介绍
ansible是自动化运维工具,由python开发,集合了众多自动化运维工具的优点,实现了批量系统部署、批量程序部署,批量运行命令等功能。ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力,真正具有批量部署能力的是ansible运行的模块,ansible只是提供一个框架。
使用背景:
假如你有一个大机房,里面有几百台机器,需要执行某条命令时,不可能一个个连进去,ansible就是批量管理他们的工具,管理大规模集群时更方便。
核心组件(架构)
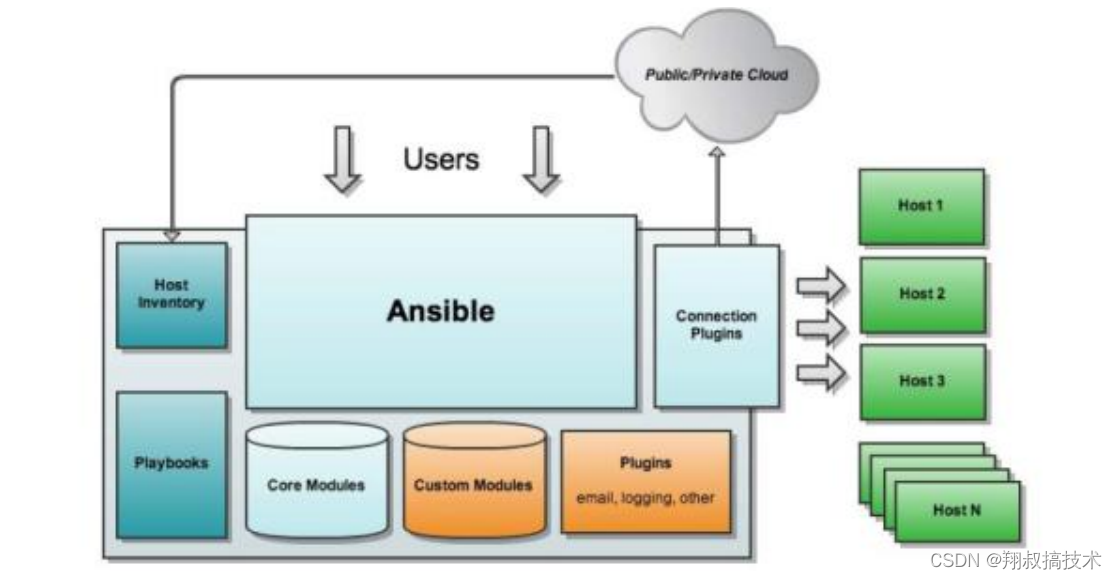
- ansible:核心程序
- modules:包含ansible自带的核心模块以及自定义模块
- plugins:完成模块功能的补充,包括连接插件,邮箱插件
- playbooks:剧本,定义ansbile多任务配置文件,由ansible自动执行
- inventory:定义ansbile管理的主机清单
- connection plugins:负责和被监控端实现通信
特点:
- 不需要在被监控端上安装任何服务程序(和zabbix的区别,zabbix需要安装agent)【因为ansible基于python开发的,linux系统自带python环境】
- 无服务器端,使用时直接运行命令即可
- 基于模块工作,可以使用任意语言开发(和prometheus类似。Prometheus是基于各种组件工作)
- 使用yaml语言编写playbook
- 基于ssh工作
- 可实现多级指挥
- 基于幂等性,一种操作重复多次执行结果相同。
- 执行过程:
- 加载主机的配置文件,默认为/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
- 加载自己对应的模块文件
- 通过ansible将模块或命令生成对应的临时py文件,并将该文件传输至远程服务器
- 对应执行用户的家目录的.ansible/tmp/xx.py文件
- 给文件+x执行
- 执行并将返回结果,删除临时py文件,sleep 0 退出
安装部署ansible
- 安装ansible
[root@localhost ~]# yum install epel-release.noarch -y
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y ansible
- 免密登录
# 三台机器设置hosts解析,方便之后用域名管理
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/hosts
192.168.175.10 server1
192.168.175.20 server2
192.168.175.30 server3
# 生成密钥对
[root@server1 ~]# ssh-keygen -P "" -t rsa
# 将公钥发送给需要被管理端,需要输入对方的免密
[root@server1 .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@server2
[root@server1 .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@server3
接下来我们使用ansible去登录这两个就不需要任何认证了
- 常用命令
- ansible:临时命令执行工具,常用于执行临时命令
- ansible-doc:常用于模块功能的查询
- ansible-playbook:用于执行剧本
- 常见配置文件
- /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg:主配置文件
- /etc/ansible/hosts:主机清单文件
- /etc/ansible/roles:角色目录
#ansible host配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
# This is the default ansible 'hosts' file.
#
# It should live in /etc/ansible/hosts
#
# - Comments begin with the '#' character
# - Blank lines are ignored
# - Groups of hosts are delimited by [header] elements
# - You can enter hostnames or ip addresses
# - A hostname/ip can be a member of multiple groups
# Ex 1: Ungrouped hosts, specify before any group headers.
## green.example.com
## blue.example.com
## 192.168.100.1
## 192.168.100.10
# Ex 2: A collection of hosts belonging to the 'webservers' group
## [webservers] #中括号代表一个组,下面的域名或者ip表示组里的成员
## alpha.example.org
## beta.example.org
## 192.168.1.100
## 192.168.1.110
# If you have multiple hosts following a pattern you can specify
# them like this:
## www[001:006].example.com
# Ex 3: A collection of database servers in the 'dbservers' group
## [dbservers]
##
## db01.intranet.mydomain.net
## db02.intranet.mydomain.net
## 10.25.1.56
## 10.25.1.57
# Here's another example of host ranges, this time there are no
# leading 0s:
## db-[99:101]-node.example.com
#定义自己的组
[all-servers]
server1
server2
server3
[node1]
server2
[node2]
server3
#ansible.cfg文件,默认可以不用改
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
[defaults]
# some basic default values...
#inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts
# 定义主机清单文件
#library = /usr/share/my_modules/ # 库
文件的存放位置
#module_utils = /usr/share/my_module_utils/
#remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp
# 生成的临时py文件在远程主机的目录
#local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp
# 生成的临时py文件在本地主机的目录
#plugin_filters_cfg = /etc/ansible/plugin_filters.yml #
#forks = 5 # 默认的并发数
#poll_interval = 15 # 默认的线程池
#sudo_user = root # 默认的sudo用户
#ask_sudo_pass = True
#ask_pass = True
#transport = smart
#remote_port = 22
#module_lang = C
#module_set_locale = False
ansible参数说明
-a MODULE_ARGS:指定模块的参数
-m MODULE_NAME:指定模块
-C:检查执行结果
-e EXTRA_VARS:指明变量名
-f FORKS:指定并发进程数
-i INVENTORY:指定主机清单文件
--syntax-check:检查执行命令是否存在语法错误
常用模块
ansible的执行状态
- 绿色:执行成功并且不需要做改变的操作
- 黄色:执行成功并且对目标主机做变更
- 红色:执行失败
- 粉色:警告信息
- 蓝色:显示ansible命令执行的过程
ping模块:主机连通性测试
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m ping node1
user模块
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -l|wc -l
3387 #共有3387个模块
[root@node1 ~]# ansible‐doc ‐s user #查看模块的参数
comment # 用户的描述信息
createhom # 是否创建家目录
force # 在使用`state=absent'是, 行为与`userdel ‐‐force'一致.
group # 指定基本组
groups # 指定附加组,如果指定为('groups=')表示删除所有组
home # 指定用户家目录
name # 指定用户名
password # 指定用户密码
remove # 在使用 `state=absent'时, 行为是与 `userdel ‐‐remove'一致.
shell # 指定默认shell
state #设置帐号状态,不指定为创建,指定值为absent表示删除
system # 当创建一个用户,设置这个用户是系统用户。这个设置不能更改现有用户
uid #指定用户的uid
update_password # 更新用户密码
expires #指明密码的过期时间
1.添加系统用户,指定uid、家目录、主组及注释
ansible -m user -a "system=yes name=zhangsan home=/home/zhangsan uid=111
group=zhangsan comment='hello zhangsan'" node1
2.删除用户及家目录
ansible -m user -a "name=zhangsan state=absent remove=yes" node1
group
[root@node1 ~]# ansible-doc -s group
‐ name: 添加或删除组
action: group
gid # 设置组的GID号
name= # 管理组的名称
state # 指定组状态,默认为创建,设置值为absent为删除
system # 设置值为yes,表示为创建系统组
ansible -m group -a "name=eagles gid=111 system=yes" node1
ansible -m group -a "name=eagles gid=111 state=absent" node1
command
1.默认使用的模块
2.不支持管道,变量及重定向等
[root@node1 ~]# ansible-doc -s command【查询文档】
- name: Execute commands on targets
command:
argv: # Passes the command as a list rather than a
string. Use `argv' to
avoid quoting values that would
otherwise be interpreted incorrectly
(for example "user name"). Only the
string or the list form can be
provided, not both. One or the other
must be provided.
chdir: # Change into this directory before running the
command.
cmd: # The command to run.
creates: # A filename or (since 2.0) glob pattern. If it
already exists, this
step *won't* be run.
free_form: # The command module takes a free form command
to run. There is no
actual parameter named 'free form'.
removes: # A filename or (since 2.0) glob pattern. If it
already exists, this
step *will* be run.
stdin: # Set the stdin of the command directly to the
specified value.
stdin_add_newline: # If set to `yes', append a newline to stdin
data.
strip_empty_ends: # Strip empty lines from the end of
stdout/stderr in result.
warn: # Enable or disable task warnings.
[root@node1 ~]# ansible -a "touch /root/ansible.txt" all-servers
[root@node1 ~]# ansible -a "find / -name ansible.txt" all-servers
shell
- 调用bash执行命令
- 但是默写复杂的操作即使使用shell也可能会失败
- 解决办法:将操作写到脚本中,通过script模块
[root@node1 ~]# ansible -m shell -a "find / -name ansible.txt" all-servers
script
free_form参数: 必须参数,指定需要执行的脚本,脚本位于 ansible 管理主机本地,并没有具体
的一个参数名叫 free_form,具体解释请参考 command 模块。
chdir参数: 此参数的作用就是指定一个远程主机中的目录,在执行对应的脚本之前,会先进入到
chdir 参数指定的目录中。
creates参数: 使用此参数指定一个远程主机中的文件,当指定的文件存在时,就不执行对应脚本,可
参考 command 模块中的解释。
removes参数: 使用此参数指定一个远程主机中的文件,当指定的文件不存在时,就不执行对应脚本,
可参考 command 模块中的解释。
[root@server1 ~]# vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in `seq 5`
do
mkdir -v /root/test_${i}.txt
rmdir -v /root/test_${i}.txt
done
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m script -a '/root/test.sh chdir=/tmp
creates=test2' node2
copy
[root@node1 ~]# ansible-doc -s copy
backup:在覆盖之前,将源文件备份,备份文件包含时间信息。
content:用于替代“src”,可以直接设定指定文件的值
dest:必选项。要将源文件复制到的远程主机的绝对路径
directory_mode:递归设定目录的权限,默认为系统默认权限
force:强制覆盖目的文件内容,默认为yes
others:所有的file模块里的选项都可以在这里使用
src:被复制到远程主机的本地文件,可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果路径是一个目录,它将
递归复制
ansible -m copy -a "src=/本地文件 dest=/远程文件" nodes
- 在创建文件时修改文件的属主和属组信息
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m copy -a "src=/root/test.sh dest=/root/test1
owner=zhangsan group=eagles" node1
- 在传输文件时修改文件的权限信息,并且备份远程主机文件
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m copy -a "src=/root/test.sh dest=/root/test1
backup=yes mode=777" node1
- 创建一个文件并直接编辑文件
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m copy -a "content='hello eagles\n'
dest=/root/test1" node1
file
[root@node1 ~]# ansible‐doc ‐s file
‐ name: Sets attributes of files
force:需要在两种情况下强制创建软链接,一种是源文件不存在,但之后会建立的情况下;另一
种是目标软链接已存在,需要先取消之前的软链,然后创建新的软链,有两个选项:yes|no
group:定义文件/目录的属组
mode:定义文件/目录的权限
owner:定义文件/目录的属主
path:必选项,定义文件/目录的路径
recurse:递归设置文件的属性,只对目录有效
src:被链接的源文件路径,只应用于state=link的情况
dest:被链接到的路径,只应用于state=link的情况
state:
absent: 删除文件
directory:如果目录不存在,就创建目录
file:验证文件是否存在,即使文件不存在,也不会被创建
link:创建软链接
hard:创建硬链接
touch:如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新的文件,如果文件或目录已存在,则更新其后修改时间
- 创建目录
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m file -a "name=test1 owner=root group=root
mode=644 state=directory " node1
- 创建文件
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m file -a "path=/root/test2 owner=root group=root
mode=644 state=touch" node1
- 删除文件/目录
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m file -a "path=/root/test2 state=absent" node1
- 创建软链接文件
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m file -a "src=/root/test1 dest=/root/test2
state=link" node2
- 创建硬链接文件
[root@server1 ~]# ansible -m file -a "src=/root/test.txt dest=/root/test2
state=hard" node2
yum
[root@node1 ~]# ansible‐doc ‐s yum
conf_file #设定远程yum安装时所依赖的配置文件。如配置文件没有在默认的位置。
disable_gpg_check #是否禁止GPG checking,只用于`present' or `latest'。
disablerepo #临时禁止使用yum库。 只用于安装或更新时。
enablerepo #临时使用的yum库。只用于安装或更新时。
name= #所安装的包的名称
state #present安装, latest安装新的, absent 卸载软件。
update_cache #强制更新yum的缓存
[root@node1 ~]# ansible -m yum -a "name=httpd state=latest" node1
service
[root@server1 ~]# ansible-doc -s service
> SERVICE (/usr/lib/python2.7/site‐
packages/ansible/modules/system/service.py)
Controls services on remote hosts. Supported init systems include
BSD init, OpenRC, SysV, Solaris
SMF, systemd, upstart. For Windows targets, use the [win_service]
module instead.
* note: This module has a corresponding action plugin.
arguments #命令行提供额外的参数
enabled #设置开机启动,可以设置为yes或者no。
name= #服务名称
runlevel #开机启动的级别,一般不用指定。
sleep #在重启服务的过程中,是否等待。如在服务关闭以后等待2秒再启动。
state #started启动服务, stopped停止服务, restarted重启服务, reloaded重载
配置
[root@node1 ~]# ansible -m service -a "name=httpd state=started" node1
selinux
[root@node1 ~]# ansible-doc -s selinux
# selinux模块针对selinux的修改操作是针对配置文件进行修改的
‐ name: Change policy and state of SELinux
selinux:
configfile: # path to the SELinux configuration file, if
non‐standard
policy: # name of the SELinux policy to use
state: # (required) The SELinux mode
[root@node1 ~]# ansible -m selinux -a "state=enforcing policy=targeted" node1
- setup
ansible -m setup node1 #获取远程主机的详细信息
ansible-doc -l # 可以查询ansible具有的所有模块
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/index.html # 官方文档
playbook
简介:
playbook是由一个或者多个play组成的列表,可以让这些列表按事先编排的机制执行;所谓task是调用ansible的具体模块,在模块参数中可以使用变量。模块执行是幂等性的,意味着多次执行结果相同。使用yaml语言编写playbook,后缀名一般为.yml
特点
yaml语言的参考博客http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/07/yaml.html
- yaml的可读性好
- yaml和脚本语言的交互性好
- yaml使用实现语言的数据类型
- yaml有一个一致性的信息模块
- yaml易于实现
- yaml可以基于流来处理
核心字段
- hosts:执行的远程主机列表
- tasks:任务,由模块定义操作列表
- variables:内置变量或者自定义变量
- templates:模板,定义模板文件,模板文件一般是由jinja2语言编写的
- handlers:和nogity结合使用,为条件触发操作,满足条件则执行
- roles:角色
官方示例
在线检测工具:http://www.yamllint.com/
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir playbook
[root@localhost ~]# vim playbook/test1.yaml
- name: update web servers
hosts: node1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ensure apache is at the latest version
yum:
name: httpd
state: latest
- name: write the apache config file
template:
src: /srv/httpd.j2
dest: /etc/httpd.conf
- name: ensure that htppd is started
- service:
name: httpd
state: started
- name: update db servers
hosts: node1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ensure mariadb is at the latest version
yum:
name: mariadb-server
state: latest
- name: ensure that mariadb is started
service:
name: mariadb
state: started
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-playbook playbook/test1.yaml
案例,apache虚拟主机
- 准备配置文件
[root@server1 playbook]# cat /root/playbook/file/site2.conf
Listen 8080
Listen 9090
<Directory "/data/">
Require all granted
</Directory>
<VirtualHost *:8080>
DocumentRoot "/data/site1/"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:9090>
DocumentRoot "/data/site2/"
</VirtualHost>
- 准备剧本文件
[root@server1 playbook]# vim apache-virtualhost-port.yaml
- name: Update web servers
hosts: node1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ensure apache is the latest version
yum:
name: httpd
state: latest
- name: copy site2.conf to apache web server
copy:
src: /root/playbook/file/site2.conf
dest: /etc/httpd/conf.d/site2.conf
- name: create directory1 for apache web server
file:
name: /data/site1/
state: directory
- name: create directory2 for apache web server
file:
name: /data/site2/
state: directory
- name: write index.html
shell: echo "site1" > /data/site1/index.html && echo "site2" >
/data/site2/index.html
- name: start apache web server
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
- name: test virtual hosts
shell: curl 192.168.175.20:8080 && curl 192.168.175.20:9090
- 执行
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook apache-virtualhost-port.yaml --
syntax-check
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook apache-virtualhost-port.yaml
- 测试
[root@server1 playbook]# curl 192.168.175.20:8080
site1
[root@server1 playbook]# curl 192.168.175.20:9090
site2
案例,安装nginx并且修改配置文件
第一步,准备文件存放目录
[root@eagle ~]# mkdir -p /root/ansible/{conf,bin}
第二步,书写YAML文件
[root@eagle bin]# cat nginx.yaml
- name: Update web servers
hosts: node1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Install epel
yum:
name: epel-release.noarch
state: latest
- name: Install nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Copy nginx configure file
- copy:
src: /root/ansible/conf/site.conf
dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/site.conf
- name: Start nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
- name: Create index.html
shell: echo "nginx1" > /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
第三步,书写conf文件
[root@eagle conf]# vim site.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name 192.168.175.20:8080;
location / {
index index.html;
}
}
第四步,检查语法错误,没有错误则继续执行
[root@eagle bin]# ansible-playbook nginx.yaml --syntax-check
[root@eagle bin]# ansible-playbook nginx.yaml
变量
- 变量的来源
- 远程主机的所有变量都可以使用 ansible -m setup node1
- 自定义变量
- 优先级
- 通过命令行指定变量优先级最高
- /etc/ansible/hosts定义变量(针对单个主机定义,针对主机组进行定义)
- playbook中定义的变量
模块
- 文本文件,内部嵌套有模板语言的脚本
- jinja2是由python编写的,在使用模板文件时jinja2是很好的解决方案
- 功能:将模板文件中的变量转换成对应的本地主机的确定值
- 语法
- 字符串:使用单引号或者双引号代表字符串
- 数字
- 列表:使用中括号括起来表示的是列表[ ]
- 元组:使用小括号表示元组( )
- 字典:使用大括号表示字典{ }
- 算数运算:+ - * / …
- 比较操作:== != > < …
- 逻辑运算:and or not
1、变量
{{name}}
2、控制语句
{% if %}
{{name}}
{% else %}
{{name2}}
{% endif %}
3、宏(类似函数,用来进行重用)
{% macro check_user(user) %}
{% if user=="wang" %}
<p> {{user}} </p>
{% endif %}
{% end macro %}
{% import 'macros.html' as macros %}
{{ macros.check_user(user) }}
4、模版继承
#base.html
<html>
<head>
{% block head%}
<title>
{% block title %}
{% end block %}
</title>
{% end block%}
</head>
<body>
{% block body %}
{% end block %}
</body>
</html>
#子模版
{% extends 'base.html'%}
{% block head %}
{{ super() }}
{% end block %}
{% block title %}
Index
{% end block %}
{% block body %}
<h1>hello world</h1>
{% end block %}
案例,生成hosts解析文件
使用模板替远程主机生成hosts解析文件(先把原来的hosts解析都去掉,在ansible配置文件里面替换为ip)
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[all-servers]
server1
server2
server3
[all_ip]
192.168.175.10
192.168.175.20
192.168.175.30
# 各台机器修改好自己的主机名
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname server1
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname server2
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname server3
- 准备模板文件
[root@server1 ~]# vim hosts.j2
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4
localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6
localhost6.localdomain6
{% for host in groups.all_ip %}
{{hostvars[host].ansible_ens33.ipv4.address}}
{{hostvars[host].ansible_hostname}}
{% endfor %}
------------------------
常见变量
主机名: "{{ ansible_hostname }}"
操作系统版本: "{{ ansible_distribution }}" "{{ ansible_distribution_version
}}"
内核版本: "{{ ansible_kernel }}"
系统位数: "{{ ansible_userspace_bits }}"
网卡:"{{ ansible_eth0["device"] }}"
IP地址: "{{ ansible_eth0["ipv4"]["address"] }}"
子网掩码: "{{ ansible_eth0["ipv4"]["netmask"] }}"
总内存: "{{ ansible_memory_mb["real"]["total"] }}"
内存空闲: "{{ ansible_memfree_mb }}"
- 编写剧本
[root@server1 ~]# vim hosts.yml
- name: Config hosts file
hosts: all_ip
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy hosts.j2 to group servers
template:
src: hosts.j2
dest: /etc/hosts
- 执行剧本
[root@server1 ~]# ansible-playbook hosts.yml
- 验证
[root@server2 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4
localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6
localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.175.10 server1
192.168.175.20 server2
192.168.175.30 server3
案例,生成nginx配置文件
[root@server1 ~]# vim template_nginx.yaml
- hosts: all_ip
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1:
listen: 8080
root: "/var/www/nginx/web1/"
- web2:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web2.baidu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web2/"
- web3:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web3.baidu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web3/"
tasks:
- name: mkdir /data
file:
name: /data
state: directory
- name: template config
template:
src=./template/nginx.conf.j2
dest=/data/nginx.conf
[root@server1 ~]# vim template/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {{ vhost.listen }}
{% if vhost.server_name is defined %}
server_name {{ vhost.server_name }}
{% endif %}
root {{ vhost.root }}
}
{% endfor %}
[root@server1 ~]# ansible-playbook template_nginx.yaml
检查结果:
[root@server2 ~]# cat nginx.conf
server {
listen 8080
root /var/www/nginx/web1/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web2.baidu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web2/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web3.baidu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web3/
}
条件判断
‐ name: restart Nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
循环迭代
#基于字符串列表
tasks:
‐ name: create rsyncd file
copy: src={{ item }} dest=/tmp/{{ item }}
with_items:
‐ a
‐ b
‐ c
‐ d
*with_itmes 嵌套子变量*
#基于字典列表
‐ hosts: eagleslab
remote_user: root
tasks:
‐ name: add several users
user: name={{ item.name }} state=present groups={{ item.groups }}
with_items:
‐ { name: 'testuser1' , groups: 'wheel'}
‐ { name: 'testuser2' , groups: 'root' }
使用循环创建用户和组,完成:
创建组
用循环创建用户
- 编写playbook
[root@server1 ~]# cat user_manage.yml
- name: Manage user
hosts: node1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ensure group eagles exists
group:
name: eagles
- name: create users zhangsan and lisi
user:
name={{ item.name }}
group={{ item.group }}
state=present
with_items:
- { name: 'zhangsan', group: 'eagles' }
- { name: 'lisi', group: 'eagles' }
- 执行
[root@server1 ~]# ansible-playbook user_manage.yml
- 验证
[root@server2 ~]# id zhangsan
uid=1000(zhangsan) gid=1001(eagles) 组=1001(eagles)
[root@server2 ~]# id lisi
uid=1001(lisi) gid=1001(eagles) 组=1001(eagles)
案例,循环创建用户
循环创建用户,用户信息如下
名称、组、家目录、shell、描述信息
zhangsan xsb /home/xsb/zhangsan /bin/bash 销售
lisi xsb /home/xsb/lisi /bin/bash 销售
wangwu jsb /home/jsb/wangwu /bin/sh java工程师
maliu jsb /home/jsb/maliu /bin/sh linux工程师
zhaoqi cwb /home/cwb/zhaoqi /bin/sh 会计
循环创建出以上用户并指定用户信息
[root@server1 ~]# vim user_manage.yml
- name: Manage user
hosts: node1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ensure group xsb/jsb/cwb exists
group:
name={{ item.group }}
with_items:
- { group: 'xsb' }
- { group: 'cwb' }
- { group: 'jsb' }
- name: create users zhangsan/lisi/wangwu/maliu/zhaoqi
user:
name={{ item.name }}
group={{ item.group }}
shell={{ item.shell }}
comment={{ item.comment }}
home={{ item.home }}
with_items:
- { name: 'zhangsan', group: 'xsb',home: '/home/xsb/zhangsan',shell:
'/bin/bash',comment: '销售'}
- { name: 'lisi', group: 'xsb',home: '/home/xsb/zhangsan',shell:
'/bin/bash',comment: '销售'}
- { name: 'wangwu', group: 'jsb',home: '/home/jsb/wangwu',shell:
'/bin/sh',comment: 'java工程师'}
- { name: 'maliu', group: 'jsb',home: '/home/jsb/maliu',shell:
'/bin/sh',comment: 'linux工程师'}
- { name: 'zhaoqi', group: 'cwb',home: '/home/cwb/zhaoqi',shell:
'/bin/sh',comment: '会计'}
[root@server1 ~]# ansible-playbook user_manage.yml
角色
[root@eagle roles]# tree /etc/ansible/roles/
/etc/ansible/roles/
├── http
│ ├── defaults
│ ├── files
│ ├── handlers
│ ├── meta
│ ├── tasks
│ ├── template
│ └── vars
├── mysql
├── redis
└── site.yaml
目录结构
- tasks:此目录中至少有一个名为main.yaml文件,用于定义各种task,其他文件需要由
main.yaml文件进行调用
- handlers:此目录中至少有一个名为main.yaml文件,用于定义各种handler,其他文件需要被
main.yaml进行调用
- vars:此目录中至少有一个名为main.yaml文件,用于定义各种变量,其他文件需要被main.yaml
进行调用
- templates:存储template模块调用的模板文件
- meta:此目录中至少有一个名为main.yaml文件,定义当前角色的设定及其依赖关系,其他的文件
需要被main.yaml文件进行调用
- default:此目录中至少有一个main.yaml文件,用于设定默认的值
- files:此目录存放copy或者script等模块调用的文件
案例,使用角色安装httpd
第一步,准备相关目录
[root@eagle tasks]# tree -a /etc/ansible/roles/
/etc/ansible/roles/
├── http
│ ├── defaults
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── files
│ ├── handlers
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── meta
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── tasks
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── template
│ └── vars
├── mysql
├── redis
└── site.yaml
[root@server1 roles]# ansible-galaxy init apache
- Role apache was created successfully
第二步,书写site.yaml文件
[root@eagle tasks]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/site.yaml
- hosts: node2
remote_user: root
roles:
- apache
第三步,书写tasks里的main.yaml文件
[root@eagle tasks]# cat main.yaml
- name: Install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
- name: Start httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
- name: Write index file
shell: echo "http" > /var/www/html/index.html
第四步,验证语法并执行
[root@eagle roles]# ansible-playbook site.yaml --syntax-check
[root@eagle tasks]# ansible-playbook /etc/ansible/roles/apache/site.yaml
第五步,验证结果
[root@eagle tasks]# curl 192.168.175.30
httpd2
案例,使用角色安装java+nginx+halo
角色参考案例:https://www.wumingx.com/linux/ansible-roles.html
使用role的方式来安装halo,相对来说,结构会比较清晰明了。还是使用ansible去自动部署halo博客系统。功能很简单,就是在一台机器上面自动部署java+halo+nginx服务
halo博客:https://halo.run/
- 准备角色
[root@server1 roles]# ansible-galaxy init halo
- Role halo was created successfully
[root@server1 roles]# ansible-galaxy init java
- Role java was created successfully
[root@server1 roles]# ansible-galaxy init nginx
- Role nginx was created successfully
- 编写site.yaml,pre_tasks为运行play之前执行的任务,post_tasks为运行play之后执行的任务
[root@server1 roles]# vim site.y
---
- hosts: node1
remote_user: root
strategy: free
pre_tasks:
- name: config nginx repo for centos 7
yum_repository:
name: nginx
description: nginx
baseurl: http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck: no
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
- name: Disable SELinux
selinux: state=disabled
roles:
- nginx
post_tasks:
- shell: echo 'Deplay halo finished.'
register: ret
- debug: var=ret.stdout
- 编写nginx角色
[root@server1 roles]# vim nginx/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for nginx
- name: make sure nginx state is installed
yum: name=nginx state=installed
- name: copy halo to nginx config file
template: src=halo.conf dest="/etc/nginx/conf.d/halo.conf"
- name: make sure nginx service is running
service: name=nginx state=started
- name: make sure port is open
wait_for: port="{{ nginx_port }}"
# meta/main.yml为role的依赖关系,要先运行这里面的内容才会运行自己的nginx这个role。
[root@server1 roles]# vim nginx/meta/main.yml
dependencies:
# List your role dependencies here, one per line. Be sure to remove the
'[]' above,
# if you add dependencies to this list.
- role: java
- role: halo
[root@server1 roles]# vim nginx/templates/halo.conf
upstream halo {
server 127.0.0.1:8090;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name {{ halo_domain }};
client_max_body_size 1024m;
location / {
proxy_pass http://halo;
proxy_set_header HOST $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
- 编写java角色,这个角色的任务就是安装java
[root@server1 roles]# vim java/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for java
- name: install java
yum: name=java-11-openjdk state=installed
- 编写halo角色
[root@server1 roles]# vim halo/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for halo
- name: get halo
get_url: url=https://dl.halo.run/release/halo-1.4.11.jar dest={{
halopath }}
- name: add halo service file
template: src=halo.service dest=/etc/systemd/system/halo.service
- name: touch ~/.halo directory
file: path=~/.halo state=directory
- name: copy halo config file
template: src=application.yaml dest="~/.halo/application.yaml"
- name: restart halo
systemd:
daemon_reload: yes
name: halo
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: wait to start halo
wait_for: port={{ halo_port }}
[root@server1 roles]# vim halo/vars/main.yml
---
# vars file for halo
memory: 512m
halo_port: 8090
halopath: /root/halo.jar
halo_domain: 192.168.175.20
nginx_port: 80
# 下载service文件并编辑
[root@server1 roles]# wget https://dl.halo.run/config/halo.service -O
halo/templates/halo.service
[root@server1 roles]# vim halo/templates/halo.service
[Unit]
Description=Halo Service
Documentation=https://docs.halo.run
After=network-online.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=root #修改
ExecStart=/usr/bin/java -server -Xms256m -Xmx256m -jar /root/halo.jar #修改
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
Restart=always
StandOutput=syslog
StandError=inherit
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@server1 roles]# wget https://dl.halo.run/config/applicationtemplate.yaml -O halo/templates/application.yaml
- 运行site.taml
[root@server1 roles]# ansible-playbook site.yaml
综合案例
环境准备:六台节点
一台管理节点
一台nginx作为负载均衡器
两台apache作为web服务器
一台作为mariadb数据库
一台作为网站存储(nfs)
- 工作流程(主机清单文件、ssh通信、免密登录、生成py脚本、sleep0退出)
- 更换远程主机的yum仓库(更换为国内的源速度更快)
- 安装httpd、mariadb、nginx
- 使用模板给httpd准备配置文件,使用ansible-galaxy安装负载均衡角色
- 使用parted模块创建分区,使用lvg模块创建卷组,使用lvol模块创建逻辑卷,逻辑卷作为nfs存使用
- 使用shell模块为数据库添加指定库、用户等操作
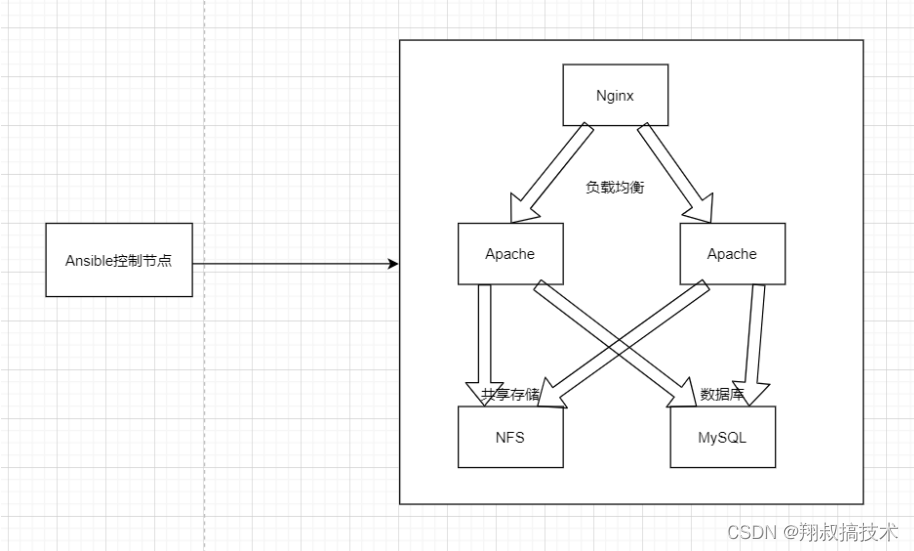 - 在管理节点编写ansible主机清单文件,server1是管理结点,server2是负载均衡结点,server3和server4是apache web结点,server5是mariadb结点,server6是nfs结点
- 在管理节点编写ansible主机清单文件,server1是管理结点,server2是负载均衡结点,server3和server4是apache web结点,server5是mariadb结点,server6是nfs结点
[root@server1 ~]# yum install -y ansible
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[all_ip]
192.168.175.10
192.168.175.20
192.168.175.30
192.168.175.40
192.168.175.50
192.168.175.60
[all_hostname]
server2
server3
server4
server5
server6
[nginx]
server2
[apache]
server3
server4
[mariadb]
server5
[nfs]
server6
#生成密钥,分发密钥
[root@server1 ~]# ssh-keygen
[root@server1 .ssh]# for i in {1..6};do ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub
root@192.168.175.${i}0;done
- 为所有主机生成hosts解析文件
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir playbook
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir template
[root@server1 playbook]# vim /root/template/hosts.j2
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4
localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6
localhost6.localdomain6
{% for host in groups.all_ip %}
{{hostvars[host].ansible_ens33.ipv4.address}}
{{hostvars[host].ansible_hostname}}
{% endfor %}
[root@server1 ~]# cd playbook
[root@server1 playbook]# vim hosts.yml
- name: Config hosts file
hosts: all_ip
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy hosts.j2 to group servers
template:
src: /root/template/hosts.j2
dest: /etc/hosts
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook hosts.yml
- 更换腾讯yum源,使用file模块把所有受控节点的/etc/yum.repos.d/下的所有文件删除,使用copy模块把准备好的.repo文件copy到所有受控节点
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-galaxy init /etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo
[root@server1 playbook]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for /etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo
- name: Find files in yum.repos.d/*
find:
paths: /etc/yum.repos.d/
patterns: '*'
register: files_to_delete
- name: Remove original yum.repos.d/*
file:
path: "{{ item.path }}"
state: absent
with_items: "{{ files_to_delete.files }}"
- name: Copy tencent yum.repo to all nodes
copy:
src: /etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo/files/yum.repo
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/
- name: Copy tencent epel.repo to all nodes
copy:
src: /etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo/files/epel.repo
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@server1 playbook]# vim yum_repo_role_use.yml
- name: Update all nodes yum.repo file
hosts: all_hostname
roles:
- tx_yum_repo
# 下载腾讯yum源和epel源
[root@server1 playbook]# wget -O
/etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo/files/yum.repo
http://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/repo/centos7_base.repo
[root@server1 playbook]# wget -O
/etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo/files/epel.repo
http://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/repo/epel-7.repo
[root@server1 playbook]# ls /etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo/files/yum.repo
/etc/ansible/roles/tx_yum_repo/files/yum.repo
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook yum_repo_role_use.yml
- 编写yml安装nginx、httpd、mariadb并打开防火墙,设置防火墙放行服务
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-galaxy init /etc/ansible/roles/apache
- Role /etc/ansible/roles/apache was created successfully
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-galaxy init /etc/ansible/roles/nginx
- Role /etc/ansible/roles/nginx was created successfully
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-galaxy init /etc/ansible/roles/mariadb
- Role /etc/ansible/roles/mariadb was created successfully
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-galaxy init /etc/ansible/roles/nfs
- Role /etc/ansible/roles/nfs was created successfully
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for /etc/ansible/roles/nginx
- name: Yum install epel
yum:
name: epel-release.noarch
state: present
- name: Yum install nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Start nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
enabled: yes
[root@server1 playbook]# vim nginx_install.yml
- name: Install nginx
hosts: nginx
roles:
- nginx
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook nginx_install.yml
[root@server1 playbook]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/apache/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for /etc/ansible/roles/apache
- name: Install lamp environment
yum:
name: httpd,php-fpm,php-mysql,mod_php
state: present
- name: Start httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
- name: Start php-fpm
service:
name: php-fpm
state: restarted
[root@server1 playbook]# vim lamp_install.yml
- name: Prepare lamp
hosts: apache
roles:
- apache
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook lamp_install.yml
[root@server1 playbook]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/mariadb/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for /etc/ansible/roles/mariadb
- name: Yum install mariadb
yum:
name: mariadb-server
state: present
- name: Start mariadb
service:
name: mariadb
state: restarted
[root@server1 playbook]# vim mariadb_install.yml
- name: Install mariadb
hosts: mariadb
roles:
- mariadb
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook mariadb_install.yml
- 准备负载均衡角色
#初始化角色
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-galaxy init /etc/ansible/roles/nginx_lb
#准备配置文件模板
[root@server1 playbook]# vim
/etc/ansible/roles/nginx_lb/templates/lb.conf.j2
upstream websers{
server server3;
server server4;
}
server{
listen 8080;
server_name 192.168.175.20:8080;
location / {
proxy_pass http://websers;
proxy_set_header HOST $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
#准备task文件
[root@server1 playbook]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx_lb/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for /etc/ansible/roles/nginx_lb
- name: Configure ngin LB conf file
template:
src: /etc/ansible/roles/nginx_lb/templates/lb.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/lb.conf
- name: Restart nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
[root@server1 playbook]# vim nginx_lb.yml
- name: Configure nginx lb server
hosts: nginx
roles:
- nginx_lb
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook nginx_lb.yml
另一种实现负载均衡的方式(haproxy):
[root@node1 balancer]# vim tasks/main.yml
---
# This playbook installs HAProxy and HTTPd and configures it.
- name: Install haproxy
yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
with_items:
- haproxy
when: inventory_hostname in groups['nginx']
- name: Configure the haproxy cnf file
template:
src: templates/haproxy.cfg.j2
dest: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
notify: restart haproxy
when: inventory_hostname in groups['nginx']
- name: Start the haproxy service
service:
name: haproxy
state: started
enabled: yes
when: inventory_hostname in groups['nginx']
- name: Install firewalld
yum:
name: firewalld
state: present
when: inventory_hostname in groups['nginx']
- name: Start and enable firewalld
service:
name: firewalld
state: started
enabled: yes
when: inventory_hostname in groups['nginx']
- name: Enable http in firewall
firewalld:
service: http
permanent: true
state: enabled
immediate: true
when: inventory_hostname in groups['nginx']
- name: Install Apache
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
when: inventory_hostname in groups['apache']
- name: Install firewalld
yum:
name: firewalld
state: present
when: inventory_hostname in groups['apache']
- name: Copy the index_ver.html.j2
template:
src: templates/index_ver.html.j2
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
notify: restart httpd
when: inventory_hostname in groups['apache']
- name: Start and enable firewalld
service:
name: firewalld
state: started
enabled: yes
when: inventory_hostname in groups['apache']
- name: Enable http in firewall
firewalld:
service: http
permanent: true
state: enabled
immediate: true
when: inventory_hostname in groups['apache']
- name: Start and enable httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
when: inventory_hostname in groups['apache']
[root@node1 balancer]# cat templates/haproxy.cfg.j2
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user root
group root
daemon
# turn on stats unix socket
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats level admin
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
frontend main
bind {{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}:80
default_backend app
backend app
balance roundrobin
server 192.168.40.103 192.168.40.103 check port 80
server 192.168.40.104 192.168.40.104 check port 80
#这里server后跟的ip改为你自己apache服务器的ip
- 使用parted模块创建分区,使用lvg模块创建卷组,使用lvol模块创建逻辑卷,把逻辑卷挂载到本地文件夹,逻辑卷作为nfs存储使用。在nfs服务器下载nfs-utils和rpcbind软件并启用服务,打开防火墙nfs和mountd服务以便后续挂载,使用mount模块把apache服务根目录挂载到nfs服务器.
- 给server6添加一块硬盘(20G)
[root@server1 playbook]# vim nfs.yaml
- name: create vg
hosts: nfs
tasks:
- name: create partition
parted:
device: /dev/sdb
number: 1
flags: [ lvm ]
state: present
part_start: 1MiB
part_end: 2GiB
- name: create nfs vg
lvg:
vg: nfs
pvs: /dev/sdb1
- name: create lv
block:
- name: create lvm 1500m
lvol:
vg: nfs
lv: data
size: 1900m
rescue:
- name: file msg
debug:
msg: create lv failed
- name: create lvm 800m
lvol:
vg: nfs
lv: data
size: 800m
always:
- name: format lvm
filesystem:
fstype: ext4
dev: /dev/nfs/data
when: "'nfs' in ansible_lvm.vgs"
- name: nfs not exists
debug:
msg: vg does not exist
when: "'nfs' not in ansible_lvm.vgs"
- name: install nfs pkg and mount nfs lvs
hosts: nfs,apache
tasks:
- name: install package
yum:
name: nfs-utils,rpcbind
state: latest
- name: config file
shell: mkdir /nfs | chmod -Rf 777 /nfs | echo "/nfs
192.168.175.0/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" > /etc/exports
- name: start services
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
loop:
- rpcbind
- nfs-server
- name: mount lv
hosts: nfs
tasks:
- name: mount lv
mount:
src: /dev/nfs/data
path: /nfs
fstype: ext4
state: mounted
- name: mount apache
hosts: apache
tasks:
- name: mount apache
mount:
src: 192.168.175.60:/nfs
path: /var/www/html
fstype: nfs
state: mounted
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook nfs.yml
#此时apache的两台服务器就实现了共享存储,/var/www/html这个挂载在/nfs下共享web服务器的
文件
[root@server3 ~]# df -h
[root@server3 ~]# echo "hello apache" >> /var/www/html/index.html
[root@server4 ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
hello apache
- 然后将上面的所有任务全部汇总到一个任务中去(提醒,如果汇总的话需要注意将有些文件或者模板的路径写成绝对路径)
[root@server1 playbook]# vim all.yml
- name: Update hosts file
hosts: all_ip
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy hosts.j2 to group servers
template:
src: ../template/hosts.j2
dest: /etc/hosts
- name: Update yum.repo file
hosts: all_hostname
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: /etc/ansible/roles/ali_yum_repo/tasks/main.yml
- name: Install nginx
hosts: nginx
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: Install apache
hosts: apache
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: /etc/ansible/roles/apache/tasks/main.yml
- name: Install mariadb
hosts: mariadb
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: /etc/ansible/roles/mariadb/tasks/main.yml
- name: Configure nginx lb server
hosts: nginx
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: /etc/ansible/roles/nginx_lb/tasks/main.yml
- name: Create lvm for nfs
hosts: nfs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: /etc/ansible/roles/lvm_create/tasks/main.yml
- 在nfs服务器nfs目录下下载typecho软件包并解压
[root@server3 nfs]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@server3 html]# wget http://typecho.org/downloads/1.1-17.10.30-
release.tar.gz
[root@server3 html]# tar -zxvf 1.1-17.10.30-release.tar.gz
[root@server3 html]# mv build/var/* .
- 使用shell模块为数据库添加指定库、用户等操作
[root@server5 ~]# mysql -uroot
MariaDB [(none)]> create database typecho;
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on typecho.* to user1@"%" identified
by '123456';
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges;
- 最后网址访问nginx负载均衡服务器:192.168.175.20:8080(负载均衡不用80端口似乎会有bug,如果出问题就去访问192.168.175.30或者192.168.175.40)





















 428
428











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








