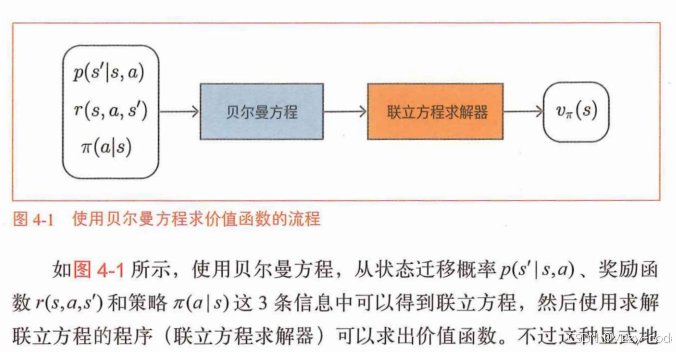

1.动态规划法(DP)进行策略评估
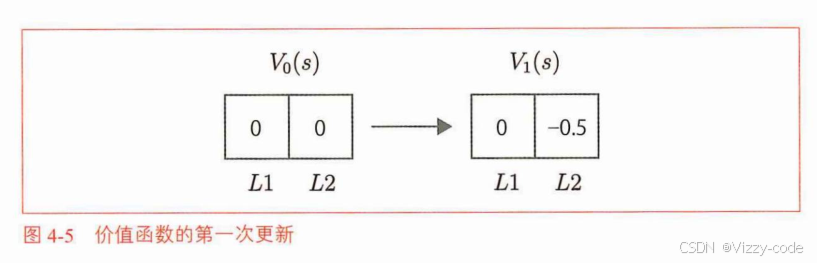
 用第k次的状态价值函数:输入s_t+1-返回价值,
更新第(k+1)次迭代的状态价值函数:输入s_t-返回价值
用第k次的状态价值函数:输入s_t+1-返回价值,
更新第(k+1)次迭代的状态价值函数:输入s_t-返回价值

动,或以0.5的概率向右移动,来采取行动。)进行评估:
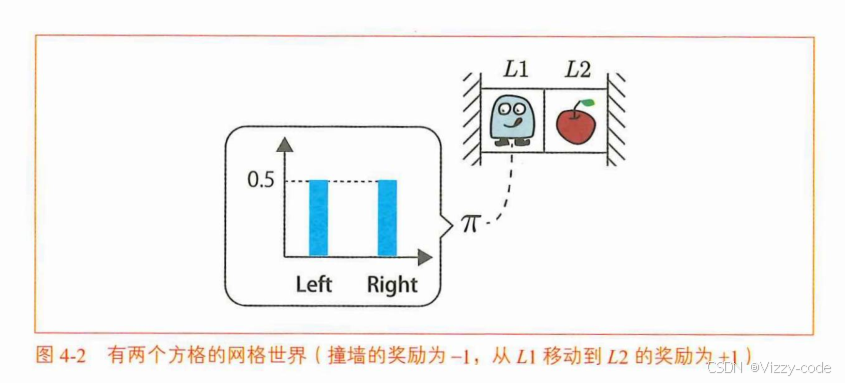


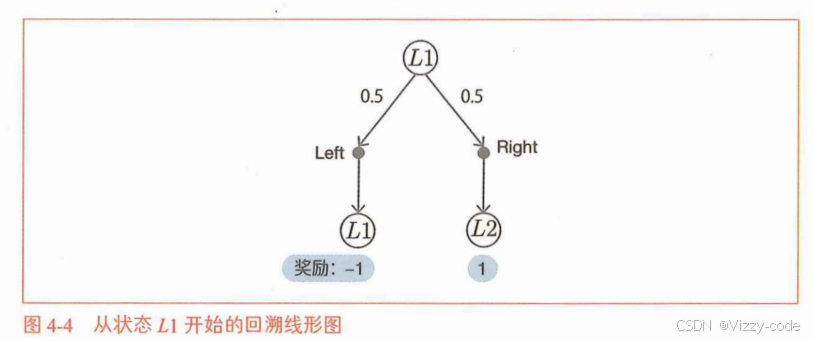
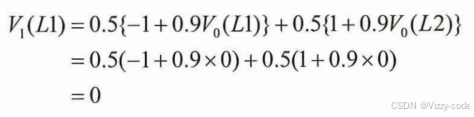


2.解决更大的问题(多个状态)
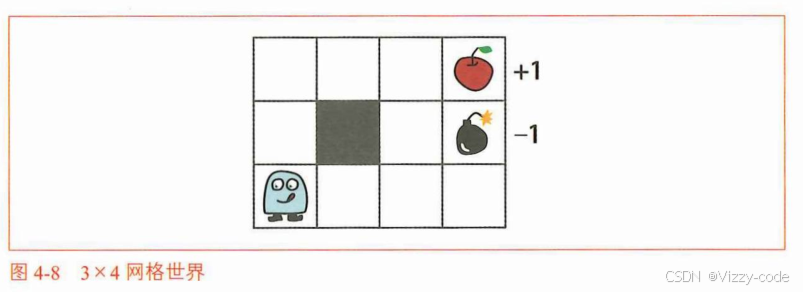

GridWorld 作为环境类,设计了一个 3x4 网格世界环境,包含奖励地图(目标状态奖励 1.0 位于 (0,3),惩罚状态 -1.0 位于 (1,3),位于墙(1,1),其他为 0)、4 个动作(上、下、左、右)和起始状态 (2,0),通过 next_state(状态迁移)、reward(提供奖励)、reset()是将游戏返回到初始状态的方法,具体来说是将智能代理返回到起始位置step(action)方法可以使智能代理执行action行动,并将时间前进一步。这两个方法实际上是被用来移动智能代理。迭代策略评估算法不使用这两个方法,因为它并不使智能代理实际采取行动。render_v 方法则利用 matplotlib 生成热力图(RdYlGn 颜色映射,负值红深、正值绿深)并显示状态价值或特殊标签(如 “Wall”、“R 1.0 (GOAL)”),原点 (0,0) 位于左上角。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class GridWorld:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化GridWorld环境"""
self.action_space = [0, 1, 2, 3] # 动作空间:0=UP, 1=DOWN, 2=LEFT, 3=RIGHT
self.action_meaning = {
0: "UP",
1: "DOWN",
2: "LEFT",
3: "RIGHT",
}
# 奖励地图,None表示墙,1.0表示目标状态,-1.0表示惩罚状态
self.reward_map = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 1.0], # R 1.0 (GOAL)
[0, None, 0, -1.0], # R -1.0
[0, 0, 0, 0]
])
self.goal_state = (0, 3) # 目标状态
self.wall_state = (1, 1) # 墙的状态
self.start_state = (2, 0) # 起始状态
self.agent_state = self.start_state # 智能代理当前状态
@property
def height(self):
"""返回网格的高度"""
return len(self.reward_map)
@property
def width(self):
"""返回网格的宽度"""
return len(self.reward_map[0])
@property
def shape(self):
"""返回网格的形状"""
return self.reward_map.shape
def actions(self):
"""返回所有可能的动作"""
return self.action_space # [0, 1, 2, 3]
def states(self):
"""生成所有可能的 states"""
for h in range(self.height):
for w in range(self.width):
yield (h, w)
def next_state(self, state, action):
"""计算下一步状态"""
action_move_map = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)] # 动作对应的移动方向
move = action_move_map[action]
next_state = (state[0] + move[0], state[1] + move[1])
ny, nx = next_state
# 检查是否超出边界或撞到墙
if nx < 0 or nx >= self.width or ny < 0 or ny >= self.height:
next_state = state
elif next_state == self.wall_state:
next_state = state
return next_state # 返回下一个状态
def reward(self, state, action, next_state):
"""根据下一个状态返回奖励"""
return self.reward_map[next_state]
def reset(self):
"""重置智能代理到起始位置"""
self.agent_state = self.start_state
return self.agent_state
def step(self, action):
"""执行动作并更新状态"""
next_state = self.next_state(self.agent_state, action)
reward = self.reward(self.agent_state, action, next_state)
self.agent_state = next_state
return next_state, reward
def render_v(self, v=None, policy=None):
"""渲染网格世界,显示价值函数和热力图效果
参数:
v (dict): 状态价值函数,键为状态坐标,值为价值
policy (dict): 策略,键为状态,值为动作
"""
# 初始化价值数组,如果v未提供,则用0填充
value_map = np.zeros(self.shape)
if v is not None:
for state in self.states():
value_map[state] = v.get(state, 0)
# 创建热力图颜色映射
plt.figure(figsize=(self.width, self.height))
plt.imshow(value_map, cmap='RdYlGn', interpolation='nearest', vmin=-1.5, vmax=1.5)
# 添加价值函数文本
for (i, j), val in np.ndenumerate(value_map):
if self.reward_map[i, j] is None: # 墙
plt.text(j, i, 'Wall', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12, weight='bold')
elif (i, j) == self.goal_state: # 目标
plt.text(j, i, f'R 1.0 (GOAL)', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
elif (i, j) == (1, 3): # 惩罚状态
plt.text(j, i, 'R -1.0', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
else:
plt.text(j, i, f'{val:.2f}', ha='center', va='center', color='black' if abs(val) < 1 else 'white',
fontsize=12)
# 设置坐标轴
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title('3 x 4 网格世界的可视化 (给定状态价值函数值)')
# 移除 invert_yaxis,确保 (0,0) 在左上角,与图片一致
plt.show()
# 示例用法
if __name__ == "__main__":
env = GridWorld()
# 随机的价值函数
V = {
(0, 0): -0.88, (0, 1): -1.17, (0, 2): -0.86, (0, 3): 0.26,
(1, 0): -0.58, (1, 1): 0, (1, 2): 0.14, (1, 3): 0.21,
(2, 0): 0.63, (2, 1): 0.10, (2, 2): -0.74, (2, 3): 0.22
}
# 渲染
env.render_v(V)
迭代策略评估的实现(互动)
首先实现只进行一个时间步的更新的方法。这里实现的eval_onestep函数接收以下4个参数。
def eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9):
"""单步价值函数更新
参数:
pi (dict): 策略,键为状态,值为动作概率字典
V (dict): 状态价值函数,键为状态,值为价值
env: GridWorld 环境对象
gamma (float): 折扣因子,默认 0.9
返回:
V (dict): 更新后的状态价值函数
"""
for state in env.states(): # ①访问各个状态
if state == env.goal_state: # ②目的地的价值函数总是为0-终止状态的未来累积奖励为 0
V[state] = 0
continue
action_probs = pi[state] # probs 是 probabilities 的缩写
new_V = 0
# ③访问各行动
for action, action_prob in action_probs.items():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
# ④新的价值函数
new_V += action_prob * (r + gamma * V[next_state])
V[state] = new_V
return V
# 主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 初始化环境
env = GridWorld()
# 定义均匀随机策略
pi = {}
for state in env.states():
pi[state] = {0: 0.25, 1: 0.25, 2: 0.25, 3: 0.25} # 每个动作概率为 0.25
# 初始化价值函数 (全为0)
V = {state: 0.0 for state in env.states()}
# 进行一次价值函数更新
V = eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9)
# 显示热力图
env.render_v(V)
代码运行的更新一次的价值函数:



from collections import defaultdict
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class GridWorld:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化GridWorld环境"""
self.action_space = [0, 1, 2, 3] # 动作空间:0=UP, 1=DOWN, 2=LEFT, 3=RIGHT
self.action_meaning = {
0: "UP",
1: "DOWN",
2: "LEFT",
3: "RIGHT",
}
# 奖励地图,None表示墙,1.0表示目标状态,-1.0表示惩罚状态
self.reward_map = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 1.0], # R 1.0 (GOAL)
[0, None, 0, -1.0], # R -1.0
[0, 0, 0, 0]
])
self.goal_state = (0, 3) # 目标状态
self.wall_state = (1, 1) # 墙的状态
self.start_state = (2, 0) # 起始状态
self.agent_state = self.start_state # 智能代理当前状态
@property
def height(self):
"""返回网格的高度"""
return len(self.reward_map)
@property
def width(self):
"""返回网格的宽度"""
return len(self.reward_map[0])
@property
def shape(self):
"""返回网格的形状"""
return self.reward_map.shape
def actions(self):
"""返回所有可能的动作"""
return self.action_space # [0, 1, 2, 3]
def states(self):
"""生成所有可能的 states"""
for h in range(self.height):
for w in range(self.width):
yield (h, w)
def next_state(self, state, action):
"""计算下一步状态"""
action_move_map = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)] # 动作对应的移动方向
move = action_move_map[action]
next_state = (state[0] + move[0], state[1] + move[1])
ny, nx = next_state
# 检查是否超出边界或撞到墙
if nx < 0 or nx >= self.width or ny < 0 or ny >= self.height:
next_state = state
elif next_state == self.wall_state:
next_state = state
return next_state # 返回下一个状态
def reward(self, state, action, next_state):
"""根据下一个状态返回奖励"""
return self.reward_map[next_state]
def reset(self):
"""重置智能代理到起始位置"""
self.agent_state = self.start_state
return self.agent_state
def step(self, action):
"""执行动作并更新状态"""
next_state = self.next_state(self.agent_state, action)
reward = self.reward(self.agent_state, action, next_state)
self.agent_state = next_state
return next_state, reward
def render_v(self, v=None, policy=None):
"""渲染网格世界,显示价值函数和热力图效果
参数:
v (dict): 状态价值函数,键为状态坐标,值为价值
policy (dict): 策略,键为状态,值为动作
"""
# 初始化价值数组,如果v未提供,则用0填充
value_map = np.zeros(self.shape)
if v is not None:
for state in self.states():
value_map[state] = v.get(state, 0)
# 创建热力图颜色映射
plt.figure(figsize=(self.width, self.height))
plt.imshow(value_map, cmap='RdYlGn', interpolation='nearest', vmin=-1.5, vmax=1.5)
# 添加价值函数文本
for (i, j), val in np.ndenumerate(value_map):
plt.text(j, i, f'{val:.2f}', ha='center', va='center', color='black' if abs(val) < 1 else 'white',
fontsize=12)
# 设置坐标轴
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title('3 x 4 网格世界的可视化 (给定状态价值函数值)')
plt.show()
def eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9):
"""单步价值函数更新
参数:
pi (dict): 策略,键为状态,值为动作概率字典
V (dict): 状态价值函数,键为状态,值为价值
env: GridWorld 环境对象
gamma (float): 折扣因子,默认 0.9
返回:
V (dict): 更新后的状态价值函数
"""
for state in env.states(): # ①访问各个状态
if state == env.goal_state: # ②目的地的价值函数总是为0
V[state] = 0
continue
action_probs = pi[state] # probs 是 probabilities 的缩写
new_V = 0
# ③访问各行动
for action, action_prob in action_probs.items():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
# ④新的价值函数
new_V += action_prob * (r + gamma * V[next_state])
V[state] = new_V
return V
def policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma, threshold=0.001):
"""策略评估直到收敛
参数:
pi (dict): 策略,键为状态,值为动作概率字典
V (dict): 状态价值函数,键为状态,值为价值
env: GridWorld 环境对象
gamma (float): 折扣因子
threshold (float): 收敛阈值,默认 0.001
返回:
V (dict): 收敛后的状态价值函数
"""
while True:
old_V = V.copy() # 更新前的价值函数
V = eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma)
# 求更新量的最大值
delta = 0
for state in V.keys():
t = abs(V[state] - old_V[state])
if delta < t:
delta = t
# 与阈值比较
if delta < threshold:
break
return V
# 主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 初始化环境
env = GridWorld()
# 定义均匀随机策略
pi = defaultdict(lambda :{0: 0.25, 1: 0.25, 2: 0.25, 3: 0.25})
# 初始化价值函数 (全为0)
V = defaultdict( lambda: 0)
'''
pi = {}
for state in env.states():
pi[state] = {0: 0.25, 1: 0.25, 2: 0.25, 3: 0.25} # 每个动作概率为 0.25
# 初始化价值函数 (全为0)
V = {state: 0.0 for state in env.states()}
'''
# 进行策略评估直到收敛
V = policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9, threshold=0.001)
# 显示热力图
env.render_v(V)为什么一定收敛? • 有限空间:只有 12 个格子,信息传完就没新东西了。 • 折扣 𝛾<1:像刹车,防止价值无限涨。 • 规则清晰:每次更新用同一个公式(贝尔曼方程)
运行结果:

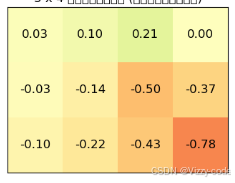
显示了随机性策略的价值函数。例如,左下角的起点的价值函数是-0.10。这意味着如果智能代理从左下角的起点随机移动,那么获得的收益的期望值将是-0.10。智能代理也可能因为随机移动而意外地得到炸弹。根据-0.10可知,得到炸弹(-1的奖励)的概率比得到苹果(+1的奖励)的概率略大一些。另外,总的来说,底部和中间的几行都是负数。这说明炸弹在这些地方的影响更大。
3.策略迭代法得到最优策略
在上节中,我们使用DP评估了策略。那是一种叫作“迭代策略评估”的算法。除了可以对策略进行评估,还可以对策略进行改进。本节将学习改进策略的方法。
首先引入如下符号:





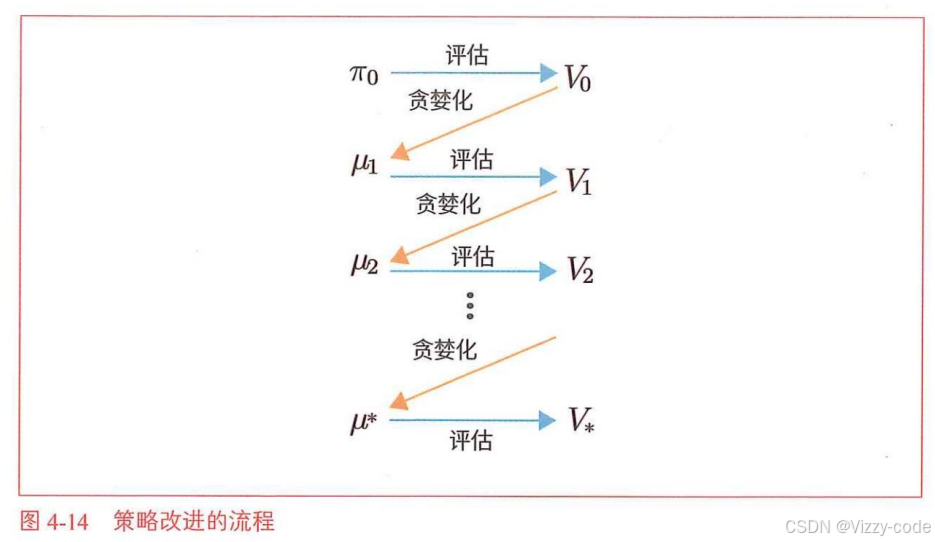


用价值函数贪婪化更新策略
 基于行动价值函数的贝尔曼最优方程:目的是根据当前状态的价值函数,选择使得
基于行动价值函数的贝尔曼最优方程:目的是根据当前状态的价值函数,选择使得![]() 最大的参数a,获得确定性的策略(在该状态下100%选择什么行动)
最大的参数a,获得确定性的策略(在该状态下100%选择什么行动)

代码(对所有的状态,遍历所有行动,记录所有行动带来的价值,选出该状态下价值最大的行动):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class GridWorld:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化GridWorld环境"""
self.action_space = [0, 1, 2, 3] # 动作空间:0=UP, 1=DOWN, 2=LEFT, 3=RIGHT
self.action_meaning = {
0: "UP",
1: "DOWN",
2: "LEFT",
3: "RIGHT",
}
# 奖励地图,None表示墙,1.0表示目标状态,-1.0表示惩罚状态
self.reward_map = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 1.0], # R 1.0 (GOAL)
[0, None, 0, -1.0], # R -1.0
[0, 0, 0, 0]
])
self.goal_state = (0, 3) # 目标状态
self.wall_state = (1, 1) # 墙的状态
self.start_state = (2, 0) # 起始状态
self.agent_state = self.start_state # 智能代理当前状态
@property
def height(self):
"""返回网格的高度"""
return len(self.reward_map)
@property
def width(self):
"""返回网格的宽度"""
return len(self.reward_map[0])
@property
def shape(self):
"""返回网格的形状"""
return self.reward_map.shape
def actions(self):
"""返回所有可能的动作"""
return self.action_space # [0, 1, 2, 3]
def states(self):
"""生成所有可能的 states"""
for h in range(self.height):
for w in range(self.width):
yield (h, w)
def next_state(self, state, action):
"""计算下一步状态"""
action_move_map = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)] # 动作对应的移动方向
move = action_move_map[action]
next_state = (state[0] + move[0], state[1] + move[1])
ny, nx = next_state
# 检查是否超出边界或撞到墙
if nx < 0 or nx >= self.width or ny < 0 or ny >= self.height:
next_state = state
elif next_state == self.wall_state:
next_state = state
return next_state # 返回下一个状态
def reward(self, state, action, next_state):
"""根据下一个状态返回奖励"""
return self.reward_map[next_state]
def reset(self):
"""重置智能代理到起始位置"""
self.agent_state = self.start_state
return self.agent_state
def step(self, action):
"""执行动作并更新状态"""
next_state = self.next_state(self.agent_state, action)
reward = self.reward(self.agent_state, action, next_state)
self.agent_state = next_state
return next_state, reward
def render_v(self, v=None, policy=None):
"""渲染网格世界,显示价值函数和热力图效果
参数:
v (dict): 状态价值函数,键为状态坐标,值为价值
policy (dict): 策略,键为状态,值为动作
"""
value_map = np.zeros(self.shape)
if v is not None:
for state in self.states():
value_map[state] = v.get(state, 0)
plt.figure(figsize=(self.width, self.height))
plt.imshow(value_map, cmap='RdYlGn', interpolation='nearest', vmin=-1.5, vmax=1.5)
for (i, j), val in np.ndenumerate(value_map):
if self.reward_map[i, j] is None:
plt.text(j, i, 'Wall', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12, weight='bold')
elif (i, j) == self.goal_state:
plt.text(j, i, f'R 1.0 (GOAL)', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
elif (i, j) == (1, 3):
plt.text(j, i, 'R -1.0', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
else:
plt.text(j, i, f'{val:.2f}', ha='center', va='center', color='black' if abs(val) < 1 else 'white', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title('3 x 4 网格世界的可视化 (给定状态价值函数值)')
plt.show()
def eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9):
"""单步价值函数更新"""
for state in env.states():
if state == env.goal_state:
V[state] = 0
continue
action_probs = pi[state]
new_V = 0
for action, action_prob in action_probs.items():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
new_V += action_prob * (r + gamma * V[next_state])
V[state] = new_V
return V
def policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma, threshold=0.001):
"""策略评估直到收敛"""
while True:
old_V = V.copy()
V = eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma)
delta = 0
for state in V.keys():
t = abs(V[state] - old_V[state])
if delta < t:
delta = t
if delta < threshold:
break
return V
def argmax(d):
"""返回字典中值最大的键"""
max_value = max(d.values())
max_key = None
for key, value in d.items():
if value == max_value:
max_key = key
break # 取第一个最大值对应的键
return max_key
def greedy_policy(V, env, gamma):
"""基于当前价值函数生成贪心策略
参数:
V (dict): 状态价值函数,键为状态,值为价值
env: GridWorld 环境对象
gamma (float): 折扣因子
返回:
pi (dict): 贪心策略,键为状态,值为动作概率字典
"""
pi = {}
for state in env.states():
# 跳过目标状态(终止状态无动作)
if state == env.goal_state:
continue
# 计算每个动作的价值
action_values = {}
for action in env.actions():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
value = r + gamma * V[next_state] # ① 计算动作价值:即时奖励 + 折扣后的未来价值
action_values[action] = value
# 选择价值最大的动作
max_action = argmax(action_values) # ② 找到最大动作价值对应的动作
# 构造贪心策略:最大价值动作概率为 1,其余为 0
action_probs = {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}
action_probs[max_action] = 1.0
pi[state] = action_probs # ③ 将策略存储到 pi 中
return pi
# 主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 初始化环境
env = GridWorld()
# 初始化价值函数 (全为0)
V = {state: 0.0 for state in env.states()}
# 定义初始均匀随机策略(排除目标状态)
pi = {}
for state in env.states():
if state != env.goal_state:
pi[state] = {0: 0.25, 1: 0.25, 2: 0.25, 3: 0.25}
# 第一次策略评估
V = policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9, threshold=0.001)
print("第一次策略评估后的价值函数:")
env.render_v(V)
# 使用贪心策略改进
pi = greedy_policy(V, env, gamma=0.9)
print("贪心策略改进后的策略:", pi)
# 第二次策略评估
V = policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9, threshold=0.001)
print("第二次策略评估后的价值函数:")
env.render_v(V)



import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class GridWorld:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化GridWorld环境"""
self.action_space = [0, 1, 2, 3] # 动作空间:0=UP, 1=DOWN, 2=LEFT, 3=RIGHT
self.action_meaning = {
0: "UP",
1: "DOWN",
2: "LEFT",
3: "RIGHT",
}
# 奖励地图,None表示墙,1.0表示目标状态,-1.0表示惩罚状态
self.reward_map = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 1.0], # R 1.0 (GOAL)
[0, None, 0, -1.0], # R -1.0
[0, 0, 0, 0]
])
self.goal_state = (0, 3) # 目标状态
self.wall_state = (1, 1) # 墙的状态
self.start_state = (2, 0) # 起始状态
self.agent_state = self.start_state # 智能代理当前状态
@property
def height(self):
"""返回网格的高度"""
return len(self.reward_map)
@property
def width(self):
"""返回网格的宽度"""
return len(self.reward_map[0])
@property
def shape(self):
"""返回网格的形状"""
return self.reward_map.shape
def actions(self):
"""返回所有可能的动作"""
return self.action_space # [0, 1, 2, 3]
def states(self):
"""生成所有可能的 states"""
for h in range(self.height):
for w in range(self.width):
yield (h, w)
def next_state(self, state, action):
"""计算下一步状态"""
action_move_map = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)] # 动作对应的移动方向
move = action_move_map[action]
next_state = (state[0] + move[0], state[1] + move[1])
ny, nx = next_state
if nx < 0 or nx >= self.width or ny < 0 or ny >= self.height:
next_state = state
elif next_state == self.wall_state:
next_state = state
return next_state # 返回下一个状态
def reward(self, state, action, next_state):
"""根据下一个状态返回奖励"""
return self.reward_map[next_state]
def reset(self):
"""重置智能代理到起始位置"""
self.agent_state = self.start_state
return self.agent_state
def step(self, action):
"""执行动作并更新状态"""
next_state = self.next_state(self.agent_state, action)
reward = self.reward(self.agent_state, action, next_state)
self.agent_state = next_state
return next_state, reward
def render_v(self, v=None, policy=None):
"""渲染网格世界,显示价值函数和热力图效果"""
value_map = np.zeros(self.shape)
if v is not None:
for state in self.states():
value_map[state] = v.get(state, 0)
plt.figure(figsize=(self.width, self.height))
plt.imshow(value_map, cmap='RdYlGn', interpolation='nearest', vmin=-1.5, vmax=1.5)
for (i, j), val in np.ndenumerate(value_map):
if self.reward_map[i, j] is None:
plt.text(j, i, 'Wall', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12, weight='bold')
elif (i, j) == self.goal_state:
plt.text(j, i, f'R 1.0 (GOAL)', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
elif (i, j) == (1, 3):
plt.text(j, i, 'R -1.0', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
else:
plt.text(j, i, f'{val:.2f}', ha='center', va='center', color='black' if abs(val) < 1 else 'white', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title('3 x 4 网格世界的可视化 (给定状态价值函数值)')
plt.show()
def eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9):
"""单步价值函数更新"""
for state in env.states():
if state == env.goal_state:
V[state] = 0
continue
if state not in pi:
continue
action_probs = pi[state]
new_V = 0
for action, action_prob in action_probs.items():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
new_V += action_prob * (r + gamma * V[next_state])
V[state] = new_V
return V
def policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma, threshold=0.001):
"""策略评估直到收敛"""
while True:
old_V = V.copy()
V = eval_onestep(pi, V, env, gamma)
delta = 0
for state in V.keys():
t = abs(V[state] - old_V[state])
if delta < t:
delta = t
if delta < threshold:
break
return V
def argmax(d):
"""返回字典中值最大的键"""
max_value = max(d.values())
max_key = None
for key, value in d.items():
if value == max_value:
max_key = key
break
return max_key
def greedy_policy(V, env, gamma):
"""基于当前价值函数生成贪心策略"""
pi = {}
for state in env.states():
if state == env.goal_state:
continue
action_values = {}
for action in env.actions():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
value = r + gamma * V[next_state]
action_values[action] = value
max_action = argmax(action_values)
action_probs = {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}
action_probs[max_action] = 1.0
pi[state] = action_probs
return pi
def policy_iter(env, gamma, threshold=0.001, is_render=False):
"""策略迭代算法
参数:
env: GridWorld 环境对象
gamma (float): 折扣因子
threshold (float): 策略评估收敛阈值
is_render (bool): 是否渲染每次迭代的价值函数
返回:
pi (dict): 最终的最优策略
"""
# 初始化策略(均匀随机策略)和价值函数
pi = {}
for state in env.states():
if state != env.goal_state:
pi[state] = {0: 0.25, 1: 0.25, 2: 0.25, 3: 0.25} # 均匀随机策略
V = {state: 0.0 for state in env.states()}
while True:
# 步骤 1:策略评估
V = policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma, threshold) # 评估当前策略的价值函数
# 步骤 2:策略改进
new_pi = greedy_policy(V, env, gamma) # 根据价值函数生成贪心策略
# 如果需要渲染,显示当前价值函数
if is_render:
env.render_v(V, pi)
# 步骤 3:检查策略是否收敛
# 比较 new_pi 和 pi 是否相同(排除目标状态)
is_same = True
for state in env.states():
if state == env.goal_state:
continue
if state not in pi or state not in new_pi:
is_same = False
break
if pi[state] != new_pi[state]:
is_same = False
break
# 更新策略
pi = new_pi
# 如果策略不再变化,退出循环
if is_same:
break
return pi
# 主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 初始化环境
env = GridWorld()
# 运行策略迭代,启用渲染
pi = policy_iter(env, gamma=0.9, threshold=0.001, is_render=True)
# 打印最终策略
print("最终策略:", pi)
# 最后一次策略评估,显示最终价值函数
V = {state: 0.0 for state in env.states()}
V = policy_eval(pi, V, env, gamma=0.9, threshold=0.001)
print("最终价值函数:")
env.render_v(V)

结果:

最优策略:
最终策略: {(0, 0): {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 1.0}, (0, 1): {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 1.0}, (0, 2): {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 1.0}, (1, 0): {0: 1.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}, (1, 1): {0: 1.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}, (1, 2): {0: 1.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}, (1, 3): {0: 1.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}, (2, 0): {0: 1.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}, (2, 1): {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 1.0}, (2, 2): {0: 1.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}, (2, 3): {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 1.0, 3: 0.0}}


进一步优化——值迭代


对每个位置S先改进,再评估(评估时的状态价值函数只更新一次)

下面是推导(对上面的数学原理做了补充-可以不看)“
”
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class GridWorld:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化GridWorld环境"""
self.action_space = [0, 1, 2, 3] # 动作空间:0=UP, 1=DOWN, 2=LEFT, 3=RIGHT
self.action_meaning = {
0: "UP",
1: "DOWN",
2: "LEFT",
3: "RIGHT",
}
# 奖励地图,None表示墙,1.0表示目标状态,-1.0表示惩罚状态
self.reward_map = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 1.0], # R 1.0 (GOAL)
[0, None, 0, -1.0], # R -1.0
[0, 0, 0, 0]
])
self.goal_state = (0, 3) # 目标状态
self.wall_state = (1, 1) # 墙的状态
self.start_state = (2, 0) # 起始状态
self.agent_state = self.start_state # 智能代理当前状态
@property
def height(self):
"""返回网格的高度"""
return len(self.reward_map)
@property
def width(self):
"""返回网格的宽度"""
return len(self.reward_map[0])
@property
def shape(self):
"""返回网格的形状"""
return self.reward_map.shape
def actions(self):
"""返回所有可能的动作"""
return self.action_space
def states(self):
"""生成所有可能的 states"""
for h in range(self.height):
for w in range(self.width):
yield (h, w)
def next_state(self, state, action):
"""计算下一步状态"""
action_move_map = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
move = action_move_map[action]
next_state = (state[0] + move[0], state[1] + move[1])
ny, nx = next_state
if nx < 0 or nx >= self.width or ny < 0 or ny >= self.height:
next_state = state
elif next_state == self.wall_state:
next_state = state
return next_state
def reward(self, state, action, next_state):
"""根据下一个状态返回奖励"""
return self.reward_map[next_state]
def reset(self):
"""重置智能代理到起始位置"""
self.agent_state = self.start_state
return self.agent_state
def step(self, action):
"""执行动作并更新状态"""
next_state = self.next_state(self.agent_state, action)
reward = self.reward(self.agent_state, action, next_state)
self.agent_state = next_state
return next_state, reward
def render_v(self, v=None, policy=None):
"""渲染网格世界,显示价值函数和热力图效果"""
value_map = np.zeros(self.shape)
if v is not None:
for state in self.states():
value_map[state] = v.get(state, 0)
plt.figure(figsize=(self.width, self.height))
plt.imshow(value_map, cmap='RdYlGn', interpolation='nearest', vmin=-1.5, vmax=1.5)
for (i, j), val in np.ndenumerate(value_map):
if self.reward_map[i, j] is None:
plt.text(j, i, 'Wall', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12, weight='bold')
elif (i, j) == self.goal_state:
plt.text(j, i, f'R 1.0 (GOAL)', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
elif (i, j) == (1, 3):
plt.text(j, i, 'R -1.0', ha='center', va='center', color='black', fontsize=12)
else:
plt.text(j, i, f'{val:.2f}', ha='center', va='center', color='black' if abs(val) < 1 else 'white', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title('3 x 4 网格世界的可视化 (给定状态价值函数值)')
plt.show()
def value_iter(env, gamma, threshold=0.001, is_render=False):
"""值迭代算法
参数:
env: GridWorld 环境对象
gamma (float): 折扣因子
threshold (float): 收敛阈值
is_render (bool): 是否渲染每次迭代的价值函数
返回:
pi (dict): 最优策略
V (dict): 最优价值函数
"""
# 初始化价值函数
V = {state: 0.0 for state in env.states()}
# 值迭代
while True:
old_V = V.copy()
delta = 0
for state in env.states():
if state == env.goal_state:
V[state] = 0
continue
# 计算每个动作的价值,选择最大值
max_value = float('-inf')
for action in env.actions():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
value = r + gamma * old_V[next_state]
if value > max_value:
max_value = value
V[state] = max_value
# 计算更新量
t = abs(V[state] - old_V[state])
if delta < t:
delta = t
# 如果需要渲染,显示当前价值函数
if is_render:
env.render_v(V)
# 检查是否收敛
if delta < threshold:
break
# 提取最优策略
pi = {}
for state in env.states():
if state == env.goal_state:
continue
action_values = {}
for action in env.actions():
next_state = env.next_state(state, action)
r = env.reward(state, action, next_state)
value = r + gamma * V[next_state]
action_values[action] = value
max_action = max(action_values, key=action_values.get)
action_probs = {0: 0.0, 1: 0.0, 2: 0.0, 3: 0.0}
action_probs[max_action] = 1.0
pi[state] = action_probs
return pi, V
# 主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 初始化环境
env = GridWorld()
# 运行值迭代,启用渲染
pi, V = value_iter(env, gamma=0.9, threshold=0.001, is_render=True)
# 打印最终策略和价值函数
print("最优策略:", pi)
print("最优价值函数:", V)
# 显示最终价值函数的热力图
env.render_v(V)

小结
我们学习了如何使用DP来获得最优策略。具体的算法是策略迭代法和价值迭代法。
策略迭代(Policy Iteration):就像你在一个迷宫里,先假设一个走法(策略),然后反复试着计算“这个走法能拿多少奖励”(价值),直到算得很准,再根据这个结果调整走法(改进策略),然后再算……反复循环,直到走法不再变。
值迭代(Value Iteration):像直接在迷宫里试着估算每个位置的“幸福指数”(价值),每次都挑最好的方向更新这个指数,直到指数稳定,最后一步决定最优走法。过程更直接,不需要中间反复调整走法。

后一章将进行蒙特卡洛算法的介绍,实现不利用状态的最优策略选择。





























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








