The Link of complete code of the calculator :
https://github.com/hhhhhhhhhhhua/ee308
Catalogue
Design and implementation process
Personal Imformation
| The Link Your Class | https: https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/ssynkqtd-04 |
| The Link of Requirement of This Assignment | https: https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/617332156 |
| The Aim of This Assignment | Create a calculator with a visual interface |
| MU STU ID and FZU STU ID | MU: 21125449 FZU:832101207 |
PSP Form
| Personal Software Process Stages | Estimated Time(minutes) | Actual Time(minutes) |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | ||
| • Estimate | 60 | 45 |
| Development | ||
| • Analysis | 60 | 100 |
| • Design Spec | 30 | 30 |
| • Design Review | 20 | 10 |
| • Coding Standard | 60 | |
| • Design | 60 | 60 |
| • Coding | 480 | 540 |
| • Code Review | 60 | 120 |
| • Test | 30 | 60 |
| Reporting | ||
| • Test Report | 90 | 90 |
| • Size Measurement | 30 | 15 |
| • Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 60 | 360 |
| Sum | 1040 | 1430 |
Problem-solving Ideas
1) General idea
After understanding the basic requirements of the assignment, I firstly confirmed the basic completion goal of this project. At the first, I design a calculator that can complete the basic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, clear and ba.
2) Programming language
Based on previous learning, I have a good command of python and have a higher interest in the language. Therefore, I finally choose python to complete the implementation and improvement of the calculator.
Design and implementation process
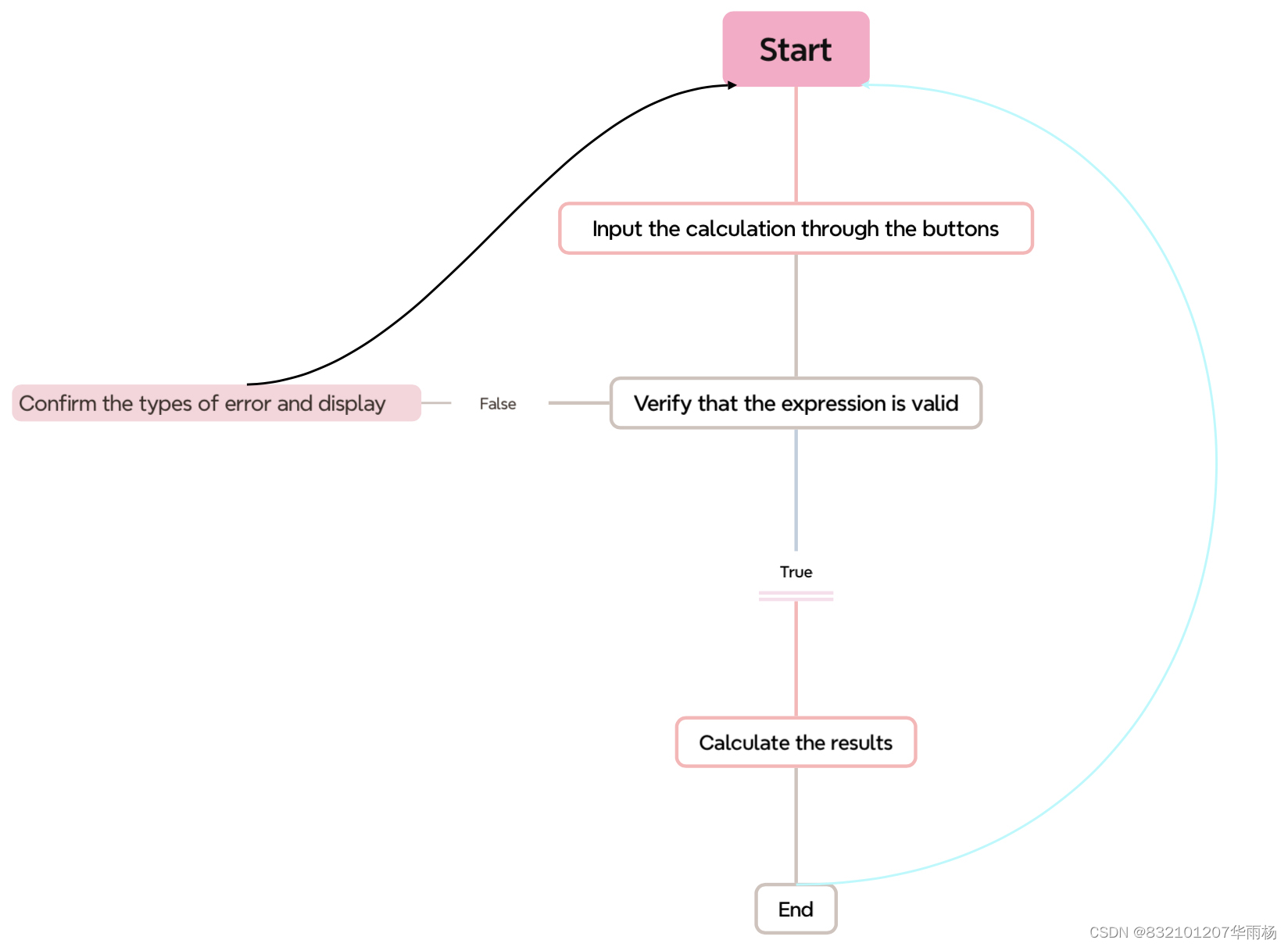
1) Mentality of designing

2) Implementation calculator
Code description
1. Importing tkinter plate, and Create the window
import tkinter
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.minsize(360,680)
def __init__(self, width, height, title):
root.minsize(height=height, width=width)
root.maxsize(height=height, width=width)
root.title(title)
self.nums = 1
self.top_frame = None
self.calList = []
self.flag = False
self.result = 0
self.result_panel1 = None
self.result_panel2 = None
self.format = True2. Implement interface layout, and Set display panel
def set_label(self):
self.top_frame = tkinter.Frame(root,width=360,height=200)
self.top_frame.place(x=0,y=0)
self.result_panel1 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.result_panel1.set('')
self.result_panel2 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.result_panel2.set(0)
result_label1 = tkinter.Label(self.top_frame, font=('微软雅黑', 25), bg='#FFFEFF', bd='9', fg='#000000', anchor='se',
textvariable=self.result_panel1)
result_label1.place(width=360, height=100)
result_label2 = tkinter.Label(self.top_frame,font=('微软雅黑', 30), bg='#FFFEFF', bd='9', fg='#000000', anchor='se',
textvariable=self.result_panel2)
result_label2.place(x=0,y=100, width=360, height=100)
3. Design number buttons and operator buttons
def set_span(self):
self.bootom_frame = tkinter.Frame(root, width=360, height=480)
self.bootom_frame.place(x=0, y=200)
button_c = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='Clear', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressC())
button_c.place(x=0, y=0, width=90, height=96)
button_back = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='Delete', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressBack())
button_back.place(x=90, y=0, width=90, height=96)
button_left = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='(', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressLeft())
button_left.place(x=180, y=0, width=90, height=96)
button_right = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text=')', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressRight())
button_right.place(x=270, y=0, width=90, height=96)
button_1 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='1', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('1'))
button_1.place(x=0, y=96, width=90, height=96)
button_2 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='2', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('2'))
button_2.place(x=90, y=96, width=90, height=96)
button_3 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='3', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('3'))
button_3.place(x=180, y=96, width=90, height=96)
button_plus = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='+', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressOperation('+'))
button_plus.place(x=270, y=96, width=90, height=96)
button_4 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='4', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('4'))
button_4.place(x=0, y=192, width=90, height=96)
button_5 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='5', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('5'))
button_5.place(x=90, y=192, width=90, height=96)
button_6 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='6', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('6'))
button_6.place(x=180, y=192, width=90, height=96)
button_sub = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='-', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressOperation('-'))
button_sub.place(x=270, y=192, width=90, height=96)
button_7 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='7', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('7'))
button_7.place(x=0, y=288, width=90, height=96)
button_8 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='8', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('8'))
button_8.place(x=90, y=288, width=90, height=96)
button_9 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='9', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('9'))
button_9.place(x=180, y=288, width=90, height=96)
button_mul = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='×', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressOperation('*'))
button_mul.place(x=270, y=288, width=90, height=96)
button_point = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='.', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('.'))
button_point.place(x=0, y=384, width=90, height=96)
button_0 = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='0', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#429488',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressNum('0'))
button_0.place(x=90, y=384, width=90, height=96)
button_eq = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='=', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 40), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressEqual())
button_eq.place(x=180, y=384, width=180, height=96)
button_div = tkinter.Button(self.bootom_frame, text='÷', bd='0', font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#69B3AD',
fg='#FFFEFF', command=lambda: self.pressOperation('/'))
button_div.place(x=270, y=384, width=90, height=96)
4. Write the numeric function and operation function corresponding to the button
def pressC(self):
if self.flag == False:
pass
else:
self.calList.clear()
self.result_panel1.set('')
self.result_panel2.set(0)
self.flag == False
def pressBack(self):
result = self.result_panel2.get()
result = result[:-1]
self.calList.clear()
self.calList.append(result)
if self.calList[0] == '':
self.result_panel2.set(0)
else:
self.result_panel2.set(''.join(self.calList))
def pressLeft(self):
self.calList.append('(')
self.result_panel2.set(''.join(self.calList))
def pressRight(self):
self.calList.append(')')
self.result_panel2.set(''.join(self.calList))
def pressNum(self, num):
oldNum = self.result_panel2.get()
if oldNum == '0' and self.flag == False:
if num == '.':
num = '0.'
self.result_panel2.set(num)
else:
if self.flag == True and oldNum[0] != '(':
if len(self.calList) == 1:
self.result_panel2.set(num)
self.calList.clear()
self.calList.append(num)
else:
self.calList.append(num)
self.result_panel2.set(''.join(self.calList).
replace('*', '×').
replace('/', '÷'))
self.flag = False
else:
self.flag = False
newNum = oldNum + num
self.result_panel2.set(newNum)
self.calList.clear()
self.calList.append(newNum)
def pressOperation(self, operation):
num = self.result_panel2.get()
if num[-1] in '+-÷×^%':
self.format = False
if len(num) > 0:
if num[0] == '(' and len(num) != 1:
self.calList.clear()
self.calList.append('(' + num[1:])
else:
self.calList.clear()
self.calList.append(num)
self.isPressOperation = True
self.calList.append(operation)
self.result_panel2.set(''.join(self.calList).replace('/','÷').replace('*','×'))
def pressEqual(self):
if self.format == False:
self.format = True
try:
raise FError("Format error")
except FError:
self.result_panel2.set('Operator error')
self.calList.clear()
self.result_panel1.set('')
return
try:
if len(self.calList) != 0:
self.result = round(eval(''.join(self.calList).replace('÷', '/').
replace('×', '*')), 3)
self.result_panel2.set(self.result)
self.result_panel1.set(''.join(self.calList))
self.calList.clear()
self.calList.append(str(self.result))
self.flag = True
else:
self.result_panel1.set(0)
5. Define the error situation and implement the display in the panel
except SyntaxError:
self.result_panel2.set('No number')
self.calList.clear()
self.result_panel1.set('')
except ZeroDivisionError:
self.result_panel2.set('The divisor cannot be 0')
self.calList.clear()
self.result_panel1.set('')
except:
self.result_panel2.set('ERROR')
self.calList.clear()
self.result_panel1.set('')
6. Enter the loop, and implement the calculator!
if __name__ == '__main__':
calculator = MyCalculator(360, 680, 'Mycalculator')
calculator.set_label()
calculator.set_span()
root.mainloop()Display

The figure illustrates the basic functions of the calculator I designed this time. Of course, the calculator can also perform four operations between decimals.
Summary
In this assignment, I was able to successfully implement a simple calculator. In the process of completion, I learned a lot of things that I did not understand and did not learn in the previous course. I learned to use tkinter module to create Windows, design interfaces, better understand the definition of classes and objects, and combine it with code writing. I also learned the basic instructions of using Github and learned how to use GitHub to record the code, which built a good foundation for the future team work. What's more, I also learned to use the blog to record my development process, so that the task is carried out more orderly and more efficient.
Although the calculator implemented this time is relatively simple, but in the future continuous learning, the function of the calculator will be continuously strengthened and improved





















 141
141











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








