple["petal\_width"], label=None,
c=iris_simple["species"], cmap=cm_dark, marker='o', edgecolors='k')
plt.xlabel("petal\_length")
plt.ylabel("petal\_width")
# 绘制图例
color = ["g", "r", "b"]
species = ["setosa", "virginica", "versicolor"]
for i in range(3):
plt.scatter([], [], c=color[i], s=40, label=species[i]) # 利用空点绘制图例
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.title('iris\_classfier')
draw(clf)
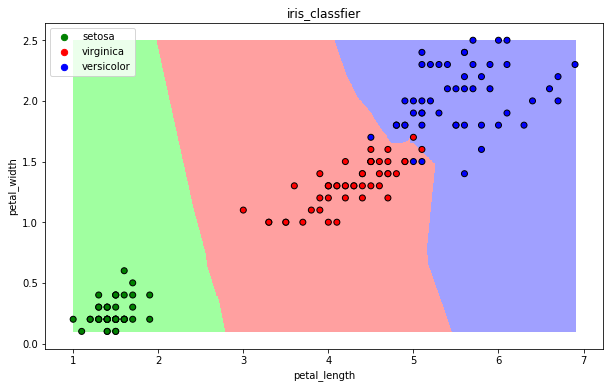
13.2 朴素贝叶斯算法
【1】基本思想
当X=(x1, x2)发生的时候,哪一个yk发生的概率最大
【2】sklearn实现
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
- 构建分类器对象
clf = GaussianNB()
clf
- 训练
clf.fit(iris_x_train, iris_y_train)
- 预测
res = clf.predict(iris_x_test)
print(res)
print(iris_y_test.values)
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
- 评估
accuracy = clf.score(iris_x_test, iris_y_test)
print("预测正确率:{:.0%}".format(accuracy))
预测正确率:97%
- 可视化
draw(clf)
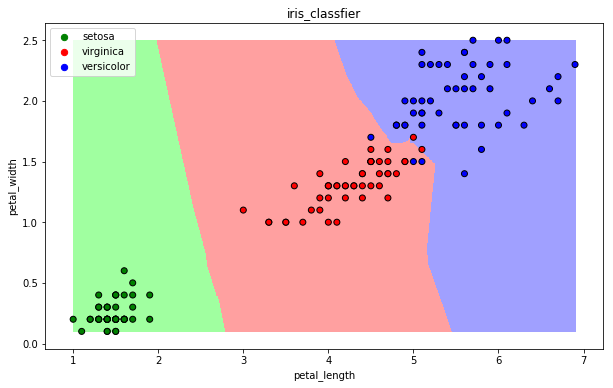
13.3 决策树算法
【1】基本思想
CART算法:每次通过一个特征,将数据尽可能的分为纯净的两类,递归的分下去
【2】sklearn实现
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
- 构建分类器对象
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=None, splitter='best')
- 训练
clf.fit(iris_x_train, iris_y_train)
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=None, splitter='best')
- 预测
res = clf.predict(iris_x_test)
print(res)
print(iris_y_test.values)
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
- 评估
accuracy = clf.score(iris_x_test, iris_y_test)
print("预测正确率:{:.0%}".format(accuracy))
预测正确率:97%
- 可视化
draw(clf)
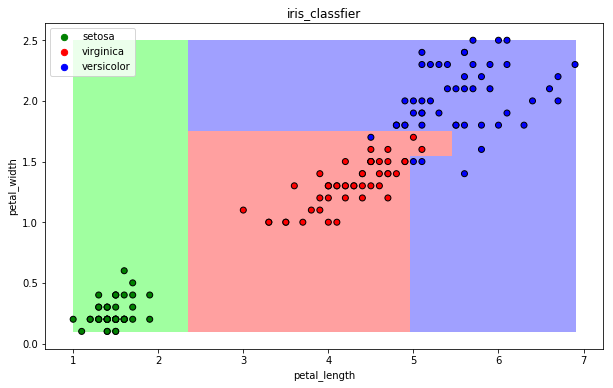
13.4 逻辑回归算法
【1】基本思想
一种解释:
训练:通过一个映射方式,将特征X=(x1, x2) 映射成 P(y=ck), 求使得所有概率之积最大化的映射方式里的参数
预测:计算p(y=ck) 取概率最大的那个类别作为预测对象的分类
【2】sklearn实现
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
- 构建分类器对象
clf = LogisticRegression(solver='saga', max_iter=1000)
clf
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=1000,
multi_class='warn', n_jobs=None, penalty='l2',
random_state=None, solver='saga', tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
- 训练
clf.fit(iris_x_train, iris_y_train)
C:\Users\ibm\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\linear_model\logistic.py:469: FutureWarning: Default multi_class will be changed to 'auto' in 0.22. Specify the multi_class option to silence this warning.
"this warning.", FutureWarning)
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=1000,
multi_class='warn', n_jobs=None, penalty='l2',
random_state=None, solver='saga', tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
- 预测
res = clf.predict(iris_x_test)
print(res)
print(iris_y_test.values)
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
- 评估
accuracy = clf.score(iris_x_test, iris_y_test)
print("预测正确率:{:.0%}".format(accuracy))
预测正确率:97%
- 可视化
draw(clf)
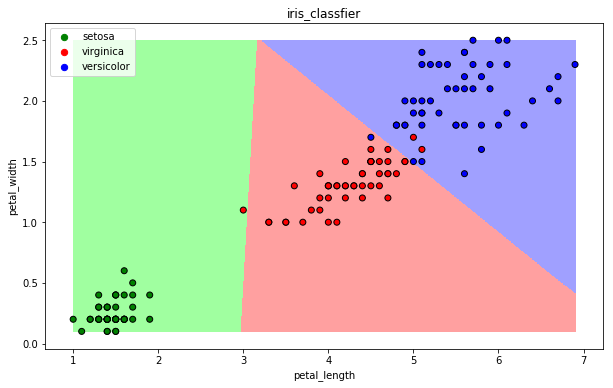
13.5 支持向量机算法
【1】基本思想
以二分类为例,假设数据可用完全分开:
用一个超平面将两类数据完全分开,且最近点到平面的距离最大
【2】sklearn实现
from sklearn.svm import SVC
- 构建分类器对象
clf = SVC()
clf
SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma='auto_deprecated',
kernel='rbf', max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None,
shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False)
- 训练
clf.fit(iris_x_train, iris_y_train)
C:\Users\ibm\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\svm\base.py:193: FutureWarning: The default value of gamma will change from 'auto' to 'scale' in version 0.22 to account better for unscaled features. Set gamma explicitly to 'auto' or 'scale' to avoid this warning.
"avoid this warning.", FutureWarning)
SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma='auto_deprecated',
kernel='rbf', max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None,
shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False)
- 预测
res = clf.predict(iris_x_test)
print(res)
print(iris_y_test.values)
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
- 评估
accuracy = clf.score(iris_x_test, iris_y_test)
print("预测正确率:{:.0%}".format(accuracy))
预测正确率:97%
- 可视化
draw(clf)
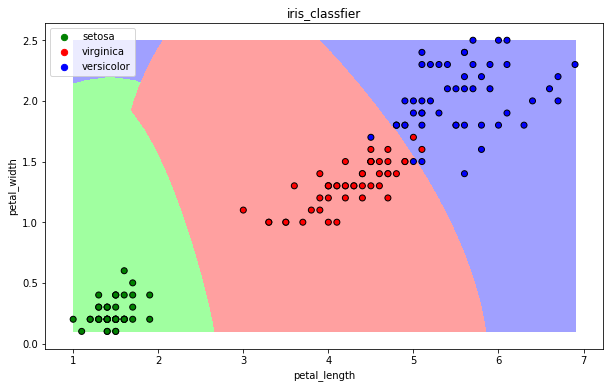
13.6 集成方法——随机森林
【1】基本思想
训练集m,有放回的随机抽取m个数据,构成一组,共抽取n组采样集
n组采样集训练得到n个弱分类器 弱分类器一般用决策树或神经网络
将n个弱分类器进行组合得到强分类器
【2】sklearn实现
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
- 构建分类器对象
clf = RandomForestClassifier()
clf
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators='warn',
n_jobs=None, oob_score=False, random_state=None,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
- 训练
clf.fit(iris_x_train, iris_y_train)
C:\Users\ibm\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\ensemble\forest.py:245: FutureWarning: The default value of n_estimators will change from 10 in version 0.20 to 100 in 0.22.
"10 in version 0.20 to 100 in 0.22.", FutureWarning)
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=10,
n_jobs=None, oob_score=False, random_state=None,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
- 预测
res = clf.predict(iris_x_test)
print(res)
print(iris_y_test.values)
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
[0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1]
- 评估
accuracy = clf.score(iris_x_test, iris_y_test)
print("预测正确率:{:.0%}".format(accuracy))
预测正确率:97%
- 可视化
draw(clf)
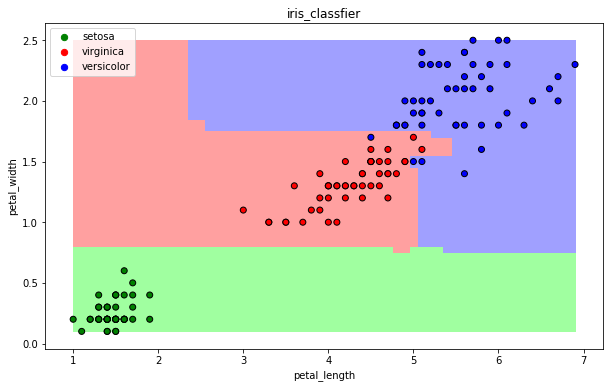
13.7 集成方法——Adaboost
【1】基本思想
训练集m,用初始数据权重训练得到第一个弱分类器,根据误差率计算弱分类器系数,更新数据的权重
使用新的权重训练得到第二个弱分类器,以此类推
根据各自系数,将所有弱分类器加权求和获得强分类器
【2】sklearn实现
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
- 构建分类器对象
clf = AdaBoostClassifier()
clf
AdaBoostClassifier(algorithm='SAMME.R', base_estimator=None, learning_rate=1.0,
n_estimators=50, random_state=None)
- 训练
clf.fit(iris_x_train, iris_y_train)
AdaBoostClassifier(algorithm='SAMME.R', base_estimator=None, learning_rate=1.0,
n_estimators=50, random_state=None)
- 预测
res = clf.predict(iris_x_test)
**自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。**
**深知大多数Python工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!**
**因此收集整理了一份《2024年Python开发全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。**

**既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Python开发知识点,真正体系化!**
**由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录大纲截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新**
**如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加V获取:vip1024c (备注Python)**

文末有福利领取哦~
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
👉**一、Python所有方向的学习路线**
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
👉**二、Python必备开发工具**
👉**三、Python视频合集**
观看零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。
👉 **四、实战案例**
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。**(文末领读者福利)**
👉**五、Python练习题**
检查学习结果。

👉**六、面试资料**
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。
👉因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,这份完整版的Python全套学习资料已经上传
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远。不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎扫码加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**

己学得较为全面。
👉**二、Python必备开发工具**

👉**三、Python视频合集**
观看零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。

👉 **四、实战案例**
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。**(文末领读者福利)**

👉**五、Python练习题**
检查学习结果。

👉**六、面试资料**
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。


👉因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,这份完整版的Python全套学习资料已经上传
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远。不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎扫码加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**
[外链图片转存中...(img-EW6BzvVN-1712850556831)]






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








