一、编解码原理
编码原理 :
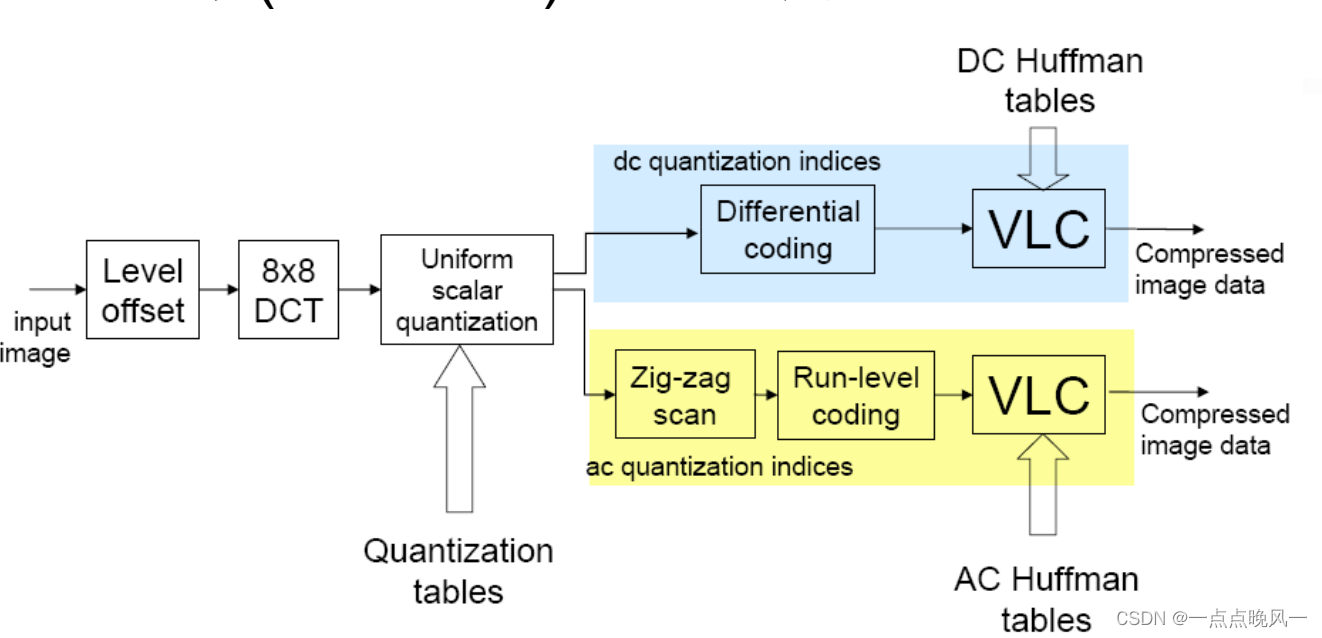
(1)零偏置电平下移(Level Offset)
对于灰度级为2^n 的像素,通过减去2^(n-1),将无符号整数变为有符号数,即值域变为正负对称。将绝对值大的数出现的概率大大减小,提高编码效率。
(2)离散余弦变换(8×8 DCT)
先将图像分为8×8的像块,如果图像的宽(高)不是8的整数倍,使用图像边缘像素填充,以不改变频谱分布。然后对每一个子块进行DCT(Discrete Cosine Transform)。DCT变换使用下式计算,C为变换核矩阵:
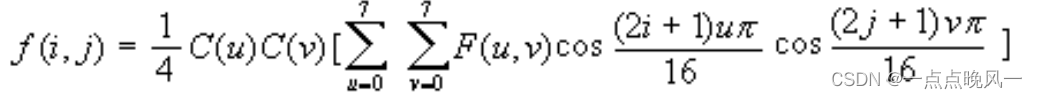
实现能量集中和去相关,便于去除空间冗余,提高编码效率。DCT是一种无损变换,不压缩图像(输出的是系数)这样做是在为下一步的量化做准备。
(3)量化(Quantization)
量化是编码流程中唯一会引入误差也是唯一会带来压缩效果的步骤,决定压缩质量,因此是JPEG压缩编码算法的核心。JPEG标准中采用中平型均匀量化,输入DCT系数,输出量化系数。
量化表有建议量化表和真正使用的量化表之分。
- 建议量化表:基于人的生理感知阈值实验,对人眼敏感的低频部分采取较细的量化,对不太敏感的高频部分采取较粗的量化,减少了视觉冗余。
- 真正的量化表:
- 质量因子≤ 50:缩放因子= 50 / 质量因子
- 质量因子> 50:缩放因子 = 2 – 质量 因子/ 50
(4)DC系数——差分编码(Differential indices)
8×8像块经过DCT后得到的DC系数有两个特点:一是系数的值较大;二是相邻像块的DC系数存在相关性(即存在冗余)。根据这个特点,JPEG标准采用了DPCM(差分脉冲编码调制),以对相邻图像块之间量化DC系数的差值DIFF进行编码:
(5) AC系数——之字形扫描和游程编码(Zig-Zag+RLE)
- 之字形扫描
经过DCT变换后,AC系数大多集中在左上角的低频分量区。因此采用Z字形按频率的高低顺序读出,可以出现很多连零的情况,便于使用RLE(Run Length Encoding,游程编码),若最后的数据均为0,则直接给出EOB(End of Block)。
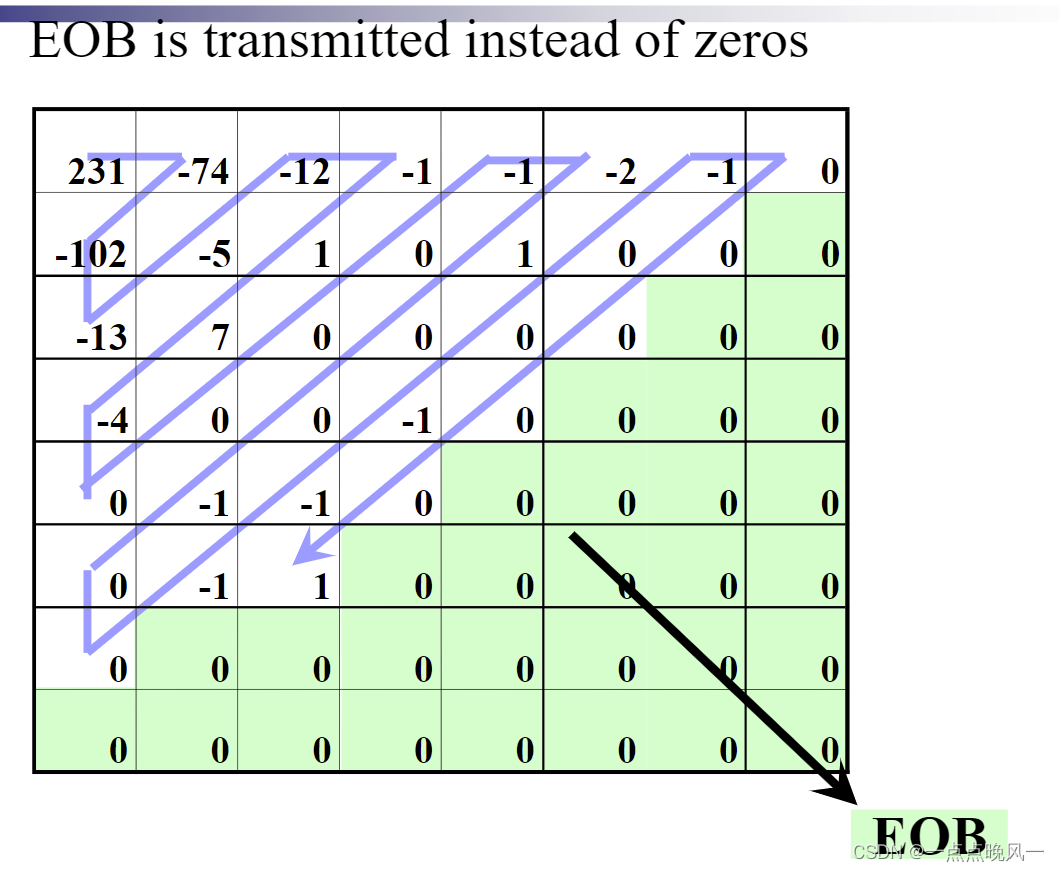
- 游程编码
当遇到很多连续的0时,为缩短数据长度,编码【非零系数level和它之前0的个数run】,(Run,level)。
如:0,-2,0,0,3,2,-4–>游程编码:(1,-2),(2,3),(0,2),(0,-4),EOB
(6)Huffman编码
对DC系数DPCM的结果和AC系数RLE的结果进行Huffman编码:
- 类别ID采用一元码编码。
- 类内索引采用定长码编码。共有亮度DC、亮度AC、色差DC、色差AC四张码表。
解码原理
① 解码huffman数据
② 解码DC差值
③ 重构量化后的系数
④ DCT逆变换
⑤ 丢弃填充的行/列
⑥ 反0偏置
⑦ 对丢弃的CbCr分量进行插值
⑧ YCbCr–>RGB
二、JPEG文件格式
JPEG文件以segment的形式组织,其中每个segment以一个marker开始(marker均以0xFF+一个marker的标识符),随后为2字节的marker长度(不包含marker的起始两字节)和对应的payload(SOI和EOI marker只有2字节的标识符)。
(1)Segment 的组织形式
JPEG 在文件中以 Segment 的形式组织,它具有以下特点:
- 均以 0xFF 开始,后跟 1 byte 的 Marker 和 2 byte 的 Segment length(包含表示Length 本身所占用的 2 byte,不含“0xFF” + “Marker” 所占用的 2 byte);
- 采用 Motorola 序(相对于 Intel 序),即保存时高位在前,低位在后;
- Data 部分中,0xFF 后若为 0x00,则跳过此字节不予处理;
SOI,Start of Image,图像开始
APP0,Application,应用程序保留标记0
DQT,Define Quantization Table,定义量化表
SOF0,Start of Frame,帧图像开始
DHT,Define Huffman Table,定义哈夫曼表
SOS,Start of Scan,扫描开始 12字节
EOI,End of Image,图像结束 2字节
- SOI ,Start of Image, 图像开始
标记代码 2字节 固定值0xFFD8 - EOI,End of Image, 图像结束 2字节
标记代码 2字节 固定值0xFFD9
标记代码 2字节 固定值0xFFE0
包含9个具体字段:
- 数据长度 2字节 9个字段的总长度
- 标识符 5字节 固定值0x4A46494600,即字符串“JFIF0”
- 版本号 2字节 一般是0x0102,表示JFIF的版本号1.2
- X和Y的密度单位 1字节 只有三个值可选 0:无单位;1:点数/英寸;2:点数/厘米
- X方向像素密度 2字节 取值范围未知
- Y方向像素密度 2字节 取值范围未知
- 缩略图水平像素数目 1字节 取值范围未知
- 缩略图垂直像素数目 1字节 取值范围未知
- 缩略图RGB位图 长度可能是3的倍数 缩略图RGB位图数据
- 标记代码 2字节 固定值0xFFDB
- 包含9个具体字段:
a.数据长度 2字节 字段a和多个字段b的总长度
b.量化表 数据长度-2字节
a) 精度及量化表ID 1字节
高4位:精度,只有两个可选值 0:8位;1:16位
低4位:量化表ID,取值范围为0~3
b) 表项 (64×(精度+1))字节
例如8位精度的量化表,其表项长度为64×(0+1)=64字节 - 本标记段中,字段b可以重复出现,表示多个量化表,但最多只能出现4次。
- 标记代码 2字节 固定值0xFFC0
- 包含9个具体字段:
a.数据长度 2字节 ①~⑥六个字段的总长度
b.精度 1字节 每个数据样本的位数
通常是8位,一般软件都不支持 12位和16位
c.图像高度 2字节 图像高度(单位:像素)
d.图像宽度 2字节 图像宽度(单位:像素)
e.颜色分量数 1字节 只有3个数值可选
1:灰度图;3:YCrCb或YIQ;4:CMYK
而JFIF中使用YCrCb,故这里颜色分量数恒为3
f.颜色分量信息 颜色分量数×3字节(通常为9字节)
a)颜色分量ID 1字节
b)水平/垂直采样因子 1字节
高4位:水平采样因子 低4位:垂直采样因子
c) 量化表 1字节 当前分量使用的量化表的ID
-
标记代码 2字节 固定值0xFFC4
-
包含2个具体字段:
a. 数据长度 2字节
b.huffman表 数据长度-2字节 -
表ID和表类型 1字节
高4位:类型,只有两个值可选 0:DC直流;1:AC交流
低4位:哈夫曼表ID,注意,DC表和AC表分开编码 -
不同位数的码字数量 16字节
-
编码内容 16个不同位数的码字数量之和(字节)
本标记段中,字段b可以重复出现(一般4次),也可以只出现1次。
-
标记代码 2字节 固定值0xFFDA
-
包含2个具体字段:
a.数据长度 2字节 a~d两个字段的总长度
b.颜色分量数 1字节 应该和SOF中的字段⑤的值相同,即:1:灰度图是;3: YCrCb或YIQ;4:CMYK。
c.颜色分量信息
a) 颜色分量ID 1字节
b) 直流/交流系数表号 1字节
高4位:直流分量使用的哈夫曼树编号
低4位:交流分量使用的哈夫曼树编号
d.压缩图像数据
a)谱选择开始 1字节 固定值0x00
b)谱选择结束 1字节 固定值0x3F
c)谱选择 1字节 在基本JPEG中总为00
三、JPEG解码流程
(1)读取文件
(2)解析segmentmarker:依次解析出SOI、APP0、DCT、SCF0、DHT、SOS、EOI
解析SOI
解析APP0
- 检查标识“JFIF”及版本
- 得到一些参数
解析DCT
- 得到量化表长度(可能包含多张量化表)
- 得到量化表的精度
- 得到及检查量化表的序号(只能是 0-3)
- 得到量化表内容(64 个数据)
解析SCF0
- 得到每个 sample 的比特数、长宽、颜色分量数
- 得到每个颜色分量的 ID、水平采样因子、垂直采样因子、使用的量化表序号(与 DQT 中序号对应)
- 解析 DHT
解析DHT
- 得到 Huffman 表的类型(AC、DC)、序号
- 依据数据重建 Huffman 表
解析SOS
- 得到解析每个颜色分量的 DC、AC 值所使用的 Huffman 表序号(与 DHT 中序号对应)
(3)依据每个分量的水平采样、垂直采样因子计算MCU(微控制单元,即RAM,即要开辟的图像内存)的大小,并得到每个MCU中8*8宏块的个数。
(4)对每个MCU解码:对每个宏块进行huffman解码得到DCT系数,进行IDCT得到变换之前的数据。
(5)解析到EOI,解码结束
(6)将得到的Y、Cb、Cr转换成需要的色彩空间并保存。
四、JPEG解码流程及核心代码说明
1. 分层结构
JPEG压缩编码算法的一大特点就是采用了分层结构设计的思想,下面说明三个主要结构体的设计意图:
(1)struct huffman_table:存储Huffman码表。
/* tinyjpeg-internal.h */
struct huffman_table
{
/* Fast look up table, using HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS bits we can have directly the symbol,
* if the symbol is <0, then we need to look into the tree table */
short int lookup[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];
/* code size: give the number of bits of a symbol is encoded */
unsigned char code_size[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];
/* some place to store value that is not encoded in the lookup table
* FIXME: Calculate if 256 value is enough to store all values
*/
uint16_t slowtable[16-HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS][256];
};
(2)struct component:储存当前8×8像块中有关解码的信息。
/* tinyjpeg-internal.h */
struct component
{
unsigned int Hfactor; // 水平采样因子
unsigned int Vfactor; // 垂直采样因子
float* Q_table; // 指向该8×8块使用的量化表
struct huffman_table *AC_table; // 指向该块使用的AC Huffman表
struct huffman_table *DC_table; // 指向该块使用的DC Huffman表
short int previous_DC; // 前一个块的直流DCT系数
short int DCT[64]; // DCT系数数组
#if SANITY_CHECK
unsigned int cid;
#endif
};
(3)struct jdec_private:JPEG数据流结构体,用于存储JPEG图像宽高、数据流指针、Huffman码表等内容,并包含struct huffman_table和struct component。
/* tinyjpeg-internal.h */
struct jdec_private
{
/* Public variables */
uint8_t *components[COMPONENTS]; /* 分别指向YUV三个分量的三个指针 */
unsigned int width, height; /* 图像宽高 */
unsigned int flags;
/* Private variables */
const unsigned char *stream_begin, *stream_end;
unsigned int stream_length;
const unsigned char *stream; /* 指向当前数据流的指针 */
unsigned int reservoir, nbits_in_reservoir;
struct component component_infos[COMPONENTS];
float Q_tables[COMPONENTS][64]; /* quantization tables */
struct huffman_table HTDC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* DC huffman tables */
struct huffman_table HTAC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* AC huffman tables */
int default_huffman_table_initialized;
int restart_interval;
int restarts_to_go; /* MCUs left in this restart interval */
int last_rst_marker_seen; /* Rst marker is incremented each time */
/* Temp space used after the IDCT to store each components */
uint8_t Y[64*4], Cr[64], Cb[64];
jmp_buf jump_state;
/* Internal Pointer use for colorspace conversion, do not modify it !!! */
uint8_t *plane[COMPONENTS];
};
2. 解码整体流程
/* 读取JPEG文件,进行解码,并存储结果 */
int convert_one_image(const char *infilename, const char *outfilename, int output_format)
{
FILE *fp;
unsigned int length_of_file; // 文件大小
unsigned int width, height; // 图像宽、高
unsigned char *buf; // 缓冲区
struct jdec_private *jdec;
unsigned char *components[3];
/* 将JPEG读入缓冲区 */
fp = fopen(infilename, "rb");
if (fp == NULL)
exitmessage("Cannot open filename\n");
length_of_file = filesize(fp);
buf = (unsigned char *)malloc(length_of_file + 4);
if (buf == NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory for loading file\n");
fread(buf, length_of_file, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
/* Decompress it */
jdec = tinyjpeg_init(); // 初始化
if (jdec == NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory to alloc the structure need for decompressing\n");
/* 解析JPEG文件头 */
if (tinyjpeg_parse_header(jdec, buf, length_of_file)<0)
exitmessage(tinyjpeg_get_errorstring(jdec));
/* 计算图像宽高 */
tinyjpeg_get_size(jdec, &width, &height);
snprintf(error_string, sizeof(error_string),"Decoding JPEG image...\n");
if (tinyjpeg_decode(jdec, output_format) < 0) // 解码实际数据
exitmessage(tinyjpeg_get_errorstring(jdec));
/*
* Get address for each plane (not only max 3 planes is supported), and
* depending of the output mode, only some components will be filled
* RGB: 1 plane, YUV420P: 3 planes, GREY: 1 plane
*/
tinyjpeg_get_components(jdec, components);
/* 按照指定的输出格式保存输出文件 */
switch (output_format)
{
case TINYJPEG_FMT_RGB24:
case TINYJPEG_FMT_BGR24:
write_tga(outfilename, output_format, width, height, components);
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_YUV420P:
write_yuv(outfilename, width, height, components);
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_GREY:
write_pgm(outfilename, width, height, components);
break;
}
/* Only called this if the buffers were allocated by tinyjpeg_decode() */
tinyjpeg_free(jdec);
/* else called just free(jdec); */
free(buf);
return 0;
}
3. 解析JPEG文件头
int tinyjpeg_parse_header(struct jdec_private *priv, const unsigned char *buf, unsigned int size)
{
int ret;
/* Identify the file */
if ((buf[0] != 0xFF) || (buf[1] != SOI)) // JPEG文件必须以SOI marker为起始,否则不是合法的JPEG文件
snprintf(error_string, sizeof(error_string),"Not a JPG file ?\n");
priv->stream_begin = buf+2; // 跳过标识符
priv->stream_length = size-2;
priv->stream_end = priv->stream_begin + priv->stream_length;
ret = parse_JFIF(priv, priv->stream_begin); // 开始解析JPEG
return ret;
}
4. 解析marker标识符
/* 略去了trace部分 */
static int parse_JFIF(struct jdec_private *priv, const unsigned char *stream)
{
int chuck_len;
int marker;
int sos_marker_found = 0;
int dht_marker_found = 0;
const unsigned char *next_chunck;
/* Parse marker */
while (sos_marker_found == 0)
{
if (*stream++ != 0xff)
goto bogus_jpeg_format;
/* Skip any padding ff byte (this is normal) */
while (*stream == 0xff)
stream++;
marker = *stream++; // 获取0xFF后的一个字节(即为marker标识符)
chuck_len = be16_to_cpu(stream); // length字段
next_chunck = stream + chuck_len;
switch (marker) // 判断marker类型
{
case SOF:
if (parse_SOF(priv, stream) < 0)
return -1;
break;
case DQT:
if (parse_DQT(priv, stream) < 0)
return -1;
break;
case SOS:
if (parse_SOS(priv, stream) < 0)
return -1;
sos_marker_found = 1;
break;
case DHT:
if (parse_DHT(priv, stream) < 0)
return -1;
dht_marker_found = 1;
break;
case DRI:
if (parse_DRI(priv, stream) < 0)
return -1;
break;
default:
break;
}
stream = next_chunck; // 解析下一个marker
}
if (!dht_marker_found) {
build_default_huffman_tables(priv);
}
return 0;
bogus_jpeg_format:
return -1;
}
5. 解析DQT
static int parse_DQT(struct jdec_private *priv, const unsigned char *stream)
{
int qi; // 量化表ID
float *table; // 指向量化表
const unsigned char *dqt_block_end; // 指向量化表结束位置
dqt_block_end = stream + be16_to_cpu(stream);
stream += 2; // 跳过长度字段
while (stream < dqt_block_end) // 检查是否还有量化表
{
qi = *stream++; // 将量化表中系数逐个赋给qi
table = priv->Q_tables[qi];
build_quantization_table(table, stream);
stream += 64;
}
return 0;
}
6. 建立量化表
static void build_quantization_table(float *qtable, const unsigned char *ref_table)
{
int i, j;
static const double aanscalefactor[8] = {
1.0, 1.387039845, 1.306562965, 1.175875602,
1.0, 0.785694958, 0.541196100, 0.275899379
}; // 比例因子
const unsigned char *zz = zigzag;
for (i=0; i<8; i++) {
for (j=0; j<8; j++) {
*qtable++ = ref_table[*zz++] * aanscalefactor[i] * aanscalefactor[j];
}
}
}
其中,zigzag数组实现了之字形扫描:
static const unsigned char zigzag[64] =
{
0, 1, 5, 6, 14, 15, 27, 28,
2, 4, 7, 13, 16, 26, 29, 42,
3, 8, 12, 17, 25, 30, 41, 43,
9, 11, 18, 24, 31, 40, 44, 53,
10, 19, 23, 32, 39, 45, 52, 54,
20, 22, 33, 38, 46, 51, 55, 60,
21, 34, 37, 47, 50, 56, 59, 61,
35, 36, 48, 49, 57, 58, 62, 63
};
7. 解析DHT
static int parse_DHT(struct jdec_private *priv, const unsigned char *stream)
{
unsigned int count, i;
unsigned char huff_bits[17]; // 码长1~16
int length, index;
length = be16_to_cpu(stream) - 2;
stream += 2; // 跳过长度字段
while (length>0) { // 检查是否还有表
index = *stream++;
/* We need to calculate the number of bytes 'vals' will takes */
huff_bits[0] = 0;
count = 0;
for (i=1; i<17; i++) {
huff_bits[i] = *stream++;
count += huff_bits[i];
}
if (index & 0xf0 )
build_huffman_table(huff_bits, stream, &priv->HTAC[index&0xf]); // 建立交流表
else
build_huffman_table(huff_bits, stream, &priv->HTDC[index&0xf]); // 建立直流表
length -= 1;
length -= 16;
length -= count;
stream += count;
}
return 0;
}
8. 建立Huffman码表
static void build_huffman_table(const unsigned char *bits, const unsigned char *vals, struct huffman_table *table) // bits为各个位数码字的数量,val为Huffval,table为要建立的Huffman表
{
unsigned int i, j, code, code_size, val, nbits;
unsigned char huffsize[HUFFMAN_BITS_SIZE + 1]; // 每个码字的长度
unsigned char* hz;
unsigned int huffcode[HUFFMAN_BITS_SIZE + 1]; // 每个码字
unsigned char* hc;
int next_free_entry;
/* 初始化 */
hz = huffsize;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++)
{
for (j=1; j<=bits[i]; j++)
*hz++ = i;
}
*hz = 0;
memset(table->lookup, 0xff, sizeof(table->lookup));
for (i=0; i<(16-HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS); i++)
table->slowtable[i][0] = 0;
code = 0;
hc = huffcode;
hz = huffsize;
nbits = *hz;
while (*hz)
{
while (*hz == nbits)
{
*hc++ = code++;
hz++;
}
code <<= 1;
nbits++;
}
/*
* Build the lookup table, and the slowtable if needed.
*/
next_free_entry = -1;
for (i=0; huffsize[i] != 0; i++)
{
/* 得到Huffval、每个码字、每个码字的长度*/
val = vals[i];
code = huffcode[i];
code_size = huffsize[i];
table->code_size[val] = code_size; // Huffval(权值)
if (code_size <= HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS)
{
/*
* Good: val can be put in the lookup table, so fill all value of this
* column with value val
*/
int repeat = 1UL<<(HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS - code_size);
code <<= HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS - code_size;
while ( repeat-- )
table->lookup[code++] = val; // 得到Huffval长度的查找表
}
else
{
/* Perhaps sorting the array will be an optimization */
uint16_t *slowtable = table->slowtable[code_size-HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS-1];
while(slowtable[0])
slowtable+=2;
slowtable[0] = code;
slowtable[1] = val;
slowtable[2] = 0;
/* TODO: NEED TO CHECK FOR AN OVERFLOW OF THE TABLE */
}
}
}
9. 解析SOS
static int parse_SOS(struct jdec_private *priv, const unsigned char *stream)
{
unsigned int i, cid, table;
unsigned int nr_components = stream[2]; // 颜色分量数
stream += 3;
for (i=0;i<nr_components;i++) {
/* 得到使用的Huffmann表号 */
cid = *stream++;
table = *stream++;
priv->component_infos[i].AC_table = &priv->HTAC[table&0xf];
priv->component_infos[i].DC_table = &priv->HTDC[table>>4];
}
priv->stream = stream+3;
return 0;
}
10. 解析SOF
static int parse_SOF(struct jdec_private *priv, const unsigned char *stream)
{
int i, width, height, nr_components, cid, sampling_factor;
int Q_table;
struct component *c;
print_SOF(stream);
height = be16_to_cpu(stream+3); // 图像高度
width = be16_to_cpu(stream+5); // 图像宽度
nr_components = stream[7]; // 颜色分量数
stream += 8;
for (i=0; i<nr_components; i++) {
/* 分别解析各分量 */
cid = *stream++; // 分量ID
sampling_factor = *stream++; // 采样因子
Q_table = *stream++;
c = &priv->component_infos[i];
c->Vfactor = sampling_factor&0xf; // 垂直采样因子
c->Hfactor = sampling_factor>>4; // 水平采样因子
c->Q_table = priv->Q_tables[Q_table]; // 使用的量化表
}
priv->width = width;
priv->height = height;
return 0;
}
11. 解析JPEG实际数据
int tinyjpeg_decode(struct jdec_private *priv, int pixfmt) // pixfmt为输出格式
{
unsigned int x, y, xstride_by_mcu, ystride_by_mcu;
unsigned int bytes_per_blocklines[3], bytes_per_mcu[3];
decode_MCU_fct decode_MCU;
const decode_MCU_fct *decode_mcu_table;
const convert_colorspace_fct *colorspace_array_conv;
convert_colorspace_fct convert_to_pixfmt;
if (setjmp(priv->jump_state))
return -1;
/* To keep gcc happy initialize some array */
bytes_per_mcu[1] = 0;
bytes_per_mcu[2] = 0;
bytes_per_blocklines[1] = 0;
bytes_per_blocklines[2] = 0;
decode_mcu_table = decode_mcu_3comp_table;
switch (pixfmt) {
/* 根据不同的输出格式确定MCU */
case TINYJPEG_FMT_YUV420P:
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_yuv420p;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height);
if (priv->components[1] == NULL)
priv->components[1] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height/4);
if (priv->components[2] == NULL)
priv->components[2] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height/4);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width;
bytes_per_blocklines[1] = priv->width/4;
bytes_per_blocklines[2] = priv->width/4;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 8;
bytes_per_mcu[1] = 4;
bytes_per_mcu[2] = 4;
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_RGB24:
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_rgb24;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height * 3);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width * 3;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 3*8;
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_BGR24:
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_bgr24;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height * 3);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width * 3;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 3*8;
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_GREY:
decode_mcu_table = decode_mcu_1comp_table;
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_grey;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 8;
break;
default:
return -1;
}
xstride_by_mcu = ystride_by_mcu = 8; // 初始化:MCU的宽高均为8px(4:4:4)
if ((priv->component_infos[cY].Hfactor | priv->component_infos[cY].Vfactor) == 1) {
/* 水平、垂直采样因子均为1 */
decode_MCU = decode_mcu_table[0]; // MCU包含1个Y
convert_to_pixfmt = colorspace_array_conv[0];
} else if (priv->component_infos[cY].Hfactor == 1) {
/* 水平采样因子为1,垂直采样因子为2 */
decode_MCU = decode_mcu_table[1]; // MCU包含2个Y
convert_to_pixfmt = colorspace_array_conv[1];
ystride_by_mcu = 16; // MCU高16px,宽8px
} else if (priv->component_infos[cY].Vfactor == 2) {
/* 水平、垂直采样因子均为2 */
decode_MCU = decode_mcu_table[3]; // MCU包含4个Y
convert_to_pixfmt = colorspace_array_conv[3];
xstride_by_mcu = 16; // MCU宽16px
ystride_by_mcu = 16; // MCU高16px
} else {
/* 水平采样因子为2,垂直采样因子为1 */
decode_MCU = decode_mcu_table[2]; // MCU包含2个Y
convert_to_pixfmt = colorspace_array_conv[2];
xstride_by_mcu = 16; // MCU宽16px,高8px
}
resync(priv);
/* Don't forget to that block can be either 8 or 16 lines */
bytes_per_blocklines[0] *= ystride_by_mcu;
bytes_per_blocklines[1] *= ystride_by_mcu;
bytes_per_blocklines[2] *= ystride_by_mcu;
bytes_per_mcu[0] *= xstride_by_mcu/8;
bytes_per_mcu[1] *= xstride_by_mcu/8;
bytes_per_mcu[2] *= xstride_by_mcu/8;
/* 对每个像块进行解码(8x8 / 8x16 / 16x16) */
for (y=0; y < priv->height/ystride_by_mcu; y++)
{
//trace("Decoding row %d\n", y);
priv->plane[0] = priv->components[0] + (y * bytes_per_blocklines[0]);
priv->plane[1] = priv->components[1] + (y * bytes_per_blocklines[1]);
priv->plane[2] = priv->components[2] + (y * bytes_per_blocklines[2]);
for (x=0; x < priv->width; x+=xstride_by_mcu)
{
decode_MCU(priv);
convert_to_pixfmt(priv);
priv->plane[0] += bytes_per_mcu[0];
priv->plane[1] += bytes_per_mcu[1];
priv->plane[2] += bytes_per_mcu[2];
if (priv->restarts_to_go>0)
{
priv->restarts_to_go--;
if (priv->restarts_to_go == 0)
{
priv->stream -= (priv->nbits_in_reservoir/8);
resync(priv);
if (find_next_rst_marker(priv) < 0)
return -1;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
12. 解析MCU
/*
* Decode a 2x2
* .-------.
* | 1 | 2 |
* |---+---|
* | 3 | 4 |
* `-------'
*/
static void decode_MCU_2x2_3planes(struct jdec_private *priv)
{
// Y
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y, 16);
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y+8, 16);
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y+64*2, 16);
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y+64*2+8, 16);
// Cb
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cCb);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cCb], priv->Cb, 8);
// Cr
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cCr);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cCr], priv->Cr, 8);
}
五、 程序调试及结果
该程序的命令行参数设置方法如下:
--benchmark 输入文件名 输出格式 输出文件名
其中:
- 第一个参数可以省略
- 输入文件名带.jpeg/.jpg后缀,输出文件名无后缀
- 输出格式:如
yuv420p
1. 将输出文件保存为.yuv格式
static void write_yuv(const char* filename, int width, int height, unsigned char** components) {
FILE* F;
char temp[1024];
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.Y", filename);
F = fopen(temp, "wb");
fwrite(components[0], width, height, F);
fclose(F);
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.U", filename);
F = fopen(temp, "wb");
fwrite(components[1], width * height / 4, 1, F);
fclose(F);
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.V", filename);
F = fopen(temp, "wb");
fwrite(components[2], width * height / 4, 1, F);
fclose(F);
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.YUV", filename);
F = fopen(temp, "wb");
fwrite(components[0], width, height, F);
fwrite(components[1], width * height / 4, 1, F);
fwrite(components[2], width * height / 4, 1, F);
fclose(F);
}
结果如下:
2. 调试TRACE
在程序中已经包含了TRACE相关的预处理器块
#if TRACE
/* TRACE */
#endif
在tinyjpeg.h文件中,我们可以看到TRACE已经是处于打开的状态(1):
#define TRACE 1 // 若设为0则可关闭TRACE
#define TRACEFILE "trace_jpeg.txt" // TRACE文件的文件名
执行程序后,得到的trace_jpeg.txt文件如下图所示:

3. 输出量化矩阵和Huffman码表
/* tinyjpeg.h中添加 */
FILE* qtabFilePtr; // 量化表文件指针
/* tinyjpeg.c中添加*/
static void build_quantization_table(float *qtable, const unsigned char *ref_table)
{
...
for (i=0; i<8; i++) {
for (j=0; j<8; j++) {
fprintf(qtabFilePtr, "%-6d", ref_table[*zz]);
if (j == 7) {
fprintf(qtabFilePtr, "\n");
}
...
}
}
fprintf(qtabFilePtr, "\n\n"); //
}
static int parse_DQT(struct jdec_private *priv, const unsigned char *stream)
{
...
while (stream < dqt_block_end) // 检查是否还有量化表
{
...
fprintf(qtabFilePtr, "Quantisation table [%d]:\n", qi); // 量化表ID
build_quantization_table(table, stream);
...
}
...
}
/* loadjpeg.c中添加 */
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
...
const char* qtabFileName = "q_table.txt"; // 量化表文件名
fopen_s(&qtabFilePtr, qtabFileName, "wb"); // 打开文件
...
fclose(qtabFilePtr);
return 0;
}
输出的量化表如下:
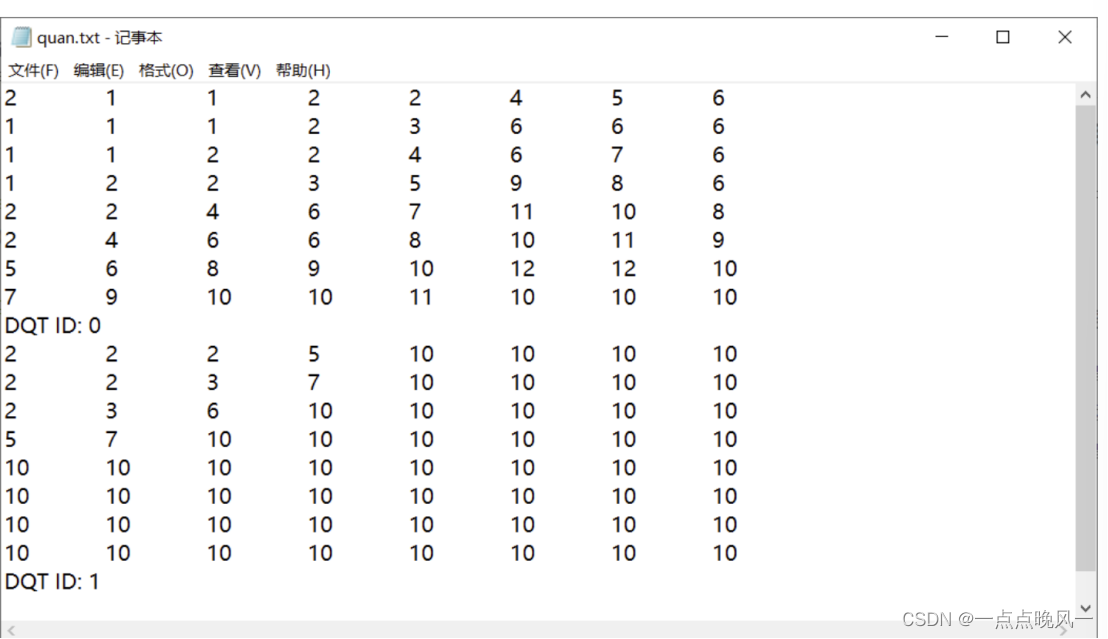
Huffman码表已包含在TRACE文件中。
4. 输出DC、AC图像
/* tinyjpeg.h中添加 */
...
FILE* dcImgFilePtr; // DC图像文件指针
FILE* acImgFilePtr; // AC图像文件指针
/* tinyjpeg.c中添加 */
int tinyjpeg_decode(struct jdec_private* priv, int pixfmt)
{
...
unsigned char* dcImgBuff;
unsigned char* acImgBuff;
unsigned char* uvBuff = 128;
int count = 0;
/* 对每个像块进行解码(8x8 / 8x16 / 16x16) */
for (y = 0; y < priv->height / ystride_by_mcu; y++) {
...
for (x = 0; x < priv->width; x += xstride_by_mcu) {
decode_MCU(priv);
dcImgBuff = (unsigned char)((priv->component_infos->DCT[0] + 512.0) / 4 + 0.5); // DCT[0]为DC系数;DC系数范围-512~512;变换到0~255
acImgBuff = (unsigned char)(priv->component_infos->DCT[1] + 128); // 选取DCT[1]作为AC的observation;+128便于观察
fwrite(&dcImgBuff, 1, 1, dcImgFilePtr);
fwrite(&acImgBuff, 1, 1, acImgFilePtr);
count++;
...
}
}
}
}
...
for (int i = 0; i < count / 4 * 2; i++) {
fwrite(&uvBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), 1, dcImgFilePtr);
fwrite(&uvBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), 1, acImgFilePtr);
}
return 0;
}
/* loadjpeg.c中添加 */
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
...
...
const char* dcImgFileName = "test_decoded_dc.yuv"; // DC图像文件名
const char* acImgFileName = "test_decoded_ac.yuv"; // AC图像文件名
...
fopen_s(&dcImgFilePtr, dcImgFileName, "wb"); // 打开DC图像文件
fopen_s(&acImgFilePtr, acImgFileName, "wb"); // 打开AC图像文件
...
...
fclose(dcImgFilePtr);
fclose(acImgFilePtr);
return 0;
}
结果如下:
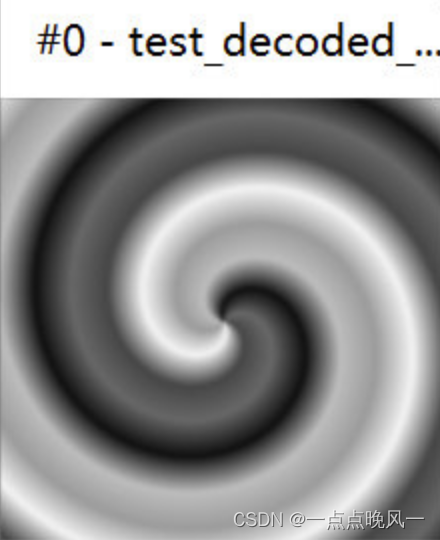


5. 计算DC、AC图像的pmf
使用求RGB图像各分量的概率分布和熵中的程序计算电平的概率分布,并绘制图像:
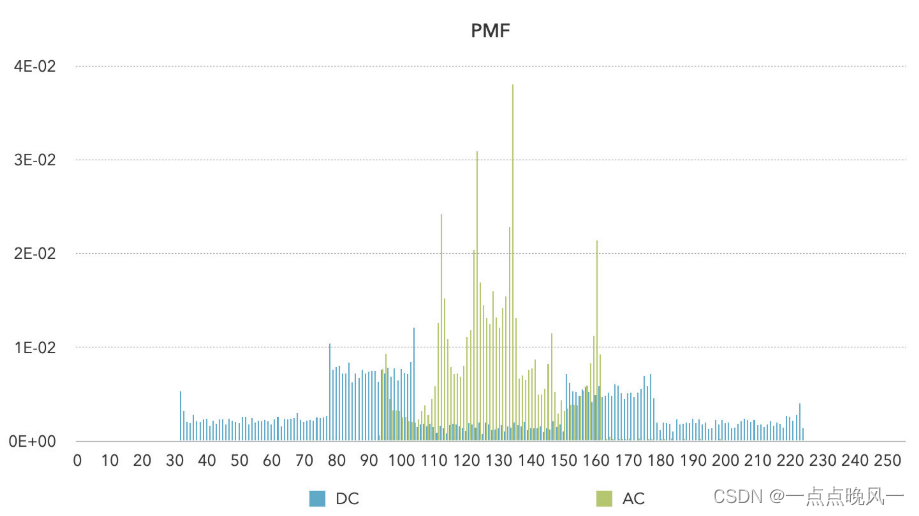





















 1289
1289











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








