1.思维导图
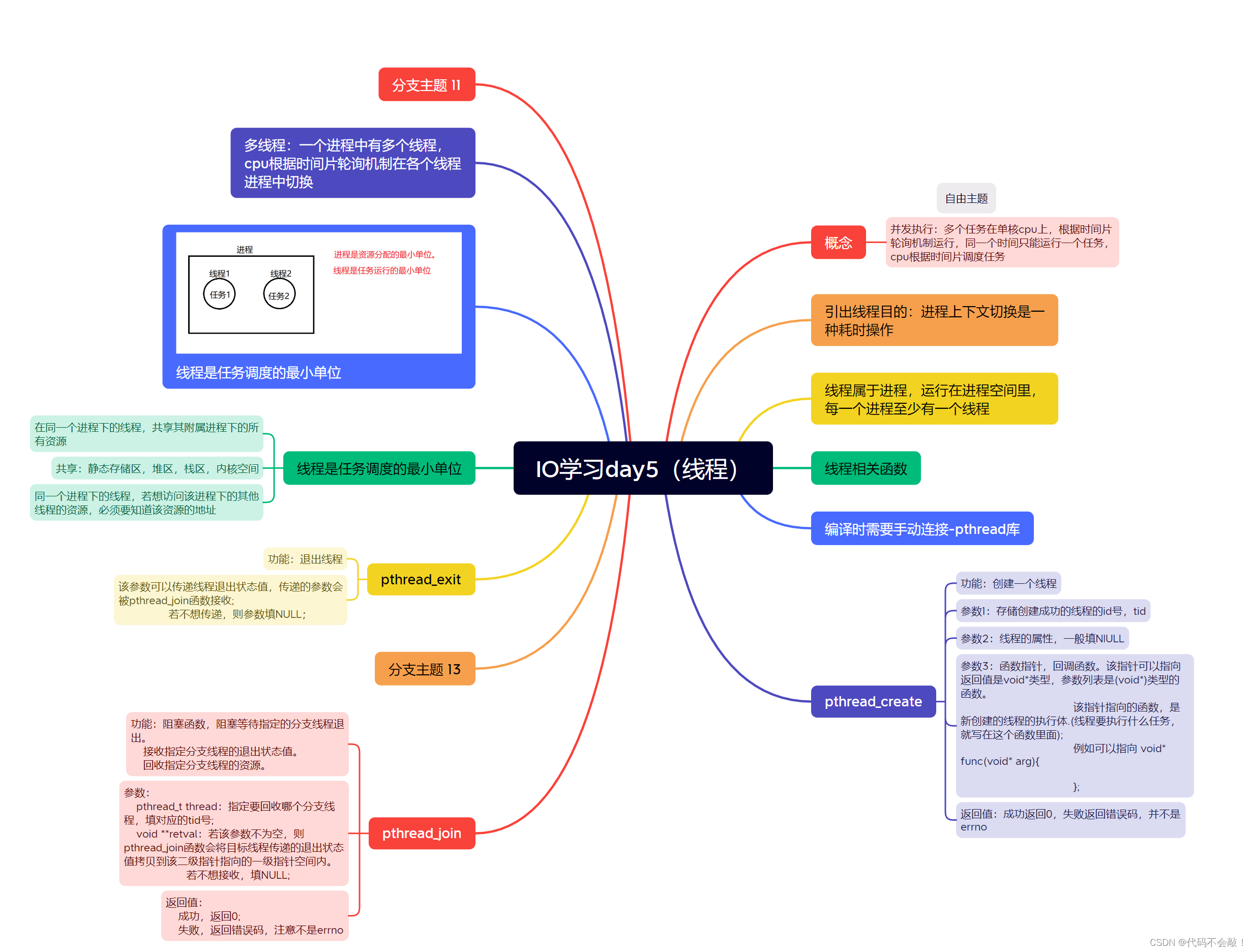
2.注意内容
- 我们将从main函数进来的线程称之为主线程,新创建的线程称之为分支线程,或者子线程
- 主线程和分支线程之间根据时间片轮询机制调度。主线程和分支线程谁先运行不确定。
- 主线程退出后,会导致进程退出,从而在该进程下的其他分支线程会强制结束;
- 分支线程退出,不会影响进程运行,所以不会导致其他线程退出。
3.思考题
任务1:思考若定义全局变量,分支线程和主线程能否访问到该全局变量
可以,且访问到的全局变量是同一个全局变量,因为线程共享其附属进程的所有资源。且全局变量的作用域为整个进程。
任务2:若定义局部变量,分支线程主线程能否直接访问对方的局部变量
不可以,因为局部变量的作用域被限制在,定义它的那个函数内部。
任务3:思考如何将主线程的数据传递给分支线程。
可以将主线程中变量的地址通过pthread_create函数的最后一个参数传递给分支线程。如下2)中的第i点
任务4:如何将分支线程的值传递给主线程。
可以将主线程中变量的地址通过pthread_create函数的最后一个参数传递给分支线程。在分支线程内做赋值。
如下2)中的第ii点
4.主线程与子线程之间的传参
1.主线程—》子进程
代码
#include<myhead.h>
//主线程给分支线程传递数据
//
//
//
//
//
//
//线程执行体
void* callback(void* arg)//void* arg = (void*)&a;
{
//void* arg指向a变量
//*arg报错:因为arg指向void类型,没有void类型的普通变量
//操作系统无法知道访问多大字节
while(1)
{
printf("this is other func a=%d %p,__%d__\n",*(int*)arg,arg,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a=10;//局部变量:作用于,在定义他的那个函数内部
pthread_t tid;
//创建一个线程,线程执行体为callback
if(pthread_create(&tid,NULL,callback,(void*)&a)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create faild __%d__\n",__LINE__);
return -1;
}
while(1){
printf("this is mian func a=%d %p__%d__\n",a,&a,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
效果图: 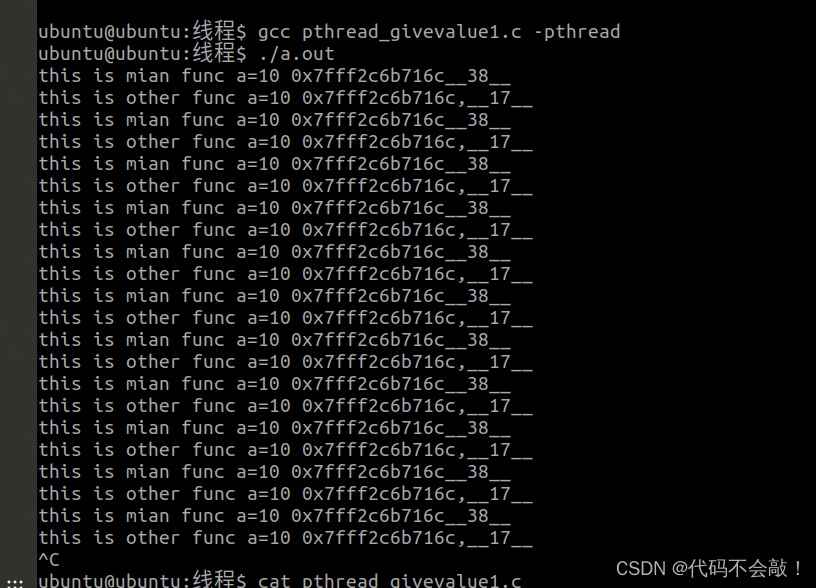
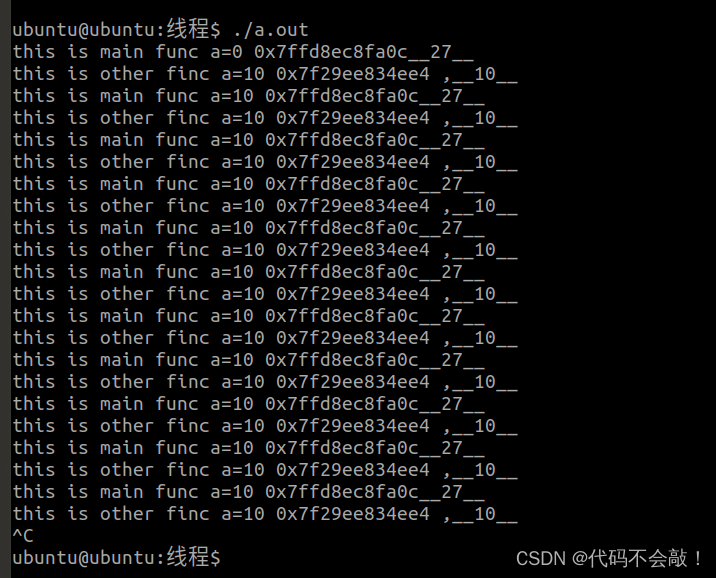
2. 子进程—》主线程
#include<myhead.h>
//线程执行体
void* callback(void* arg)//void* arg =(void*)&tmp_a;
{
int a=10;//局部变量:作用域,在定义它的那个内部函数
*(int *)arg=a;//*arg等价与tmp_a----->tmp_a=a;
while(1)
{
printf("this is other finc a=%d %p ,__%d__\n",a,&a,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int tmp_a=0;
pthread_t tid;
//创建一个线程,线程执行体为callback
if(pthread_create(&tid,NULL,callback,&tmp_a)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
printf("this is main func a=%d %p__%d__\n",tmp_a,&tmp_a,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
效果图:
作业:
1.完成图片拷贝,要求主线程拷贝一半,分支线程拷贝另一半。
/****************************作业1代码***********************************/ #include<myhead.h> //创建子线程函数 void* callback(void* arg ) { //子线程拷贝图片后一半 int fd_r=open("./qq.png",O_RDONLY); if(fd_r<0) { ERR_MSG("open"); } int fd_w=open("./qq1.png",O_WRONLY); if(fd_w<0) { ERR_MSG("open"); } off_t size=lseek(fd_r,0,SEEK_END);//求文件大小 char c=0; //初始化文件偏移量 lseek(fd_r,size/2,SEEK_SET);//读文件偏移量置位到开头 lseek(fd_w,size/2,SEEK_SET);//写文件偏移量置位到开头 //开始读取写入 for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++) { bzero(&c,sizeof(c));//避免上次读取的内容影响 //从fd_r文件中读取 read(fd_r,&c,1); //写入到fd_w文件中 write(fd_w,&c,1); } close(fd_r); close(fd_w); printf("后半部分拷贝完毕,子线程退出\n"); pthread_exit(NULL); } int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { int fd=open("./qq1.png",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);//打开文件为了创建一个空文件进行写入工作 if(fd<0) { ERR_MSG("open"); return -1; } //关闭文件,避免影响文件偏移量 close(fd); //创建线程 pthread_t tid; if(pthread_create(&tid,NULL,callback,NULL)!=0) { fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create filed __%d__\n",__LINE__ ); return -1;//创建失败 } //主线程拷贝图片前一半 int fd_r=open("./qq.png",O_RDONLY); if(fd_r<0) { ERR_MSG("open"); } int fd_w=open("./qq1.png",O_WRONLY); if(fd_w<0) { ERR_MSG("open"); } off_t size=lseek(fd_r,0,SEEK_END);//求文件大小 char c=0; //初始化文件偏移量 lseek(fd_r,0,SEEK_SET);//读文件偏移量置位到开头 lseek(fd_w,0,SEEK_SET);//写文件偏移量置位到开头 //开始读取写入 for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++) { bzero(&c,sizeof(c));//避免上次读取的内容影响 //从fd_r文件中读取 read(fd_r,&c,1); //写入到fd_w文件中 write(fd_w,&c,1); } close(fd_r); close(fd_w); printf("前半部分拷贝完毕,主线程退出\n"); //阻塞等待tid线程退出 pthread_join(tid,NULL); return 0; }
要求定义一个全局变量 char buf[] = "1234567",创建两个线程,不考虑退出条件。
A线程循环打印buf字符串,
B线程循环倒置buf字符串,即buf中本来存储1234567,倒置后buf中存储7654321. B线程中不打印!!
倒置不允许使用辅助数组。
要求A线程打印出来的结果只能为 1234567 或者 7654321 不允许出现7634521 7234567
不允许使用sleep函数
分析出现错误的原因。
/*********************************作业2**********************************/ #include<myhead.h> char buf[]="1234567"; int flag= 0 ; void* callback_1(void* arg)//打印 { while(1) { if(0 == flag) { printf("%s\n",buf); flag=1; } } pthread_exit(NULL); } void* callback_2(void* arg)//逆置 不打印 { char t=0; while(1) { if(1 == flag) { for(int i=0;i<strlen(buf)/2;i++) { t=buf[i]; buf[i] = buf[strlen(buf)-1-i]; buf[strlen(buf)-1-i] = t; } flag=0; } } pthread_exit(NULL); } int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { pthread_t tid_1,tid_2; if(pthread_create(&tid_1,NULL,callback_1,NULL)!=0) { fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__); return -1; } pthread_detach(tid_1); //分离线程1 if(pthread_create(&tid_2,NULL,callback_2,NULL)!=0) { fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__); return -1; } pthread_join(tid_2,NULL); printf("主线程准备退出"); return 0; }




















 1221
1221











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








