回文链表的判断
-
给出一个链表,判断其是否为回文链表,那什么是回文链表?
-
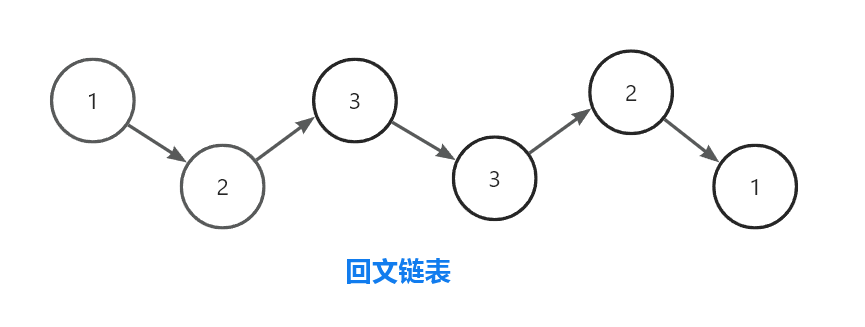
以下即为一条回文链表:
-
即对回文链表正序遍历和倒序遍历,得到的结果是一样的
-
这种题解法很多,我们列举常见的、简单的且容易理解的解法:
/**
* 方法1:全部压栈遍历 全部出栈遍历
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindromeByAllStack(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp = head;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 1.压栈 遍历
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
}
// 2.出栈 遍历
while (head != null) {
if (head.val != stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 方法2:全部压栈遍历 一半出栈遍历
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindromeByHalfStack(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return true;
ListNode temp = head;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
//链表的长度
int len = 0;
//把链表节点的值存放到栈中
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
len++;
}
//len长度除以2
len >>= 1;
//然后再出栈
while (len-- >= 0) {
if (head.val != stack.pop())
return false;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
-
倒序链表法,代码如下:
-
根据原链表构造一条倒序链表,遍历这两条链表,
/**
* 构造倒序链表
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindromeByReverseList(ListNode head) {
// 1.构造反转链表
ListNode newHead = head, temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(temp.val);
node.next = newHead;
newHead = node;
temp = temp.next;
}
// 2.同时遍历两链表
while (newHead != null && head != null) {
if (head.val != newHead.val)
return false;
head = head.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
}
return true;
}
-
此外还有双指针法(之后双指针专题练习结束后回来补充)、递归法(不推荐掌握,容易绕晕)
合并两条有序链表
-
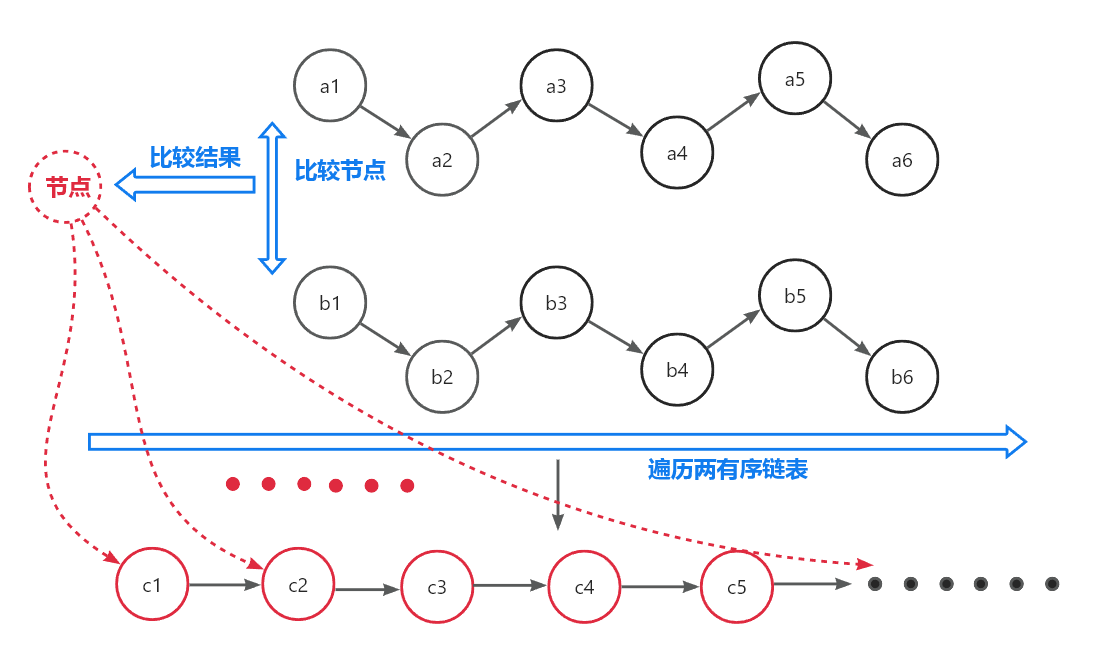
常见的解法就是构造第三条链表,然后依次遍历两条有序链表,比较各节点大小,依次连接到新链表中,整个过程如下图所示:
-
由于两条链表长度不一定相同,可能出现一条链表遍历完,另一条链表还没有的情况,这其实是一个优化点
-
具体代码如下:
/**
* 方法1:面试时就能写出来的方法
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// write code here
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode res = newHead;
while (list1 != null || list2 != null) {
if (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else if (list1.val > list2.val) {
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
} else { //相等的情况,分别接两个链
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
newHead = newHead.next;
} else if (list1 != null && list2 == null) {
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
} else if (list1 == null && list2 != null) {
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
}
}
return res.next;
}
-
上面的解法当中,我们把两条链表是否都为空/只有一条为空放在了一个循环下,这次我们把它拆开来:
/**
* 思路更清晰的写法
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists2(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// write code here
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode res = newHead;
// 1.两链表均不为空
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else if (list1.val > list2.val) {
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
} else { //相等的情况,分别接两个链
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
newHead = newHead.next;
}
// 2.链表a为空
while (list1 != null) {
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
}
// 3.链表b为空
while (list2 != null) {
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
}
return res.next;
}
/**
* 方法2:比方法1更加精简的实现方法
*
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoListsMoreSimple(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = prehead;
// 节点之间的比较,简化为两种情况
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 一条链表合并完成,直接拼接剩余链表的节点即可
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
合并K个链表
/**
* 合并K个链表
*
* @param lists
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode res = null;
for (ListNode list : lists) {
res = mergeTwoListsMoreSimple(res, list);
}
return res;
}
简单的合并链表
-
随便给你两条链表,你会怎么连接这两条链表?(比如:将链表b连接到链表a后面)
-
正确的思路只有一个,那就是拿到链表a的尾节点,拿到链表b的头节点,作:a.next = b,连接完成
-
举个例子:将链表a的[a,b]区间删掉,把链表b连接进去,代码如下:
/**
* 简单的合并链表
*
* @param listA
* @param a
* @param b
* @param listB
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode listA, int a, int b, ListNode listB) {
ListNode preA = listA;
ListNode postA = listA;
ListNode postB = listB;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (postA != null && preA != null && j < b) {
// 1.拿到listA的前半段preA的尾节点
if (i < a - 1) {
preA = preA.next;
i++;
}
// 2.拿到listA的后半段postA的头节点
if (j != b) {
postA = postA.next;
j++;
}
}
// 3.分别连接preA与listB, postA与listB
while (postB.next != null) {
postB = postB.next;
}
preA.next = listB;
postB.next = postA;
return preA;
}
























 105
105











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








