前言
哈夫曼树又称最优二叉树,可以对带权节点进行编码并且保证每个数据的编码都不会是其他数据的前缀,保证了编码的唯一性,因此,哈夫曼编码又称为前缀码。
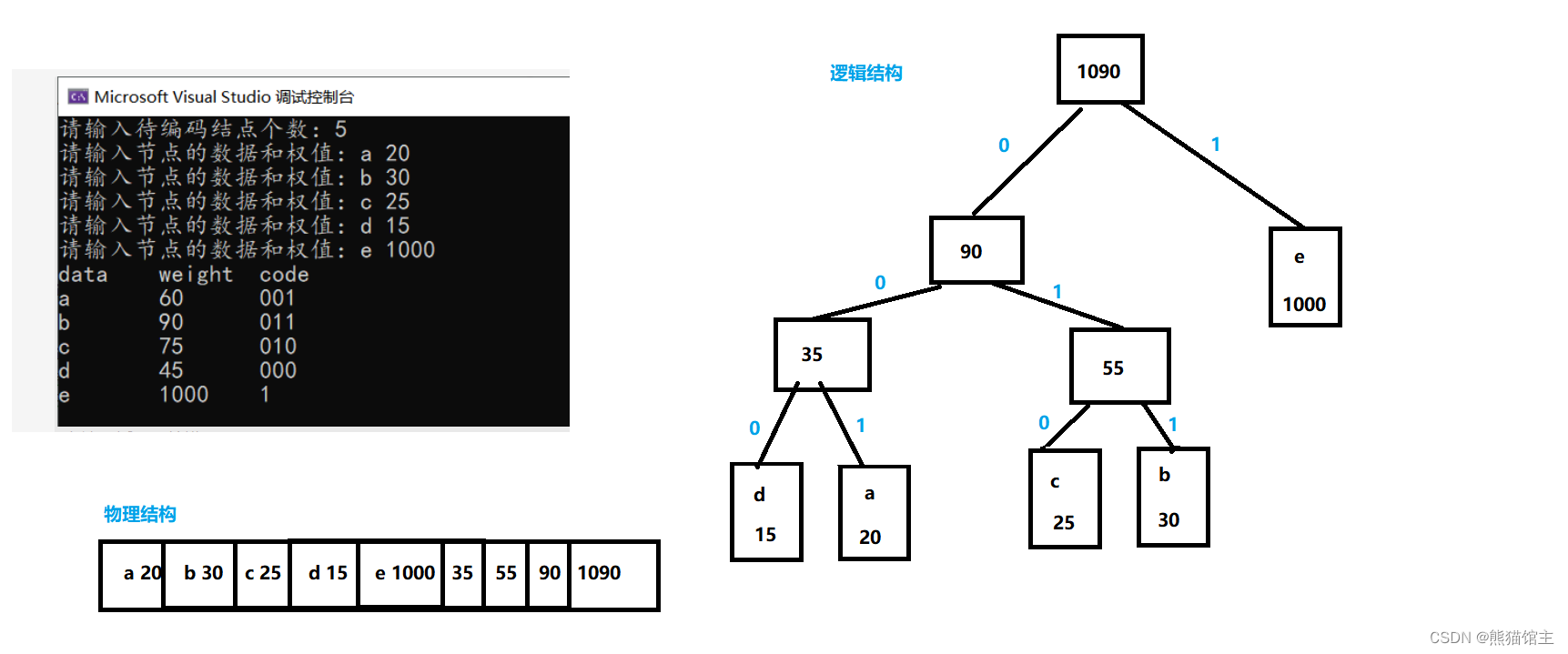
(注意:哈夫曼编码方式是可以根据要求改变的,所以按照方案1编码的数据需要按照方案1的编码要求进行解释,否则可能得不到正确的结果)
由于哈夫曼树中只有没有孩子的叶子节点和有两个孩子的二叉节点,根据n0=n2+1, 得到总节点数N:N=2*n0+1
我们可以创建哈夫曼树编码表,前n0个为待编码节点,后N-n0个为parent节点,由于是用数组存放,并且它们的位置不会改变,孩子和双亲指针都用下标表示即可。
这里我们规定:左孩子的权值要小于右孩子,并且左孩子编码为0,右孩子编码为1,之后就是连接叶子节点并且找到对应的编码即可。
1.哈夫曼树结构
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct HTNode
{
char data; // 数据
int weight; // 权值
int lchild; // 左孩子下标
int rchild; //右孩子下标
int parent; //父亲节点下标,设置父节点是为了从叶子结点向上查找获取哈夫曼编码
}HTNode, * PHT;
typedef char** PPCHAR;
2.初始化
我们这里将数据放到数组中并且在后序操作中不改变数据的位置,可以方便之后的操作。
void InitHuffmanNode(PHT hf, int con) // con为待编码节点个数
{
for (int i = 0; i < con; i++)
{
printf("请输入节点的数据和权值:");
scanf("%c %d", &hf[i].data, &hf[i].weight); // 前con个节点为待编码节点
getchar();
hf[i].lchild = hf[i].rchild = hf[i].parent = -1; // 初始化为空,此时每个节点都是独立的
}
// 后面的节点可以在连接时赋值
}
3.构造哈夫曼树
每次选出两个 权值最小 并且 没有父节点 的节点连接。
void CreateHuffman(PHT& hf, int con)
{
for (int i = 0; i < con - 1; i++) // 连接次数
{
int minsub1 = 0; // 第一个节点的下标
int minweight1 = INT_MAX; // 第一个节点的权值,找到比它小的就交换
int minsub2 = 0;
int minweight2 = INT_MAX;
for (int j = 0; j < con + i; j++) // 选取节点时的范围,由于会不断设置父节点,所以每连接一次节点总数多一个
{
if (hf[j].parent == -1 && hf[j].weight < minweight1) // 没有父节点,权值小
{
minweight1 = hf[j].weight;
minsub1 = j;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < con + i; j++) // 选取第二个节点
{
if (hf[j].parent == -1 && j != minsub1 && hf[j].weight < minweight2) // 没有父节点,和第一个不重复,权值小
{
minweight2 = hf[j].weight;
minsub2 = j;
}
}
// 连接
hf[con + i].weight = hf[minsub1].weight + hf[minsub2].weight; // 赋权值
hf[con + i].lchild = minsub1; // 连接两个子节点
hf[con + i].rchild = minsub2;
hf[con + i].parent = -1;
hf[minsub1].parent = con + i; // 为子节点赋值父节点
hf[minsub2].parent = con + i;
}
}
4. 获取Huffman编码
我们要找到各个节点的哈夫曼编码,就需要先找到该节点,然后从该节点往上走到根节点,记录下走过的路径,就是它的哈夫曼编码。
void GetHuffmanCode(PHT hf, PPCHAR str, int* weight, int con)
{
char* tmp = (char*)malloc(con); // 记录每个叶子结点的编码
if (tmp == NULL)
exit(-1);
tmp[con - 1] = '\0'; // 字符串结束
// 叶子结点位置就是前con个
for (int i = 0; i < con; i++)
{
int t = con - 2; // tmp有效下标
int child = i; // 从叶子结点向上遍历
int parent = hf[i].parent;
weight[i] = hf[i].weight; // 权值
int len = 0; // 记录经过的路径个数
while (parent != -1)
{
len++;
if (hf[parent].lchild == child) // 左孩子编码为‘0’,右孩子编码为‘1’
tmp[t--] = '0';
else
tmp[t--] = '1';
child = parent; // 孩子和父亲都向上走,更新下标
parent = hf[parent].parent;
}
weight[i] *= len; // 该节点的WPL
str[i] = (char*)malloc(len + 1); // 编码和 '\0' 总数
if (str[i] == NULL)
exit(-1);
strcpy(str[i], tmp + t + 1); // 将有效字符拷贝过去
}
free(tmp);
}
整体代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct HTNode
{
char data; // 数据
int weight; // 权值
int lchild; // 左孩子下标
int rchild; //右孩子下标
int parent; //父亲节点下标,设置父节点是为了从叶子结点向上查找获取哈夫曼编码
}HTNode, * PHT;
typedef char** PPCHAR;
// 建立哈夫曼编码表
void InitHuffmanNode(PHT hf, int con)
{
for (int i = 0; i < con; i++)
{
printf("请输入节点的数据和权值:");
scanf("%c %d", &hf[i].data, &hf[i].weight); // 前con个节点为待编码节点
getchar();
hf[i].lchild = hf[i].rchild = hf[i].parent = -1; // 初始化为空,此时每个节点都是独立的
}
// 后面的节点可以在连接时赋值
}
// 每次选出两个 权值最小 并且 没有父节点 的节点连接
void CreateHuffman(PHT hf, int con)
{
for (int i = 0; i < con - 1; i++) // 连接次数
{
int minsub1 = 0; // 第一个节点的下标
int minweight1 = INT_MAX; // 第一个节点的权值,找到比它小的就交换
int minsub2 = 0;
int minweight2 = INT_MAX;
for (int j = 0; j < con + i; j++) // 选取节点时的范围,由于会不断设置父节点,所以每连接一次节点总数多一个
{
if (hf[j].parent == -1 && hf[j].weight < minweight1) // 没有父节点,权值小
{
minweight1 = hf[j].weight;
minsub1 = j;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < con + i; j++) // 选取第二个节点
{
if (hf[j].parent == -1 && j != minsub1 && hf[j].weight < minweight2) // 没有父节点,和第一个不重复,权值小
{
minweight2 = hf[j].weight;
minsub2 = j;
}
}
// 连接
hf[con + i].weight = hf[minsub1].weight + hf[minsub2].weight; // 赋权值
hf[con + i].lchild = minsub1; // 连接两个子节点
hf[con + i].rchild = minsub2;
hf[con + i].parent = -1;
hf[minsub1].parent = con + i; // 为子节点赋值父节点
hf[minsub2].parent = con + i;
}
}
// 获取Huffman编码
void GetHuffmanCode(PHT hf, PPCHAR str, int* weight, int con)
{
char* tmp = (char*)malloc(con); // 记录每个叶子结点的编码
if (tmp == NULL)
exit(-1);
tmp[con - 1] = '\0'; // 字符串结束
// 叶子结点位置就是前con个
for (int i = 0; i < con; i++)
{
int t = con - 2; // tmp有效下标
int child = i; // 从叶子结点向上遍历
int parent = hf[i].parent;
weight[i] = hf[i].weight; // 权值
int len = 0; // 记录经过的路径个数
while (parent != -1)
{
len++;
if (hf[parent].lchild == child) // 左孩子编码为‘0’,右孩子编码为‘1’
tmp[t--] = '0';
else
tmp[t--] = '1';
child = parent; // 孩子和父亲都向上走,更新下标
parent = hf[parent].parent;
}
weight[i] *= len; // 该节点的WPL
str[i] = (char*)malloc(len + 1); // 编码和 '\0' 总数
if (str[i] == NULL)
exit(-1);
strcpy(str[i], tmp + t + 1); // 将有效字符拷贝过去
}
free(tmp);
}
void HuffmanCodePrint(PHT hf, PPCHAR str, int* weight, int con)
{
printf("data\tweight\tcode\n");
int i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < con; i++)
{
printf("%c\t%d\t%s\n", hf[i].data, weight[i], str[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
PHT hf; // 节点数组
PPCHAR str; // 二级指针,字符数组数组
int* weight; // 存放每个叶子节点的带权路径长度
int con = 0; // 叶子节点个数
printf("请输入待编码结点个数:");
scanf("%d", &con);
getchar(); //吃掉换行
hf = (PHT)malloc(sizeof(HTNode) * (con * 2 - 1));
if (hf == NULL)
exit(-1);
str = (PPCHAR)malloc(sizeof(char*) * con);
if (str == NULL)
exit(-1);
weight = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * con);
if (weight == NULL)
exit(-1);
InitHuffmanNode(hf, con);
CreateHuffman(hf, con);
GetHuffmanCode(hf, str, weight, con);
HuffmanCodePrint(hf, str, weight, con);
free(hf);
for (int i = 0; i < con; i++)
free(str[i]);
free(str);
free(weight);
return 0;
}
运行实例:






















 52
52











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








