通常MCU,MPU,FPGA等控制类芯片都会外挂FLASH芯片存储程序,这也是非常常见的。一般的,控制芯片和Flash之间采用最多通信方式是SPI协议。SPI分为二线,三线,四线,具体根据实际情况选择。那么四线制使用是比较广泛的。
SPI:Serial Peripheral Interface,即串行外设接口协议。
SPI Flash四线制信号解释:
①CS:Chip select;也写作NSS或SS(Slave select),表示从设备选择信号,低电平有效。
②MOSI:Master output Slave input;也叫SDI(Serial data input),表示从设备的数据输入。
③MISO:Master input Slave output;也叫SDO(Serial data output),表示从设备的数据输出。
④SCLK:Serial clock;也写作SCK,表示串行时钟。
为了初步了解SPI-FLASH实际通讯波形和时序,以下图为例,采用四线制测量了上电瞬间控制芯片和flash之间的通讯信号:即CS,MOSI,MISO,SCLK。目的是为了验证程序启动时的工作情况,从而进一步了解SPI通信的工作过程。
电路原理图:
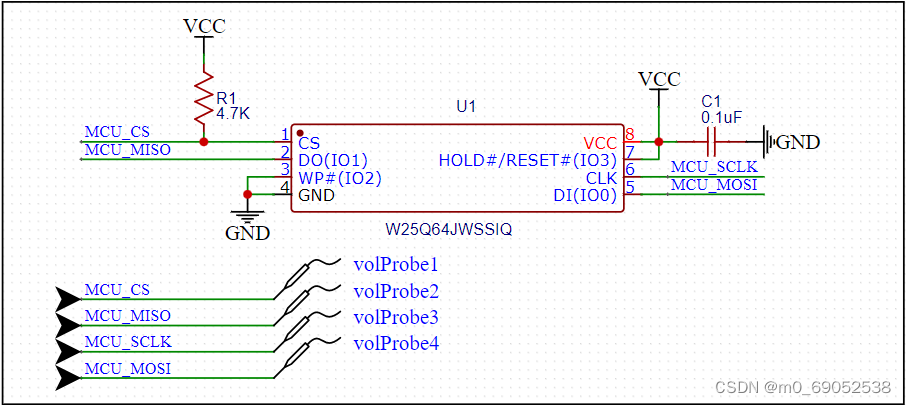
分别用示波器测量CS、SCLK、MISO(DO)、MOSI(DI)波形如下,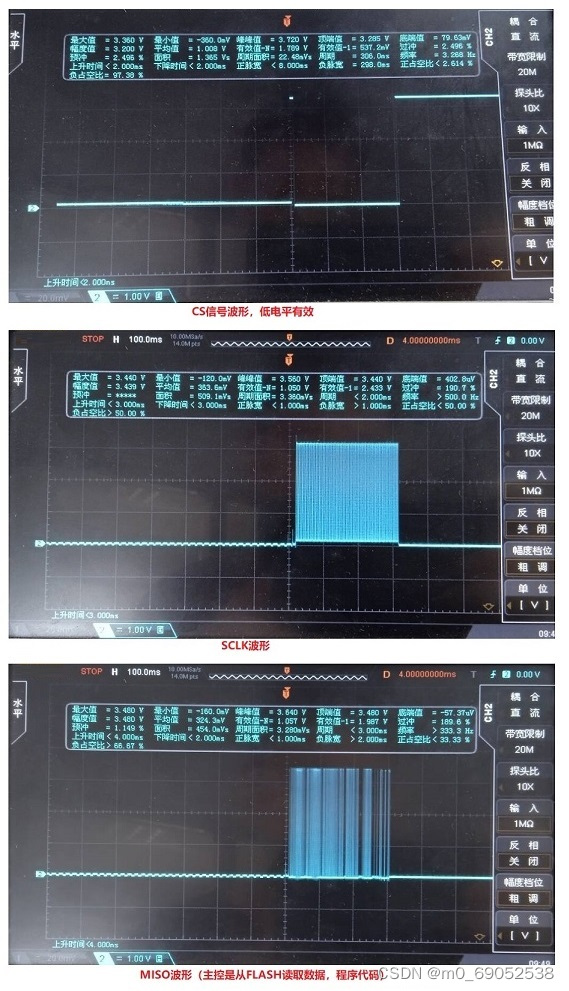
其中在MOSI引脚没有测试到波形,这是因为主设备是向Flash中读取数据即代码。如果是主设备往从设备Flash中写数据的话,在MOSI引脚上是可以测试到一连串的数据的。
如果以上对大家有些帮助的话,请点赞支持一下或分享,谢谢~







 本文详细介绍了SPI Flash的四线制通信,包括CS(选通信号)、SCLK(时钟)、MISO(数据输出)和MOSI(数据输入)。通过示波器测量实例,探讨了SPI在控制芯片与Flash间的通信过程,适合初学者理解SPI工作流程。
本文详细介绍了SPI Flash的四线制通信,包括CS(选通信号)、SCLK(时钟)、MISO(数据输出)和MOSI(数据输入)。通过示波器测量实例,探讨了SPI在控制芯片与Flash间的通信过程,适合初学者理解SPI工作流程。
















 1239
1239

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








