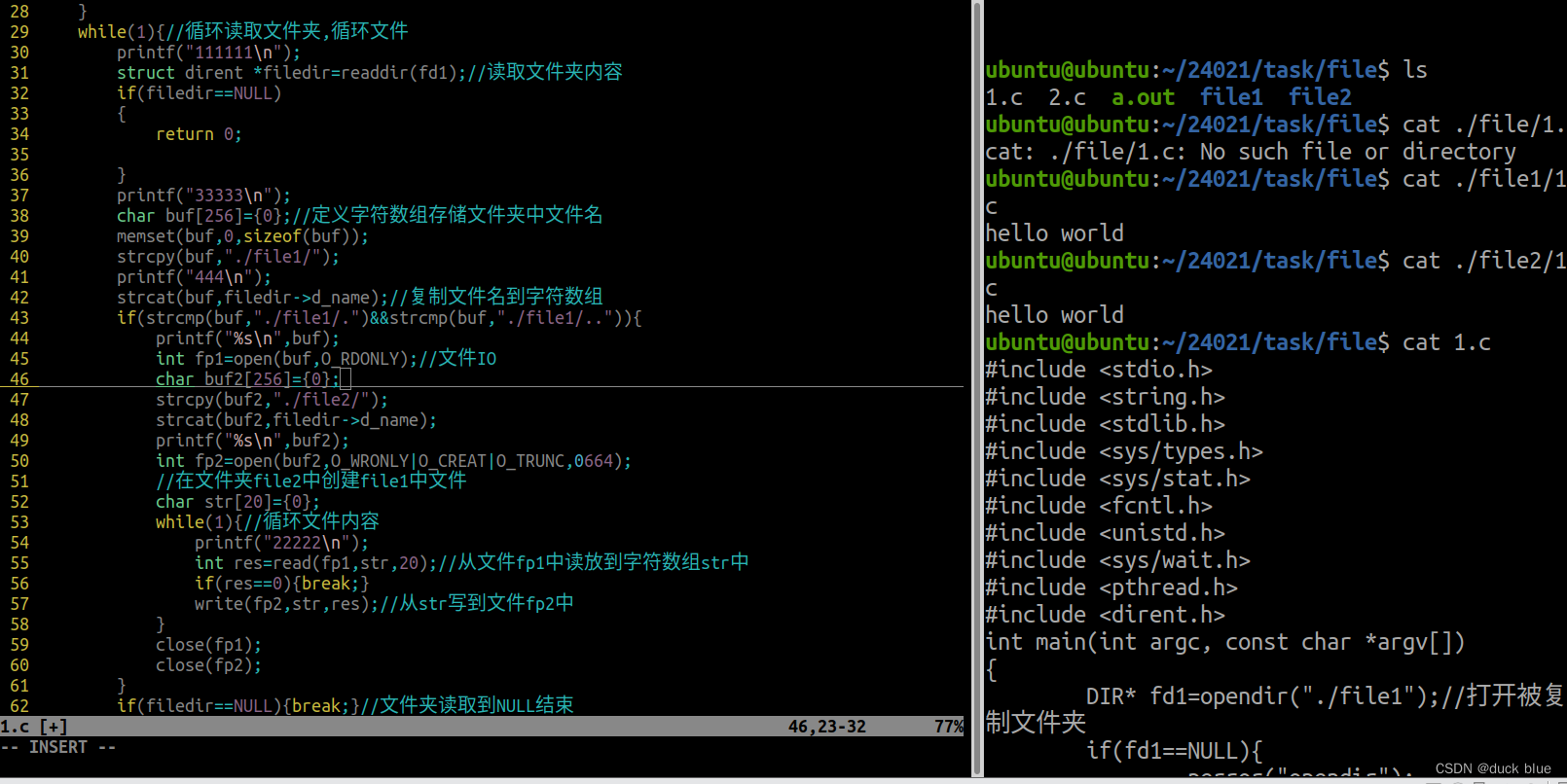
1:实现文件夹的拷贝功能
注意判断被拷贝的文件夹是否存在,如果不存在则提前创建,创建文件夹的函数为 mkdir
不考虑递归拷贝的问题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
DIR* fd1=opendir("./file1");//打开被复制文件夹
if(fd1==NULL){
perror("opendir");
if(mkdir("./file1",S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG|S_IRWXO)==-1){
perror("mkdir");
return -1;
}
}
DIR* fd2=opendir("./file2");//打开目的文件夹
if(fd2==NULL){
perror("opendir");
if(mkdir("./file2",S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG|S_IRWXO)==-1){
perror("mkdir");
return -1;
}
}
while(1){//循环读取文件夹,循环文件
printf("111111\n");
struct dirent *filedir=readdir(fd1);//读取文件夹内容
if(filedir==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
printf("33333\n");
char buf[256]={0};//定义字符数组存储文件夹中文件名
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
strcpy(buf,"./file1/");
printf("444\n");
strcat(buf,filedir->d_name);//复制文件名到字符数组
if(strcmp(buf,"./file1/.")&&strcmp(buf,"./file1/..")){
printf("%s\n",buf);
int fp1=open(buf,O_RDONLY);//文件IO
char buf2[256]={0};
strcpy(buf2,"./file2/");
strcat(buf2,filedir->d_name);
printf("%s\n",buf2);
int fp2=open(buf2,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);
//在文件夹file2中创建file1中文件
char str[20]={0};
while(1){//循环文件内容
printf("22222\n");
int res=read(fp1,str,20);//从文件fp1中读放到字符数组str中
if(res==0){break;}
write(fp2,str,res);//从str写到文件fp2中
}
close(fp1);
close(fp2);
}
if(filedir==NULL){break;}//文件夹读取到NULL结束
}
closedir(fd1);
closedir(fd2);
return 0;
}
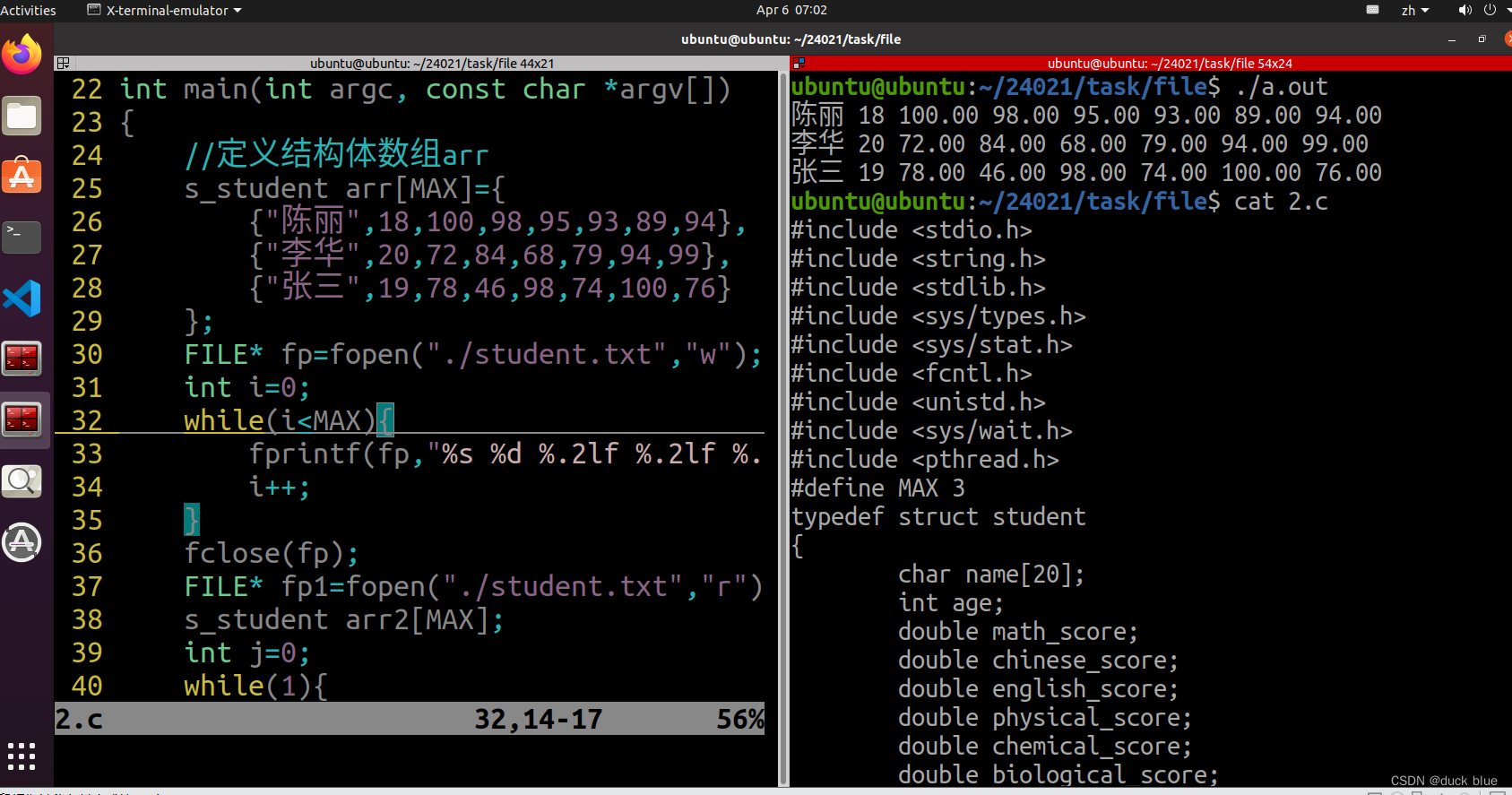
2:有如下结构体 struct Student{
char name[20];
int age;
double math_score;
double chinese_score;
double english_score;
double physical_score;
double chemical_score;
double biological_score; } 申请一个该结构体数组,使用 fprintf / fscanf,将该结构体数组中的所有数据,写入文件中,然后重新加载到数组中 同样的操作,使用fwrite/fread 和 write/read再做一遍
一:用fprintf和fscanf写
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define MAX 3
typedef struct student
{
char name[20];
int age;
double math_score;
double chinese_score;
double english_score;
double physical_score;
double chemical_score;
double biological_score;
}s_student;
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//定义结构体数组arr
s_student arr[MAX]={
{"陈丽",18,100,98,95,93,89,94},
{"李华",20,72,84,68,79,94,99},
{"张三",19,78,46,98,74,100,76}
};
FILE* fp=fopen("./student.txt","w");
int i=0;
while(i<MAX){
fprintf(fp,"%s %d %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf\n",arr[i].name,arr[i].age,arr[i].math_score,arr[i].chinese_score,arr[i].english_score,arr[i].physical_score,arr[i].chemical_score,arr[i].biological_score);
i++;
}
fclose(fp);
FILE* fp1=fopen("./student.txt","r");
s_student arr2[MAX];
int j=0;
while(1){
int res=fscanf(fp1,"%s %d %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf\n",arr2[j].name,&arr2[j].age,&arr2[j].math_score,&arr2[j].chinese_score,&arr2[j].english_score,&arr2[j].physical_score,&arr2[j].chemical_score,&arr2[j].biological_score);
if(res<0){break;}
printf("%s %d %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf\n",arr2[j].name,arr2[j].age,arr2[j].math_score,arr2[j].chinese_score,arr2[j].english_score,arr2[j].physical_score,arr2[j].chemical_score,arr2[j].biological_score);
j++;
}
fclose(fp1);
return 0;
}
二:用read和write写
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
// 定义Student结构体
struct Student {
char name[20];
int age;
double math_score;
double chinese_score;
double english_score;
double physical_score;
double chemical_score;
double biological_score;
};
int main() {
// 定义并初始化一个Student结构体数组
struct Student students[3] = {
{"Alice", 20, 85.5, 90.0, 88.0, 75.0, 80.0, 82.0},
{"Bob", 21, 90.0, 85.0, 80.0, 70.0, 75.0, 77.0},
{"Charlie", 19, 80.0, 88.0, 75.0, 65.0, 70.0, 72.0}
};
// 打开文件用于写入
int fd = open("students.bin", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("Error opening file for writing");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 将结构体数组写入文件
size_t size = sizeof(struct Student);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
ssize_t written = write(fd, &students[i], size);
if (written != size) {
perror("Error writing to file");
close(fd);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
// 关闭文件
close(fd);
// 定义另一个Student结构体数组用于读取数据
struct Student new_students[3];
// 打开同一个文件用于读取
fd = open("students.bin", O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("Error opening file for reading");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 从文件中读取数据到另一个结构体数组
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
ssize_t read_bytes = read(fd, &new_students[i], size);
if (read_bytes != size) {
perror("Error reading from file");
close(fd);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
// 关闭文件
close(fd);
// 打印读取的数据以验证
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
printf("Name: %s, Age: %d\n", new_students[i].name, new_students[i].age);
// 打印其他分数...
}
return 0;
}
3:创建一对父进程,在父进程能够向子进程发送消息的基础上发 同时子进程也能够向父进程发送消息
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
int main() {
int fd_to_child[2]; // 父进程到子进程的管道
int fd_to_parent[2]; // 子进程到父进程的管道
pid_t pid;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
// 创建两个管道
if (pipe(fd_to_child) == -1 || pipe(fd_to_parent) == -1) {
perror("pipe");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 创建子进程
pid = fork();
if (pid == -1) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
// 关闭父进程到子进程的写端和子进程到父进程的读端
close(fd_to_child[1]);
close(fd_to_parent[0]);
// 从父进程接收消息
read(fd_to_child[0], buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
printf("Child received: %s\n", buffer);
// 向父进程发送消息
const char *msg_to_parent = "Hello from child!";
write(fd_to_parent[1], msg_to_parent, strlen(msg_to_parent) + 1);
// 关闭管道文件描述符
close(fd_to_child[0]);
close(fd_to_parent[1]);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { // 父进程
// 关闭父进程到子进程的读端和子进程到父进程的写端
close(fd_to_child[0]);
close(fd_to_parent[1]);
// 向子进程发送消息
const char *msg_to_child = "Hello from parent!";
write(fd_to_child[1], msg_to_child, strlen(msg_to_child) + 1);
// 从子进程接收消息
read(fd_to_parent[0], buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
printf("Parent received: %s\n", buffer);
// 关闭管道文件描述符
close(fd_to_child[1]);
close(fd_to_parent[0]);
// 等待子进程结束
wait(NULL);
}
return 0;
}























 252
252











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








