一.字符串的常见方法练习
1.String.Format()
基本语法是:string.Format(format, arg0, arg1, arg2, ...)
format是一个字符串,其中包含要格式化的文本和占位符。占位符使用花括号 {} 括起来,并可以包含格式说明符,用于定义值的显示方式。
arg0, arg1, arg2, ... 是要插入到格式字符串中的参数。这些参数将按照顺序替换占位符。
string name = "Bob";
int age = 25;
string message = String.Format("Hello, {0}! You are {1} years old.", name, age);
Console.WriteLine(message);
//Hello, Bob! You are 25 years old.
string fruit = "apple";
int quantity = 3;
double price = 1.99;
string message = "I bought {0} {1}(s) for {2:C2}";
Console.WriteLine(string.Format(message, quantity, fruit, price));
//I bought 3 apple(s) for ¥1.99
2.IsNullOrEmpty和IsNullOrWhiteSpace
在C#中,string.IsNullOrEmpty 和 string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace 都是用于检查字符串是否为空的方法,但它们有一些细微的差别。
1. string.IsNullOrEmpty
string.IsNullOrEmpty 方法用于检查一个字符串是否为 null 或者空字符串 ("")。
如果字符串是 null,则返回 true。
如果字符串是空字符串 (""),则返回 true。
否则,返回 false。
示例使用:
string str1 = null;
string str2 = "";
string str3 = " "; // 包含空格的字符串
bool isEmptyOrNull1 = string.IsNullOrEmpty(str1); // true
bool isEmptyOrNull2 = string.IsNullOrEmpty(str2); // true
bool isEmptyOrNull3 = string.IsNullOrEmpty(str3); // false
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1},{2}",isEmptyOrNull1, isEmptyOrNull2, isEmptyOrNull3);
2. string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace
string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace 方法与 string.IsNullOrEmpty 类似,但它会更严格地检查字符串是否为 null 或者是否仅由空白字符组成。
如果字符串是 null,则返回 true。
如果字符串是空字符串 (""),则返回 true。
如果字符串只包含空格、制表符、换行符等空白字符,则也返回 true。
否则,返回 false。
示例使用:
string str1 = null;
string str2 = "";
string str3 = " "; // 包含空格的字符串
bool isNullOrWhiteSpace1 = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(str1); // true
bool isNullOrWhiteSpace2 = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(str2); // true
bool isNullOrWhiteSpace3 = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(str3); // true
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1},{2}", isNullOrWhiteSpace1, isNullOrWhiteSpace2, isNullOrWhiteSpace3);
区别总结:
使用 string.IsNullOrEmpty 当只需要检查字符串是否为 null 或空字符串时。
使用 string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace 当希望连带检查字符串是否只包含空白字符时,例如用户输入的情况下,以确保用户没有仅仅输入了空格。
3.Equals
语法: Equals 方法是 System.Object 类中定义的虚方法,可以被子类重写以提供特定类型的相等性比较逻辑。
默认情况下,在默认情况下,Equals()方法的行为与"=="操作符相同,即它用于比较两个对象的值是否相等。
"=="操作符:
"“操作符用于比较两个对象的值是否相等。当使用”"操作符比较两个引用类型的对象时,它会比较它们的引用是否指向相同的内存地址。
对于值类型(如int、double等),"=="操作符比较它们的实际值。如果值相等,则返回true,否则返回false。
总结:
"=="操作符用于比较引用类型的对象的引用或值类型的实际值。
Equals()方法用于比较对象的值是否相等,且可以被重写以自定义相等性比较规则。
因此,一般情况下,对于引用类型,应该使用"=="操作符来比较对象的引用,而对于值类型或者自定义类,应该使用Equals()方法来比较它们的值。
string str1 = "hello";
string str2 = "world";
bool isEqual = str1.Equals(str2);
4.Contains
在字符串类型中,Contains 方法用于判断一个字符串是否包含另一个字符串。
在默认情况下,Contains 方法对字符串的匹配是区分大小写的。
string mainString = "Hello, world!";
string subString = "world";
bool contains = mainString.Contains(subString);
5.Length
Length 是用于获取数组长度或字符串长度的属性。
1. 字符串的 Length
对于字符串类型,Length 属性用于获取字符串中字符的数量(即字符串的长度)。
string text = "Hello, world!";
int length = text.Length; // length 等于 13,因为 text 字符串包含 13 个字符
2. 数组的 Length
对于数组类型,Length 属性用于获取数组中元素的数量(即数组的长度)。
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int length = numbers.Length; // length 等于 5,因为 numbers 数组有 5 个元素
6.Substring
Substring 方法用于从字符串中获取一个子字符串。
使用方法
string str = "Hello, world!";
string substr1 = str.Substring(7); // 从索引 7 开始截取到字符串末尾,substr1 = "world!"
string substr2 = str.Substring(7, 5); // 从索引 7 开始截取长度为 5 的子字符串,substr2 = "world"
参数说明
startIndex: 这是必需的参数,指定从哪个索引位置开始截取子字符串。索引从 0 开始,负数表示从字符串末尾开始计数。
length: 可选参数,指定要截取的子字符串的长度。如果不指定,将截取从 startIndex 开始直到字符串末尾的所有字符。
注意事项
如果 startIndex 超出字符串范围或为负数,并不会引发异常,而是返回一个空字符串或截取尽可能多的字符。
Substring 方法返回的是一个新的字符串,原始字符串保持不变。
7.IndexOf
在 C# 中,IndexOf 方法用于查找字符串中特定子字符串或字符的第一个匹配位置。它返回找到的子字符串或字符在原始字符串中的起始索引,如果未找到则返回 -1。
使用方法
string str = "Hello, world!";
int index1 = str.IndexOf("world"); // index1 = 7,从索引 7 开始是子字符串 "world"
int index2 = str.IndexOf('o'); // index2 = 4,第一个 'o' 出现在索引 4 处
参数说明
value: 这是必需的参数,指定要查找的子字符串或字符。
startIndex: 可选参数,指定从哪个索引位置开始搜索。默认值为 0,即从字符串的开头开始搜索。
注意事项
如果未找到指定的子字符串或字符,IndexOf 方法将返回 -1。
如果指定了 startIndex 参数,将从该索引位置开始向后搜索,而不是从字符串开头。
IndexOf 方法对大小写敏感,例如在 "Hello" 中查找 "hello" 将返回 -1。
示例
string message = "C# programming is powerful!";
int index1 = message.IndexOf("is"); // index1 = 14
int index2 = message.IndexOf("power", 10); // index2 = 19,从索引 10 开始搜索
int index3 = message.IndexOf('z'); // index3 = -1,未找到字符 'z'
8.StartsWith 和 EndsWith
StartsWith 和 EndsWith 是两个常用的字符串方法,用于检查字符串是否以特定的子字符串开始或结束。
1. StartsWith 方法
StartsWith 方法用于确定字符串是否以指定的前缀开始,并返回一个布尔值(true 或 false)。
使用方法:
string str = "Hello, world!";
bool startsWithHello = str.StartsWith("Hello"); // startsWithHello = true
bool startsWithHi = str.StartsWith("Hi"); // startsWithHi = false
参数说明:
prefix: 这是必需的参数,指定要检查的前缀子字符串。
comparisonType(可选): 指定比较规则,默认为区分大小写的当前文化规则。
2. EndsWith 方法
EndsWith 方法用于确定字符串是否以指定的后缀结束,并返回一个布尔值(true 或 false)。
使用方法:
string str = "Hello, world!";
bool endsWithWorld = str.EndsWith("world!"); // endsWithWorld = true
bool endsWithDot = str.EndsWith("."); // endsWithDot = false
参数说明:
suffix: 这是必需的参数,指定要检查的后缀子字符串。
comparisonType(可选): 指定比较规则,默认为区分大小写的当前文化规则。
9.Remove
Remove 方法是从字符串中移除从指定位置开始的指定数量的字符序列,并返回修改后的字符串。Remove(startIndex, count);
startIndex: 指定从哪个索引位置开始移除字符。
count: 指定要移除的字符数。
string str = "Hello, world!";
string modifiedStr = str.Remove(7, 6);
Console.WriteLine(modifiedStr); // 输出:Hello!
索引越界:如果 startIndex 超出了字符串的范围,或者 count 指定的移除字符数超过了字符串剩余的长度,将会抛出 ArgumentOutOfRangeException 异常。
负数参数:startIndex 和 count 都不能是负数。如果其中任何一个参数为负数,将会抛出 ArgumentOutOfRangeException 异常。
返回值:Remove 方法返回一个新的字符串,而不会修改原始字符串 str。在上面的例子中,str 仍然是 "Hello, world!",而 modifiedStr 是修改后的 "Hello!"。
空字符串处理:如果 startIndex 等于字符串的长度,并且 count 为 0,则不会移除任何字符,直接返回原始字符串。
10.Reverse
反转一个字符串
使用 Array.Reverse 方法
string original = "Hello, world!";
char[] charArray = original.ToCharArray();
Array.Reverse(charArray);
string reversed = new string(charArray);
Console.WriteLine(reversed); // 输出:!dlrow ,olleH
解释:
original.ToCharArray() 将原始字符串转换为字符数组。
Array.Reverse(charArray) 反转字符数组中的元素。
new string(charArray) 将反转后的字符数组重新转换为字符串。
Console.WriteLine(reversed) 输出反转后的字符串。
11.Trim
Trim 方法用于去除字符串的开头和结尾处的空白字符(空格、制表符、换行符等)。
示例
string str = " Hello, world! ";
string trimmed = str.Trim();
Console.WriteLine(trimmed); // 输出:Hello, world!
注意事项
Trim 方法只会移除字符串开头和结尾的空白字符,不会影响字符串中间的空白。
12.Replace
Replace 方法用于在字符串中替换指定的字符或字符串为新的字符或字符串。它也有多个重载形式,允许你指定不同的参数组合来进行替换操作。
示例
string str = "Hello, world!";
string replaced = str.Replace("world", "everyone");
Console.WriteLine(replaced); // 输出:Hello, everyone!
注意事项
Replace 方法会在整个字符串中查找并替换所有匹配项,可以替换为空字符串来删除指定的字符或子字符串。
13.Concat
Concat 方法用于连接多个字符串或对象的集合成为一个单一的字符串。它通常与字符串或者字符串数组一起使用,允许将它们按顺序连接起来形成一个新的字符串。
示例 1: 连接两个字符串
string str1 = "Hello, ";
string str2 = "world!";
string result = string.Concat(str1, str2);
Console.WriteLine(result); // 输出:Hello, world
示例 2: 连接字符串数组
string[] parts = { "Hello", ", ", "world", "!" };
string result = string.Concat(parts);
Console.WriteLine(result); // 输出:Hello, world!
14.Join和Split
1. Join 方法
Join 方法用于将字符串数组的元素连接成一个单一的字符串,并可以通过指定分隔符来分隔每个元素。
示例
string[] parts = { "Hello", "world", "!" };
string joined = string.Join(" ", parts);
Console.WriteLine(joined); // 输出:Hello world !
注意事项
Join 方法的第一个参数是分隔符,可以是任何字符串。
如果数组中的元素是对象而不是字符串,会自动调用每个对象的 ToString() 方法来获取其字符串表示形式。
2. Split 方法
Split 方法用于将一个字符串根据指定的分隔符分割成一个字符串数组。
示例
string sentence = "Hello, world!";
string[] words = sentence.Split(new char[] { ' ', ',', '!' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (string word in words)
{
Console.WriteLine(word);
}
注意事项
Split 方法的第一个参数可以是字符数组或者字符串数组,用来指定一个或多个分隔符。
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries 选项可用于移除结果数组中的空白项。
二.实现身份证的解析
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace KeTangLianXi
{
class Identificationcard
{
public void Idanalysis()
{
string Idcard;
int maxLength = 18;
while (true)
{
string userInput = Console.ReadLine();
Idcard = userInput;
if (userInput.Length > maxLength)
{
Console.WriteLine("输入超过了最大长度限制!");
}
else
{
break;
}
}
string idcard1 = Idcard.Substring(0, 6);
string idcard2 = Idcard.Substring(6, 8);
string idcard3 = Idcard.Substring(14, 3);
string idcard4 = Idcard.Substring(17,1);
Console.WriteLine("前六位代表省区市:{0}", idcard1);
string date = string.Format("{0:yyyy/MM/dd}", idcard2);
//string formattedDate = $"{year}/{month}/{day}";
Console.WriteLine($"出生年月日:{date}");
Console.WriteLine("顺序码:{0}", idcard3);
string genderString = idcard3.Substring(2,1);
int gender;
if (int.TryParse(genderString, out gender))
{
// 这里的 gender 变量现在应该是一个整数,表示性别信息
// 一般约定:0 表示女性,1 表示男性
if (gender % 2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("女 ");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("男 ");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Unable to parse gender.");
}
Console.WriteLine("校验码:{0}", idcard4);
}
}
}
using KeTangLianXi;
Identificationcard s=new Identificationcard();
s.Idanalysis();
运行结果

三.遍历磁盘,列出目录和文件、统计文件个数,统计不同类型(后缀)的文件个数。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
namespace KeTangLianXi
{
class Epan
{
public void Ergodic()
{
string rootPath = @"E:\SteamLibrary"; // 设置要遍历的根目录
// 调用方法遍历目录和统计文件
var result = TraverseDirectory(rootPath);
// 输出统计结果
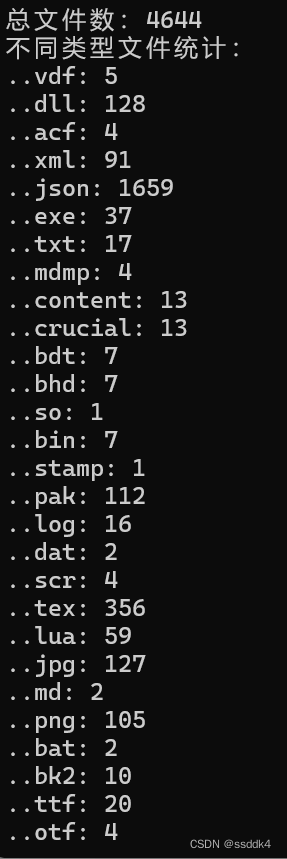
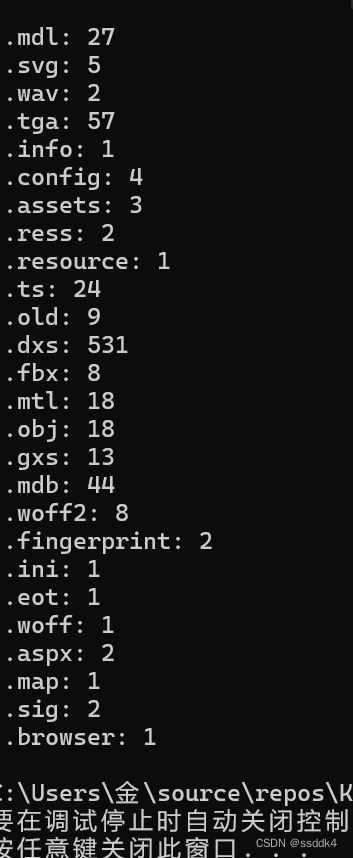
Console.WriteLine($"总文件数:{result.TotalFiles}");
Console.WriteLine("不同类型文件统计:");
foreach (var fileType in result.FileTypeCount)
{
Console.WriteLine($".{fileType.Key}: {fileType.Value}");
}
}
// 定义方法遍历目录和统计文件
static (int TotalFiles, Dictionary<string, int> FileTypeCount) TraverseDirectory(string rootPath)
{
int totalFiles = 0;
var fileTypeCount = new Dictionary<string, int>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase); // 忽略大小写比较
try
{
// 遍历所有文件
foreach (string filePath in Directory.EnumerateFiles(rootPath, "*.*", SearchOption.AllDirectories))
{
try
{
// 使用 Path.GetExtension 方法获取文件后缀
string fileExtension = Path.GetExtension(filePath)?.ToLower(); // 获取并转换为小写
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(fileExtension))
{
// 统计文件总数
totalFiles++;
// 统计文件类型(后缀)
if (!fileTypeCount.ContainsKey(fileExtension))
{
fileTypeCount[fileExtension] = 0;
}
fileTypeCount[fileExtension]++;
}
}
catch (UnauthorizedAccessException)
{
// 处理无权限访问的文件或目录
Console.WriteLine($"无权限访问:{filePath}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 处理其他异常
Console.WriteLine($"访问文件时发生错误:{ex.Message}");
}
}
}
catch (UnauthorizedAccessException ex)
{
// 处理无权限访问根目录的情况
Console.WriteLine($"无权限访问根目录:{rootPath}");
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
catch (DirectoryNotFoundException ex)
{
// 处理根目录不存在的情况
Console.WriteLine($"根目录不存在:{rootPath}");
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 处理其他异常
Console.WriteLine($"遍历目录时发生错误:{ex.Message}");
}
return (totalFiles, fileTypeCount);
}
}
}
using KeTangLianXi;
Epan a=new Epan();
a.Ergodic();





















 1649
1649

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








