合并多组文件,本次要求将不同CSV文件合并至一个CSV中,并对每一条数据加入名称并对总数据进行排序处理
1.需要提取每个CVS的colomn name 并在头添加id,尾添加file name 原代码为
output_column = get_output_column(folders)
output_column.insert(0, "Id")
output_column.append('file')
def get_output_column(folders):
for dirpath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(folders):
for file in filenames:
if file.startswith('output_200G_PRBS'):
df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(dirpath, file), encoding="utf-8", sep=',')
return df.columns.tolist()该代码寻找一个符合‘output_200G_PRBS’的文件并加入名字,修改后的代码为
sample_file = next((f for f in os.listdir(folders) if f.startswith(type[type_num])), None) # 遍历文件夹中以 'output_200G_PRBS' 开头的文件,返回第一个找到的文件名
if sample_file:
sample_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(folders, sample_file), encoding="utf-8", sep=',')
output_column = ['Id'] + sample_df.columns[1:].tolist() + ['file']
else:
print("No sample file found.")
return首先简化代码内容,利用next循环寻找符合‘output_200G_PRBS’的文件的文件名
然而,之前代码一直崩溃,是因为原文件包含第一列序号,这样,按照之前的写法,会存在一个unnamed:1的字符,这也是代码崩溃的原因,因为在输出的时候
for j in range(df.shape[0]):
output_port_0[j + cols_num][:len(output_column)-2] = df.iloc[j,
1:len(output_column)-1].tolist()
output_port_0[j + cols_num][len(output_column)-1] = file
cols_num += df.shape[0]并没有考虑到这个未命名的序号内容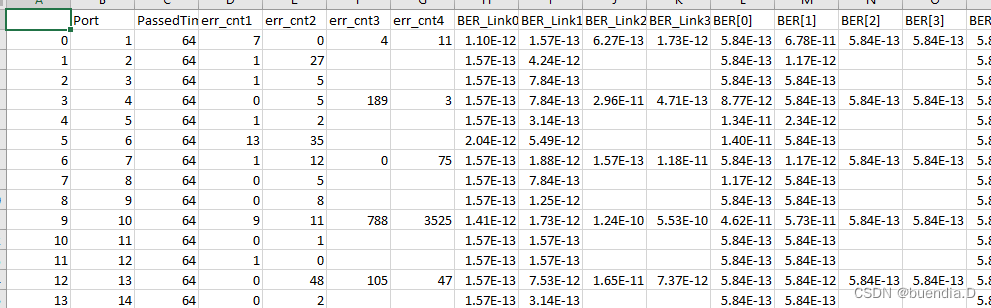
2.在计算数据总数的时候,需要遍历全文件,造成时间复杂度高,且计算出的总数会多一个文件总数的数值。
loop = 0
for dirpath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(folders):
for file in filenames:
if file.startswith('output_200G_PRBS'):
i = i + read_csv_get_line_num(folders + "\\" + file)
loop += 1
output_port_0 = [[0] * len(output_column) for _ in range(0, i-loop)]
cols_num = 0代码修改后并不对需要保存的数据开辟存储空间(C语言的要求),而是直接运行
for dirpath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(folders):
for file in filenames:
if file.startswith(type[type_num]):
print(file, "has done")
file_count += 1
df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(dirpath, file), encoding="utf-8", sep=',')
for j in range(df.shape[0]):
row_data = [cols_num, *df.iloc[j, 1:].tolist(), file]
output_data.append(row_data)
cols_num += 1该代码利用*解码df的文件,将其包含至cols_num和file之间,并通过tolist转换,如果不加*则会出现[id,[df],file]的问题
检测文件夹内的多个子文件,并将符合一定要求的文字提取出来
1.每次遍历一个文件夹后,将对应的信息打印出来
for file in files:
if 'test_report' in file:
f = open(os.path.join(root, file), 'r', encoding='gbk',errors='ignore')
lines = f.readlines() # Read each line of the file
for line in lines:
if 'FAIL' in line and 'IGNORED' not in line:
fail_lines.append(line.strip()) # Add the line to the list
f.close()
result.append(root)
# Print the accumulated lines for each file
if fail_lines:
shutil.copytree(root, os.path.join(copy_path, os.path.basename(root)))
print(f"Fail condition occur in {root}:")
Fail_num += 1
print('\n'.join(fail_lines))
print()在将文件夹的内容复制出来的时候,写了一个小function, 该函数首先提取文件路径,并复制进新路径,最后确定路径并进行递归。
old_path = r'C:\Users\buendia.deng\Downloads\4T213S23330024\4T213S23330024\link\A\s1234567' # 要复制的文件所在目录
new_path1 = r'C:\Users\buendia.deng\Downloads\4T213S23330024\4T213S23330024\link\A\test' #新路径
def FindFile(path, new_path):
if not os.path.exists(new_path):
os.makedirs(new_path)
for ipath in os.listdir(path):
fulldir = os.path.join(path, ipath) # 拼接成绝对路径
print(ipath) #打印相关后缀的文件路径及名称
if os.path.isfile(ipath): # 文件,匹配->打印
shutil.copy(ipath, new_path)
if os.path.isdir(ipath): # 目录,递归
FindFile(ipath, new_path)
FindFile(old_path, new_path1)然而,该代码复制文件夹内所有文件,而需求是复制子文件夹,因此,修改后的代码提取每个需要复制的子文件名(os.path.basement()函数),并在所需的路径中创建一个新的子文件,并将数据拷贝至此。
shutil.copytree(root, os.path.join(copy_path, os.path.basename(root)))2.将生成在console的文件打印出来
def check_qual_test_log():
while True:
result = []
test_cycle = []
fail_log = []
source_log_folder = input('please input location: ')
copy_path = source_log_folder[:source_log_folder.rfind("\\")] + '\\Fail folder gathered'
log_file_path = 'log_output.txt' # Specify the path for the log file
Fail_info = []
Fail_num = 0
log_content = '' # Variable to store log content
for root, dir, files in os.walk(source_log_folder):
test_length = len(dir)
test_cycle.append(test_length)
fail_lines = []
for file in files:
if 'test_report' in file:
f = open(os.path.join(root, file), 'r', encoding='gbk', errors='ignore')
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
if 'FAIL' in line and 'IGNORED' not in line:
fail_lines.append(line.strip())
f.close()
result.append(root)
if fail_lines:
shutil.copytree(root, os.path.join(copy_path, os.path.basename(root)))
log_content += f"Fail condition occur in {root}:\n"
log_content += '\n'.join(fail_lines) + '\n\n'
Fail_num += 1
final_result = list(set(result))
log_content += f'Total fail in this part is {Fail_num}\n'
log_content += f'Total number of file to check is {test_cycle[0]}\n'
log_content += 'Done!\n'
list_txt(os.path.join(copy_path, 'log.txt'), log_content)
# Save log content to a text file
with open(log_file_path, 'a') as log_file:
log_file.write(log_content)
print(log_content)
def list_txt(path, list=None):
'''
:param path: 储存list的位置
:param list: list数据
:return: None/relist 当仅有path参数输入时为读取模式将txt读取为list
当path参数和list都有输入时为保存模式将list保存为txt
'''
if list != None:
file = open(path, 'w')
file.write(str(list))
file.close()
return None
else:
file = open(path, 'r')
rdlist = eval(file.read())
file.close()
return rdlist这里的 “log_content”并不能采用list类型,这样就保存的是文字消息,而不能保存所需的格式,因此,这里采用的str格式
二进制转十进制计算,在负数的进位问题,
原本在计算负数转换时候,针对补码的处理,只是将0变成1,1变成0,而忽视了进位的问题,特意写了个函数用于解决进位问题
def add_one(self, binary_str):
# 向二进制数中加1
result = ''
carry = 1
for bit in reversed(binary_str):
current_sum = int(bit) + carry
result = str(current_sum % 2) + result
carry = current_sum // 2
if carry:
result = '1' + result
return result利用carry作为进位的标识符,对每个数值加上carry生成current_sum,对2取余数就知道计算的结果,并除2得出进位符号。
反码的计算可以由下属代码实现
self.inv_dict = {'0': '1',
'1': '0'}
def inverse(self):
# 求它的反码
inv_code = ''
for i in self.tem_cal:
inv_code += self.inv_dict[i]
return inv_code





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








