目录
编写ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
Spring IoC容器的实现原理:工厂模式 + 解析XML + 反射机制。
创建模块
采用Maven方式新建Module:myIocSpring

引入dom4j和jaxen的依赖,因为要使用它解析XML文件,还有junit依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
准备测试阶段测试用的Bean
这里我们准备2个bean,一个是学生类,一个是班级类,在本文中我们就书写简单的ref和基本数据类型的IOC(即使用value给简单属性赋值。使用ref给非简单属性赋值。)。放在com.study包下
public class Clazz {
private String name;
private Integer total;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Clazz{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", total=" + total +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getTotal() {
return total;
}
public void setTotal(Integer total) {
this.total = total;
}
}public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Clazz clazz;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", clazz=" + clazz +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Clazz getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(Clazz clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
}
准备测试阶段测试用的XML配置文件:IOC.xml文件放在类路径当中即可,我们这里把文件放到类的根路径下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="clazz" class="com.study.Clazz">
<property name="name" value="21软件工程c"/>
<property name="total" value="59"/>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.study.Student">
<property name="name" value="zzh"/>
<property name="age" value="19"/>
<property name="clazz" ref="clazz"/>
</bean>
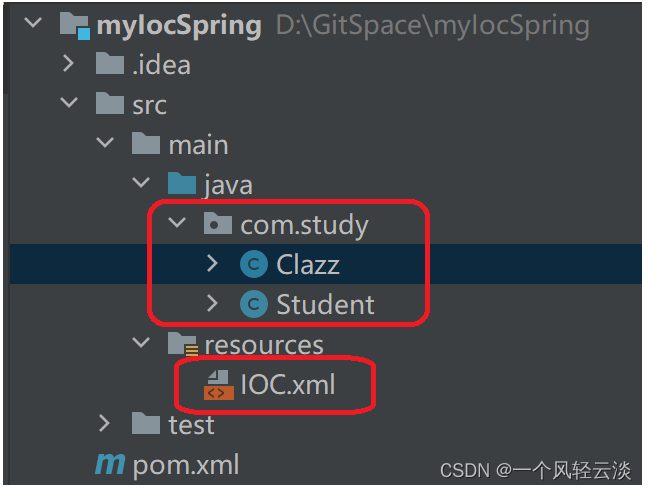
</beans>这时的目录结构如下:
编写ApplicationContext接口
ApplicationContext接口中提供一个getBean()方法,通过该方法可以获取Bean对象。
public interface ApplicationContext {
/**
* 根据bean的id获取bean实例。
* @param beanId bean的id
* @return bean实例
*/
Object getBean(String beanId);
}编写ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是ApplicationContext接口的实现类。该类从类路径当中加载myspring.xml配置文件。
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanId) {
return null;
}
}
采用Map集合存储Bean
采用Map集合存储Bean实例。Map集合的key存储beanId,value存储Bean实例。Map<String,Object>在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类中添加Map<String,Object>属性。并且在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类中添加构造方法,该构造方法的参数接收myspring.xml文件。同时实现getBean方法。
/**
* 存储bean的Map集合
*/
private Map<String,Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 在该构造方法中,解析myspring.xml文件,创建所有的Bean实例,并将Bean实例存放到Map集合中。
* @param resource 配置文件路径(要求在类路径当中)
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String resource) {
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanId) {
return beanMap.get(beanId);
}解析配置文件实例化所有Bean
在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的构造方法中解析配置文件,获取所有bean的类名,通过反射机制调用无参数构造方法创建Bean。并且将Bean对象存放到Map集合中。
解析配置文件实例化所有Bean
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{
/**
* 存储bean的Map集合
*/
private Map<String,Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 在该构造方法中,解析myspring.xml文件,创建所有的Bean实例,并将Bean实例存放到Map集合中。
* @param resource 配置文件路径(要求在类路径当中)
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String resource) {
SAXReader reader=new SAXReader();
try {
//读取配置文件
Document document = reader.read(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(resource));
//拿到所有的bean标签
List<Node> beanNodes = document.selectNodes("//bean");
//遍历集合拿到对bean进行处理
beanNodes.forEach(beanNode->{
Element beanElt= (Element)beanNode;
//获取id
String id = beanElt.attributeValue("id");
//获取className
String className = beanElt.attributeValue("class");
try {
//反射获取对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
Object bean = constructor.newInstance();
//存储到Map集合中
beanMap.put(id,bean);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanId) {
return beanMap.get(beanId);
}
}测试阶段1(实例化bean)
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("IOC.XML");
Object clazz = applicationContext.getBean("clazz");
Object student = applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(clazz);
System.out.println(student);
}
}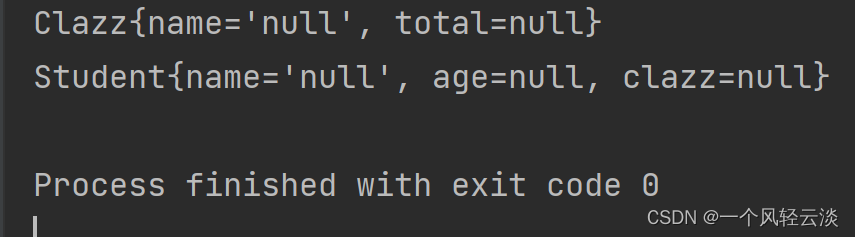
通过测试Bean已经实例化成功了,属性的值是null,因为我们调用的都是无参构造方法,所以属性值都是默认值,接下来给bean赋值即可。
Bean的属性赋值
通过反射机制调用set方法,给Bean的属性赋值。
对每个bean标签下的所有property 标签,对标签内容进行解析,这里需要注意点的是判断是引用数据类型还是简单数据类型。
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{
/**
* 存储bean的Map集合
*/
private Map<String,Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 在该构造方法中,解析myspring.xml文件,创建所有的Bean实例,并将Bean实例存放到Map集合中。
* @param resource 配置文件路径(要求在类路径当中)
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String resource) {
SAXReader reader=new SAXReader();
try {
//读取配置文件
Document document = reader.read(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(resource));
//拿到所有的bean标签
List<Node> beanNodes = document.selectNodes("//bean");
//遍历集合拿到对bean进行处理
beanNodes.forEach(beanNode->{
Element beanElt= (Element)beanNode;
//获取id
String id = beanElt.attributeValue("id");
//获取className
String className = beanElt.attributeValue("class");
try {
//反射获取对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
Object bean = constructor.newInstance();
//存储到Map集合中
beanMap.put(id,bean);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
beanNodes.forEach(beanNode->{
Element beanElt= (Element)beanNode;
//获取bean的id
String beanId = beanElt.attributeValue("id");
//获取所有的property标签
List<Element> propertyEls = beanElt.elements("property");
propertyEls.forEach(propertyElt->{
try {
//获取属性名
String propertyName = propertyElt.attributeValue("name");
//获取属性类型
Class<?> propertyType = beanMap.get(beanId).getClass().getDeclaredField(propertyName).getType();
//获取set方法名
String setMethodName= "set"+propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0)+ propertyName.substring(1);
//获取set方法
Method setMethod = beanMap.get(beanId).getClass().getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName, propertyType);
//获取value的值
String propertyValue = propertyElt.attributeValue("value");
//获取ref
String propertyRef=propertyElt.attributeValue("ref");
Object propertyVal=null;
//如果不是简单属性
if(propertyValue!=null){
//获取属性类型名
String simpleName = propertyType.getSimpleName();
switch (simpleName) {
case "byte": case "Byte":
propertyVal = Byte.valueOf(propertyValue);
break;
case "short": case "Short":
propertyVal = Short.valueOf(propertyValue);
break;
case "int": case "Integer":
propertyVal = Integer.valueOf(propertyValue);
break;
case "long": case "Long":
propertyVal = Long.valueOf(propertyValue);
break;
case "float": case "Float":
propertyVal = Float.valueOf(propertyValue);
break;
case "double": case "Double":
propertyVal = Double.valueOf(propertyValue);
break;
case "boolean": case "Boolean":
propertyVal = Boolean.valueOf(propertyValue);
break;
case "char": case "Character":
propertyVal = propertyValue.charAt(0);
break;
case "String":
propertyVal = propertyValue;
break;
}
setMethod.invoke(beanMap.get(beanId),propertyVal);
}
//如果不是简单属性
if(propertyRef!=null){
setMethod.invoke(beanMap.get(beanId),beanMap.get(propertyRef));
}
}catch ( Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
});
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanId) {
return beanMap.get(beanId);
}
}思考:为什么不在上面的循环中给Bean的属性赋值,而在这里再重新遍历一次呢?
解答:很简单为了解决循环依赖问题,先生成bean对象进行曝光再赋值,实例化和属性赋值分开。
测试阶段2(为bean对象进行赋值)
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("IOC.XML");
Object clazz = applicationContext.getBean("clazz");
Object student = applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(clazz);
System.out.println(student);
}
}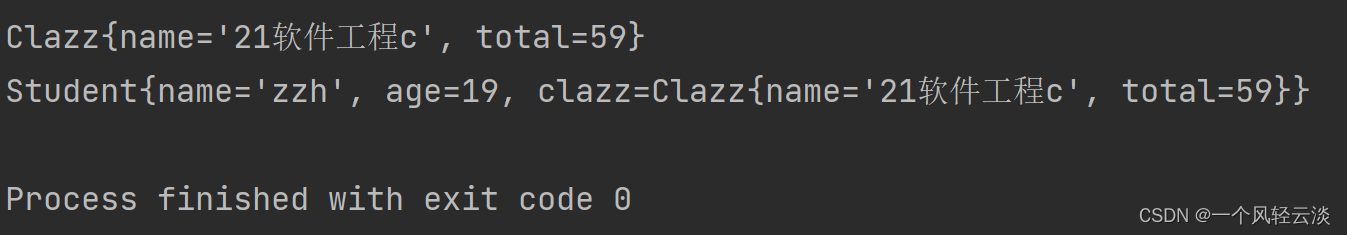
到这里一个简单的IOC已经实现,只实现的基本数据类型和ref类型。还是不能对LIst map等类型进行注入。
























 262
262











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










