目录
一 线程介绍
1 线程相关概念
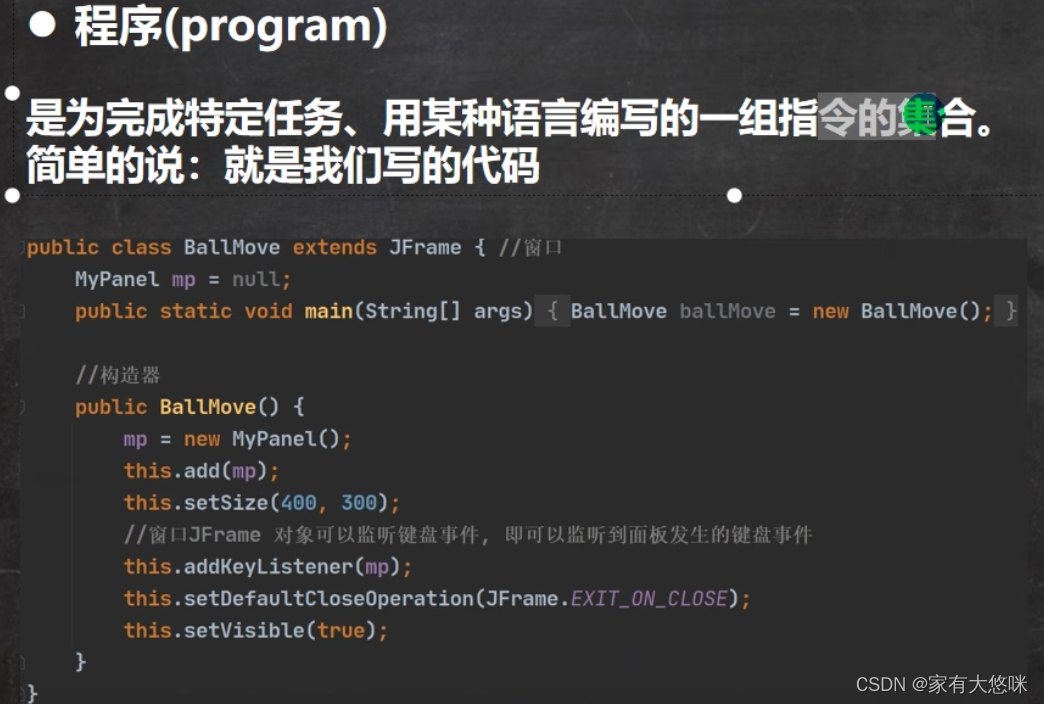
- 程序
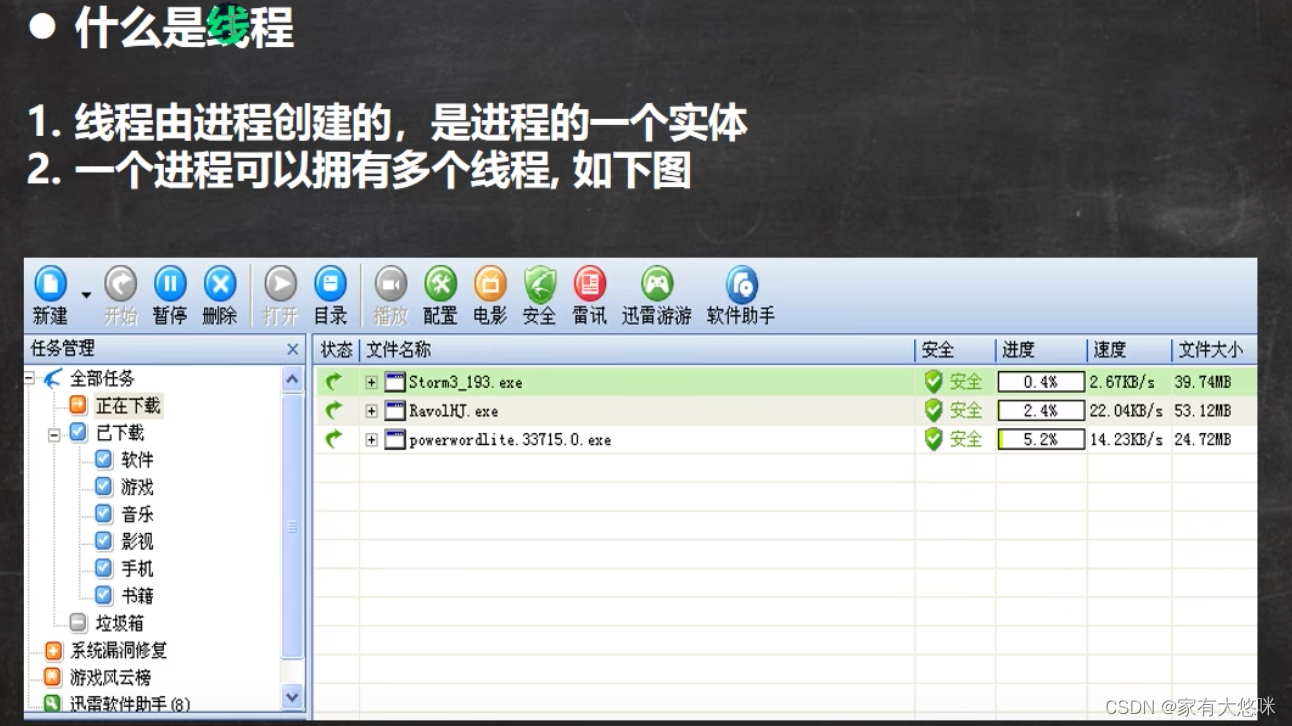
- 进程
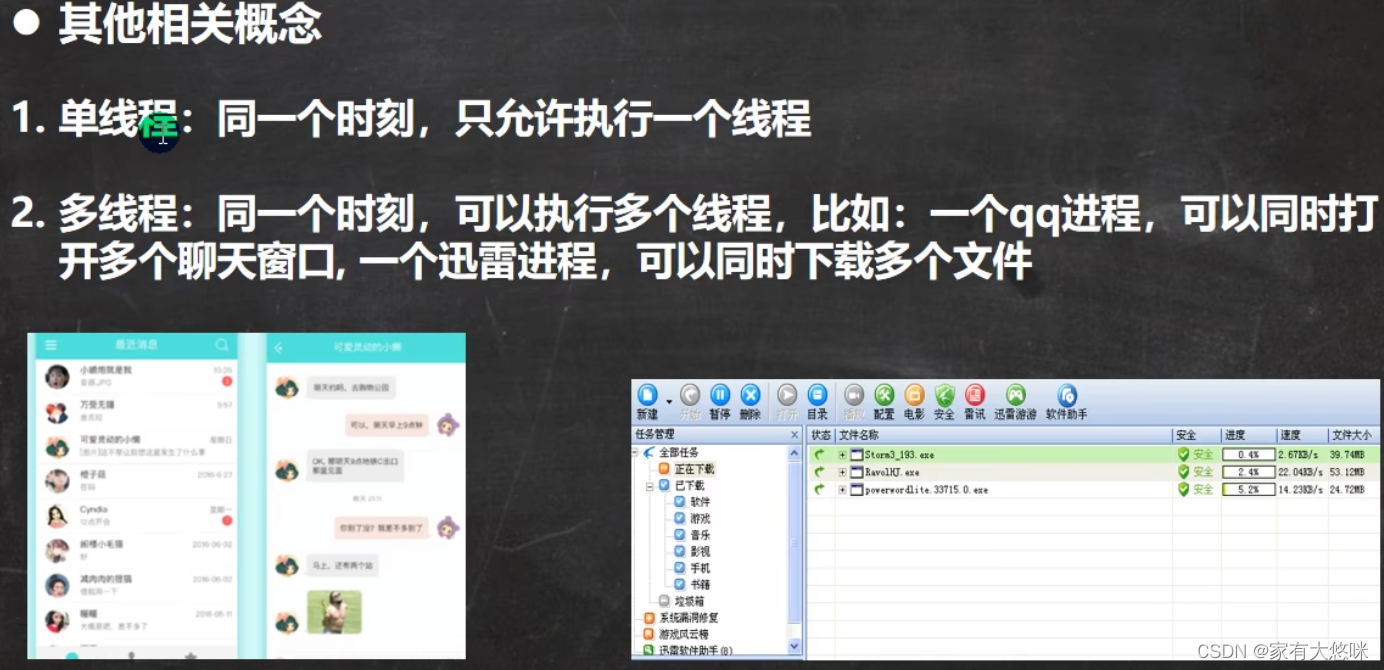
- 线程: 单线程, 多线程
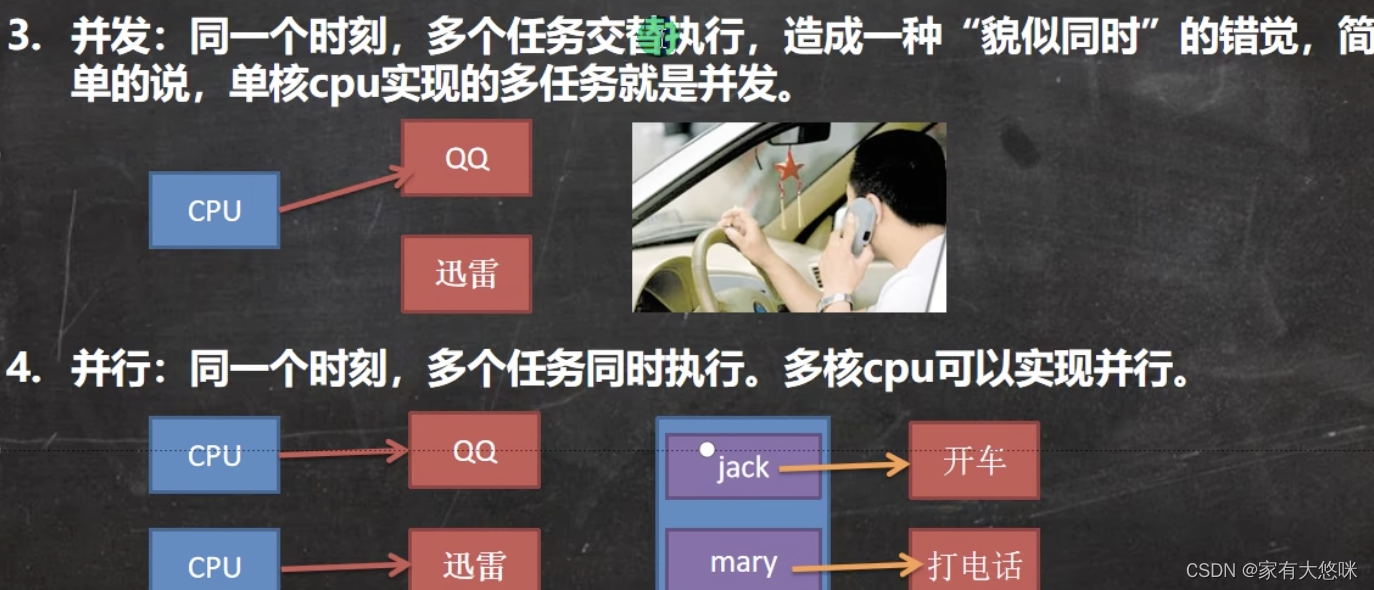
- 并发
- 并行

Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
int i = runtime.availableProcessors();//获取当前电脑的cpu数量
System.out.println(i);二 线程使用
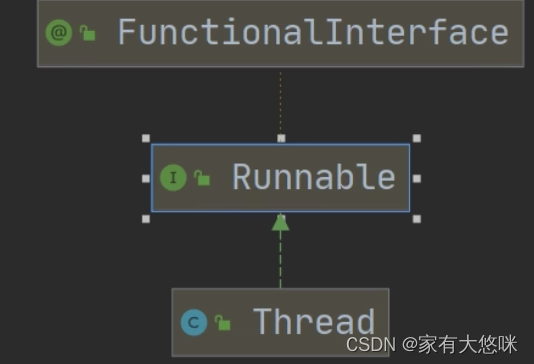
1 创建线程的两种方式
1. 继承Thread类,重写run方法
2. 实现Runnable接口,重写run方法
类图:
案例一_实现Thread接口:

public class Thread01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建cat对象,可以当做线程使用
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.start();
//说明: 当main线程启动一个子线程 Thread-0,主线程不会阻塞,会继续执行
//这时主线程和子线程是交替执行的
System.out.println("主线程继续执行" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程i=" + i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
//1.当一个类继承了Thread类,该类就可以当线程使用
//2.需要重写run方法( 实现了Runnable接口的run方法)
/*
@Override
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
*/
class Cat extends Thread {
int times = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
//每隔一秒要输出"喵喵,我是小猫咪"
System.out.println("喵喵,我是小猫咪" + (++times) + "线程名=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if (times == 80){
break; //当times到8,就退出while循环
}
}
}
} 案例二_实现Runnable接口
案例二_实现Runnable接口
![]()
public class Thread02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
// dog.start(); 这里不能调用start()
Thread thread = new Thread(dog);//创建thread对象,把dog对象(实现了runnable),放入thread
thread.start();
}
}
class Dog implements Runnable{
int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("小狗汪汪叫...hi" + (++count) + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if (count == 10){
break;
}
}
}
}Note: 这里底层使用了设计模式[代理模式]
代码模拟代理模式,方便理解:
Tiger tiger = new Tiger();
ThreadProxy threadProxy = new ThreadProxy(tiger);
threadProxy.start();
class Animal{}
class Tiger extends Animal implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("老虎嗷嗷叫...");
}
}
class ThreadProxy implements Runnable{ //把proxy看做Thread
private Runnable target = null;//属性,类型是Runnable
@Override
public void run() {
if (target != null){
target.run();
}
}
public ThreadProxy(Runnable target) {
this.target = target;
}
public void start(){
start0();
}
public void start0(){
run();
}
}2 线程的基本使用

建议使用Runnable

// System.out.println("==使用继承接口方式来售票");
// SellTicket01 sell01 = new SellTicket01();
// SellTicket01 sell02 = new SellTicket01();
// SellTicket01 sell03 = new SellTicket01();
// sell01.start();
// sell02.start();
// sell03.start();
System.out.println("==使用实现接口方式来售票");
SellTicket02 sellTicket02 = new SellTicket02();
new Thread(sellTicket02).start();
new Thread(sellTicket02).start();
new Thread(sellTicket02).start();
class SellTicket01 extends Thread{
private static int ticketNum = 100;//让多个线程共享num
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
if (ticketNum <= 0){ //会出现票数超卖现象
System.out.println("售票结束");
break;
}
//休眠50毫秒,模拟人的休息
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("窗口 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出一张票"
+ "剩余票数=" + (--ticketNum));
}
}
}
class SellTicket02 implements Runnable{
private int ticketNum = 100;//让多个线程共享num
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
if (ticketNum <= 0){ //会出现票数超卖现象
System.out.println("售票结束");
break;
}
//休眠50毫秒,模拟人的休息
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("窗口 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出一张票"
+ "剩余票数=" + (--ticketNum));
}
}
}三 线程方法
1 线程终止

案例:启动线程后中止
public class ThreadExit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
T t = new T();
t.start();
//如果希望主线程可以控制t线程的中止,需要修改loop
//让主线程休眠10秒,再通知t线程退出
Thread.sleep(10000);
t.setLoop(false);
}
}
class T extends Thread {
private int count = 0;
private boolean loop = true;
@Override
public void run(){
while(loop){
try{
Thread.sleep(50);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("T 运行中...." + (++count));
}
}
public void setLoop(boolean loop){
this.loop = loop;
}
}2 常用方法



public class ThreadMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
T2 t2 = new T2();
t2.start();
for (int i = 1; i<=20; i++){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("主线程(小弟)吃了" + i + "个包子");
if (i == 5){
System.out.println("主线程(小弟)让子线程(老大)先吃");
// //join,线程插队
// t2.join();//这里相当于让子线程先执行完毕
System.out.println("子线程(老大)吃完了,主线程(小弟)接着吃");
Thread.yield();//礼让,不一定成功
}
}
}
}
class T2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run(){
for (int i=0; i<=20;i++){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("子线程吃了" + i + "个包子");
}
}
} 
public class ThreadPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
T3 t3 = new T3();
Thread thread = new Thread(t3);
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("hi" + i);
if (i == 5){
thread.start();
thread.join();
}
if (i== 10){
System.out.println("主线程结束");
}
}
}
}
class T3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1;i < 11; i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("hello" + i);
}
System.out.println("子线程结束");
}
}3 用户线程和守护线程

线程名.setDaemon(true)
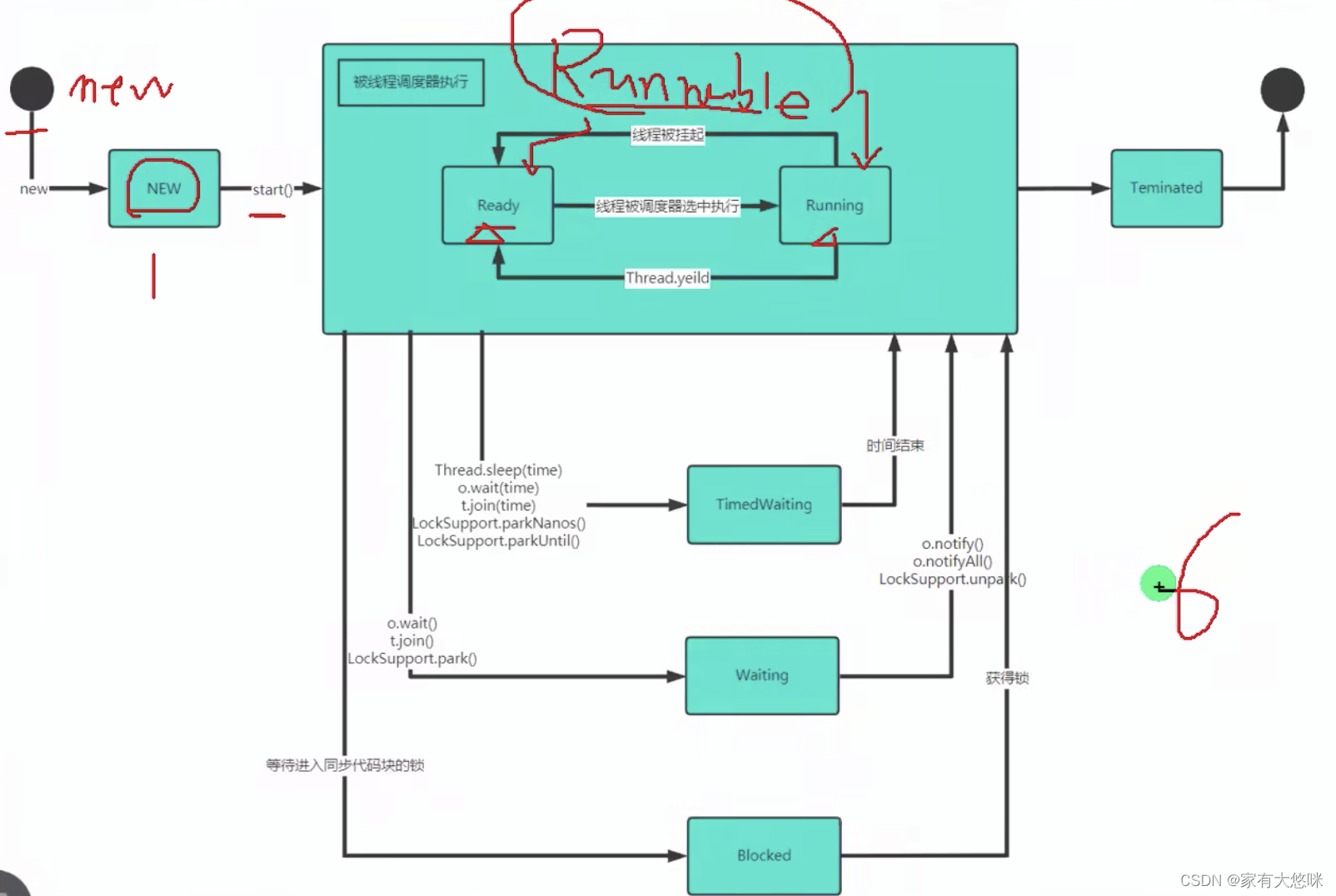
四 线程生命周期
NEW: 尚未启动的线程
RUNNABLE:运行的
READY: 准备运行的
BLOCKED: 被阻塞的
WAITING: 等待中
TIMEDWAITING: 等待另一个线程执行动作达到指定等待时间
TERMINATED: 已退出的
五 Sychronized
1.线程同步机制
线程同步机制:
1. 在多线程编程,一些敏感数据不允许被多个线程同时访问,此时就用同步访问技术,保证数据在任何同一时刻,最多有一个线程访问,以保证数据的完整性;
2. 这样理解: 线程同步,即当有一个线程在对内存进行操作时,其他线程都不可以对这个内存地址进行操作,直到该线程完成操作,其他线程才能对该内存地址进行操作
2. 同步具体方法
(1) 同步代码块
synchronized (对象){
//需要被同步的代码
}
(2) synchronized放在方法声明中,表示整个方法为同步方法
public synchronzed void m (String name){
//需要被同步的代码
}
3. 案例
SellTicket03 sellTicket03 = new SellTicket03();
new Thread(sellTicket03).start();
new Thread(sellTicket03).start();
new Thread(sellTicket03).start();
class SellTicket03 implements Runnable{
private int ticketNum = 100;//让多个线程共享num
private boolean loop = true;//控制run方法变量
public synchronized void sell(){//同步方法,同一时刻只能有一个线程执行run方法
if (ticketNum <= 0){ //会出现票数超卖现象
System.out.println("售票结束");
loop = false;
return;
}
//休眠50毫秒,模拟人的休息
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("窗口 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出一张票"
+ "剩余票数=" + (--ticketNum));
}
@Override
public void run(){
while(loop){
sell();
}
}
}4.同步原理分析

六 互斥锁
1.基本介绍

2.注意事项和细节

Note: 这里如果使用继承Thread来创建多线程,那么只能使用静态方法锁类,否则不是同一对象;如果实现Runnable接口,则只能创建一个对象!
3.线程的死锁
多个线程都占用了对方的锁资源,但不肯相让,导致了死锁,在编程是一定要避免死锁的发生
4.释放锁


七 练习题

思路分析: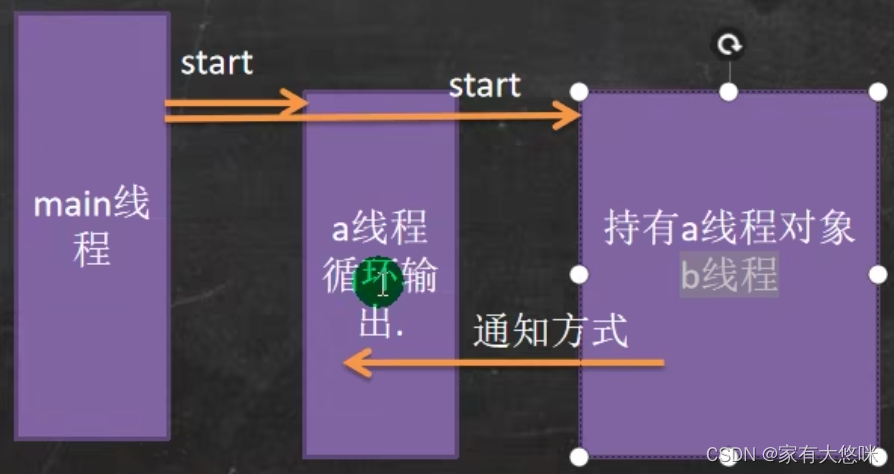
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread01 thread01 = new Thread01();
new Thread(thread01).start();
Thread02 thread02 = new Thread02(thread01);
new Thread(thread02).start();
}
}
class Thread01 implements Runnable {
public boolean loop = true;
public boolean isLoop() {
return loop;
}
public void setLoop(boolean loop) {
this.loop = loop;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (loop) {
System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 100 + 1));
//休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
class Thread02 implements Runnable {
private Thread01 thread01;
private Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public Thread02(Thread01 thread01) {
this.thread01 = thread01;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入你的指令(Q表示退出):");
char next = scanner.next().toUpperCase().charAt(0);
if (next == 'Q') {
//以通知的方式结束01线程
this.thread01.setLoop(false);
System.out.println("thread02 线程结束");
break;
}
}
}
} 
public class Homework02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
extractMoney extractMoney = new extractMoney();
new Thread(extractMoney).start();
new Thread(extractMoney).start();
}
}
class extractMoney implements Runnable {
private static int money = 10000;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
if (money < 1000) {
System.out.println("余额不足");
break;
}
money = money - 1000;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取走了1000 余额为" + money);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}Note: 只获取到一个线程的 注意锁的位置!!!






















 3402
3402











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








