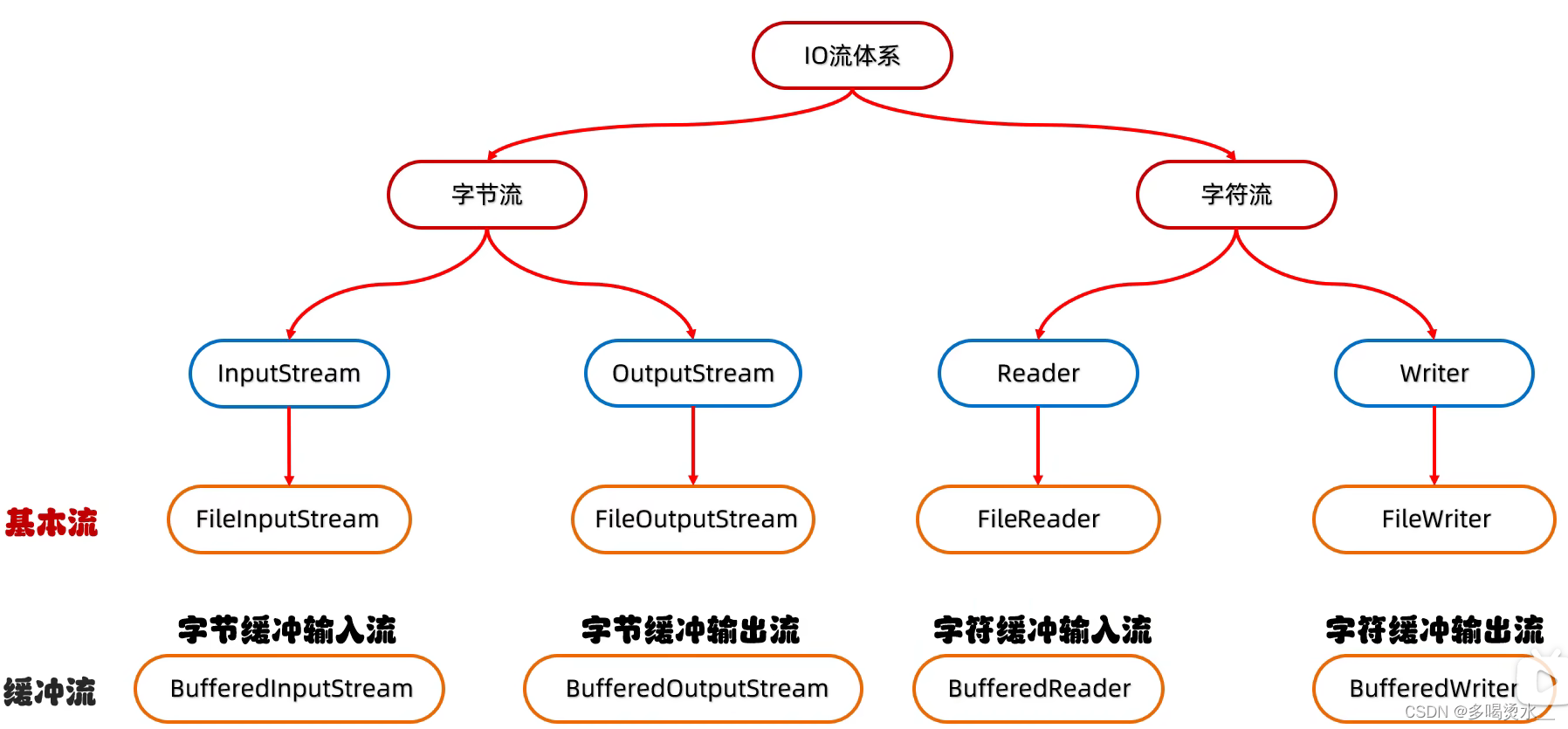
 缓冲流
缓冲流
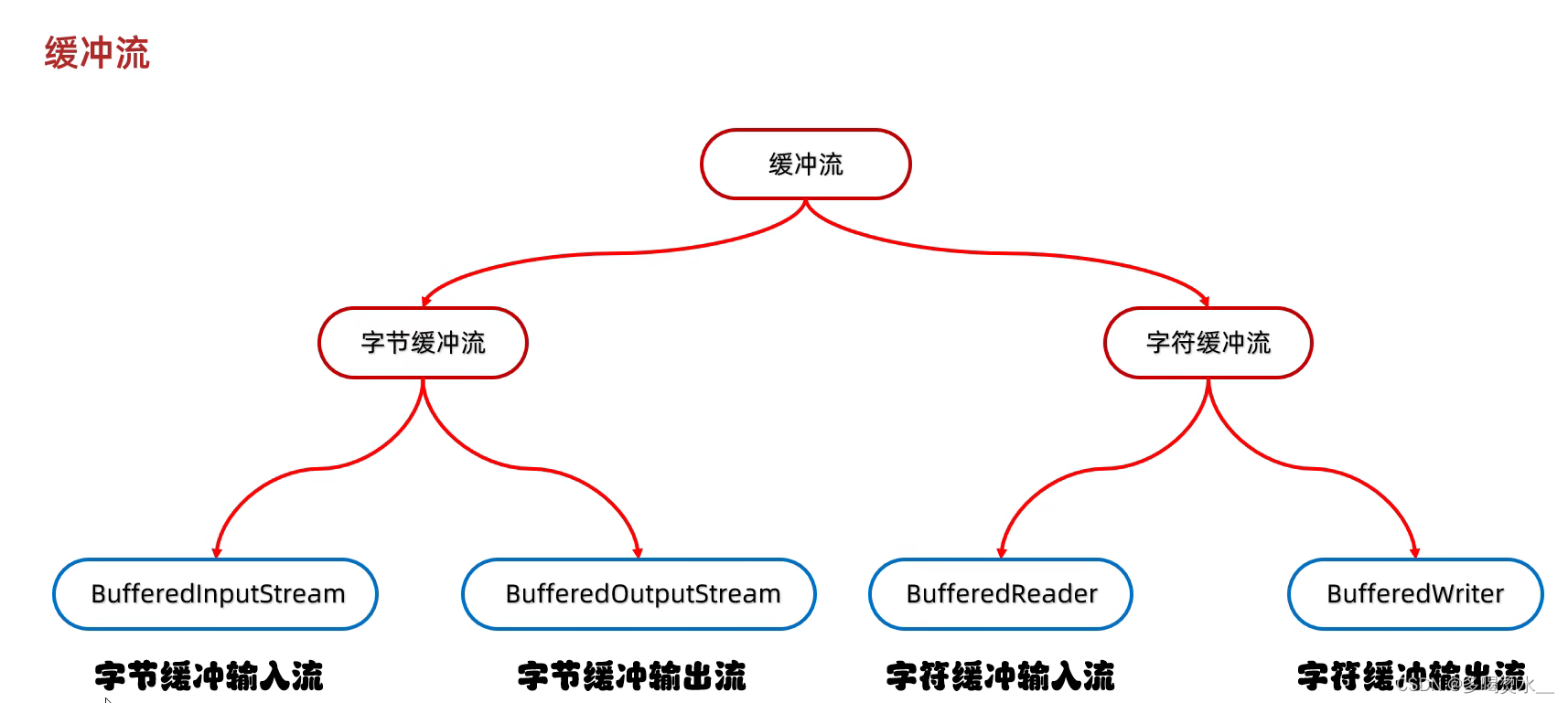
字节缓冲流

利用字节缓冲区拷贝文件,一次读取一个字节:
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//利用字节缓冲区来拷贝文件
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c.txt"));
//一次读取一个字节
int b;
while((b=bis.read())!=-1) {
bos.write(b);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
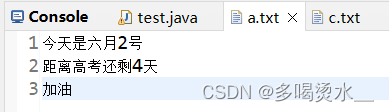
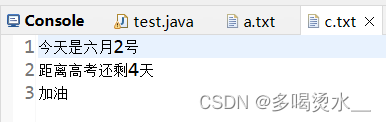
一次读取多个字节:
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//利用字节缓冲区来拷贝文件
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c.txt"));
//一次读取多个字节
int len;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}字符缓冲流
底层自带了长度为8192缓冲区提高性能。
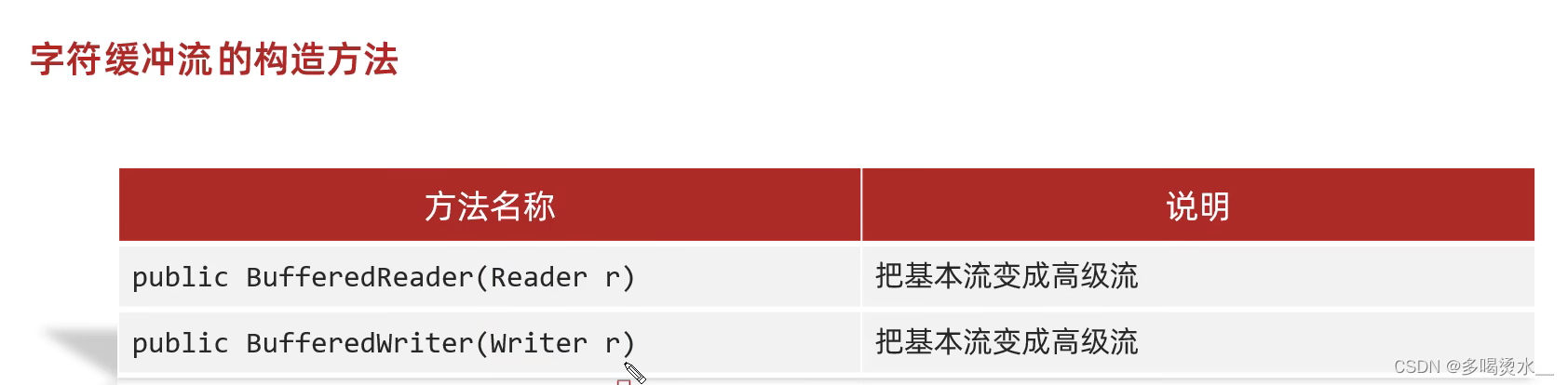

字符缓冲输入流
特有方法:br.readLine()——读取一行数据
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
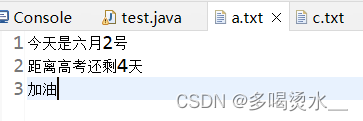
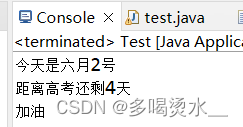
//字符缓冲输入流读取文件
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
String len;
while((len=br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(len);
}
//释放资源
br.close();
}
}
字符缓冲输出流
特有方法:bw.newLine——换行
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
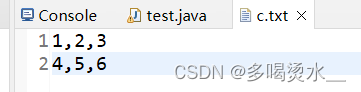
//利用字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c.txt"));
bw.write("1,2,3");
bw.newLine();//换行
bw.write("4,5,6");
//释放资源
bw.close();
}
}
综合练习
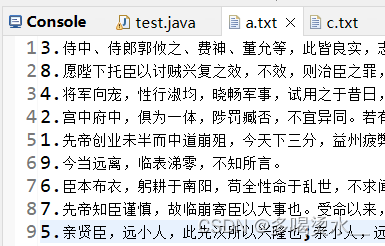
练习1:修改文本顺序
将《出师表》这个文章顺序恢复到新文件中。
分析:两种方法,一种使用ArrayList集合,一种使用TreeMap(Tree中有默认的排序规则)
第一种方法:先读取,再排序,再写入
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//读取
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
String len;
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();//将读取到的数据放入集合中
while((len=br.readLine())!=null) {
list.add(len);
}
br.close();
//排序
list.sort(new Comparator<String>() {//指定排序规则
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
int i1=Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]);
int i2=Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);
return i1-i2;
}
});
//写入
//需要换行写入
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c.txt"));
for(String s:list) {
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}
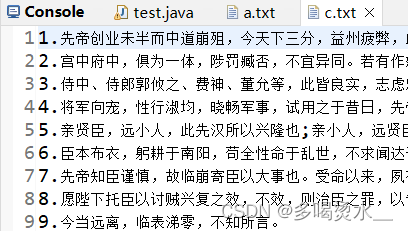
第二种方法:利用TreeMap集合,键为序号,值为后面的字符串
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//读取
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
String len;
TreeMap<Integer, String> tm=new TreeMap<>();
while((len=br.readLine())!=null) {
//将键值放入tm中
int i=Integer.parseInt(len.split("\\.")[0]);
String j=len.split("\\.")[1];
tm.put(i, j);
}
br.close();
//读取
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c.txt"));
//获取键值对,利用循环
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries=tm.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry:entries) {
String value=entry.getValue();
bw.write(value);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}
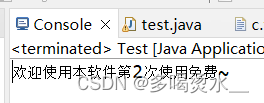
练习2:软件运行次数
实现一个验证程序运行次数的小程序,要求如下:
当程序运行超过3次时给出提示:本软件只能免费使用3次,欢迎您注册会员后继续使用~2.程序运行演示如下:
第一次运行控制台输出:欢迎使用本软件第1次使用免费~
第二次运行控制台输出:欢迎使用本软件第2次使用免费~
第三次运行控制台输出:欢迎使用本软件,第3次使用免费~
第四次及之后运行控制台输出:本软件只能免费使用3次,欢迎您注册会员后继续使用~
分析:
这是一个计数器问题,利用count++完成,但如果将count写入到程序中,运行控制台重新运行后,count将恢复原始数据0,所以需要将count写入到文件中,利用读写完成。
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c.txt"));
String c=br.readLine();//读取文件中count的值
int count=Integer.parseInt(c);
count++;
if(count<=3) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用本软件第"+count+"次使用免费~");
}else {
System.out.println("本软件只能免费使用3次,欢迎您注册会员后继续使用~");
}
//将读取的count++值再写入文件中
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c.txt"));
bw.write(count+"");//加入一个“”是将count变为字符串
bw.close();
}
}
转换流
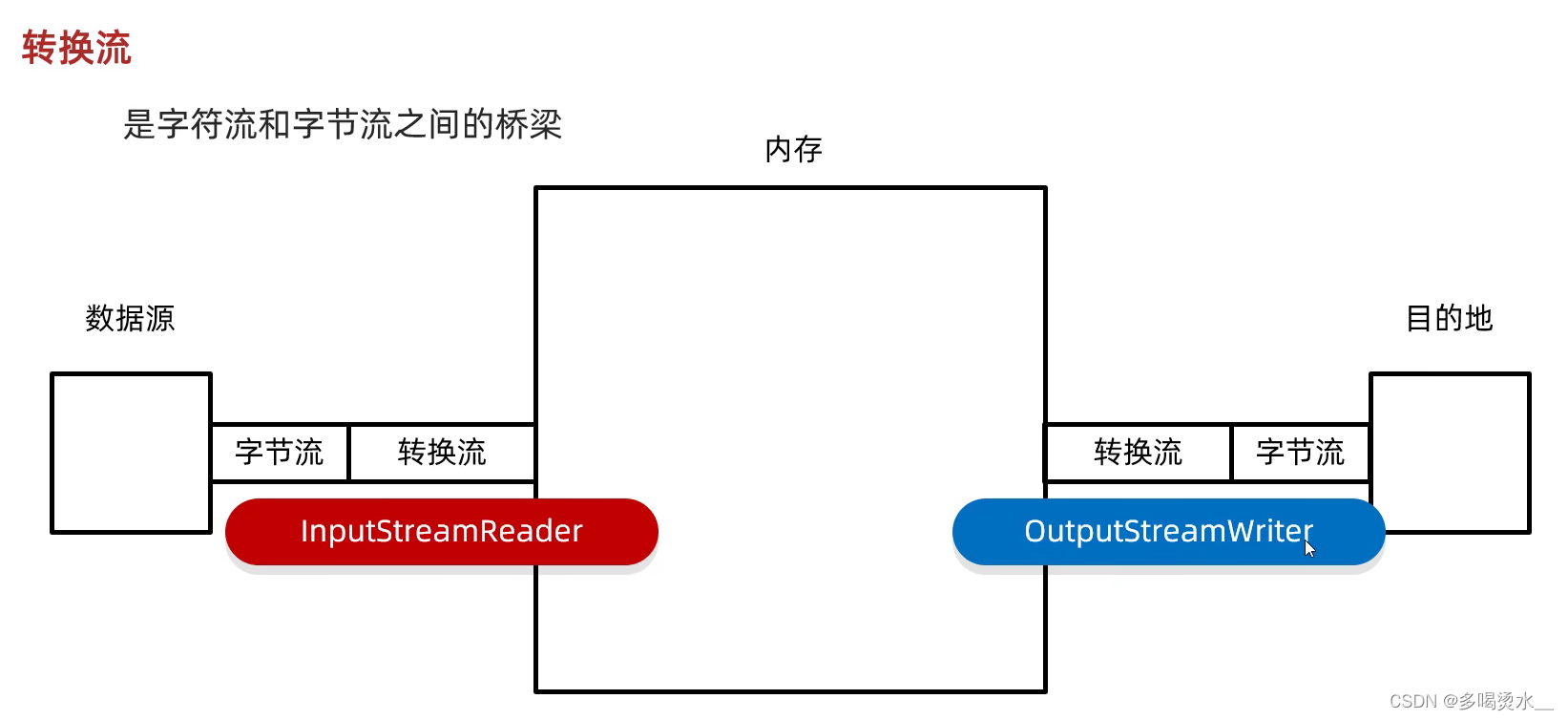
作用:字节流想要使用字符流中的方法。
利用转换流按照指定字符编码读取,只做了解
练习::手动创建一个GBK的文件,把文件中的中文读取到内存中,不能出现乱码需求
方法1:转换流,只做了解
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//利用转换流进行编码转换
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("c.txt"),"GBK");//指定读码的字符集
int ch;
while((ch=isr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
isr.close();
}
}
方法2:利用字符流按照指定编码读取(JDK11)
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//字符流按照指定字符编码读取
FileReader fr =new FileReader("c.txt",Charset.forName("gbk"));
int ch;
while((ch=fr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.println((char)ch);
}
fr.close();
}
}
练习:把一段中文按照GBK的方式写到本地文件。
方法1:转换流
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//利用转换流
OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("c.txt"),"GBK");
osw.write("你好");
osw.close();
}
}
方法2:字符流
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//利用转换流
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("c.txt",Charset.forName("GBK"));
fw.write("你好");
fw.close();
}
}
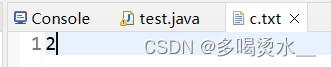
练习3:利用字节流读取文件中的数据,每次读一整行,而且不能出现乱码
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//利用字节流读取文件中的数据,每次读一整行,而且不能出现乱码
//先是字节流,再是转换流,再是缓冲字符流
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("c.txt")));
String str;
while((str=br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
br.close();
}
}
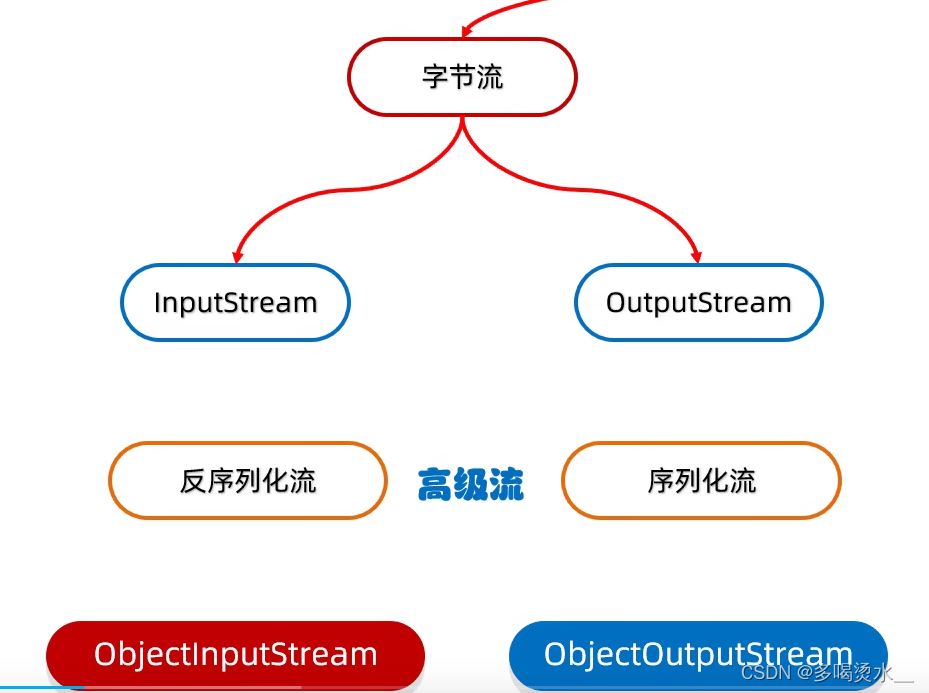
序列化流


package test02;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name,int age) {
this.setName(name);
this.setAge(age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//序列化流:将一个java对象写入到文件中
//先创建对象
Student s=new Student("张三",23);
//再创建序列流
ObjectOutputStream os=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c.txt"));
os.writeObject(s);
os.close();
}
}

反序列化流

public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//反序列化流
ObjectInputStream oi=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("c.txt"));
//读取
Student o=(Student)oi.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
oi.close();
}
}

练习:用对象流读写多个对象
将多个自定义对象序列化到文件中,但是由于对象的个数不确定,反序列化流该如何读取呢?
分析:由于对象的不确定性,所以将对象放入Arraylist集合中,在读取的时候调用集合。
package test02;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name,int age) {
this.setName(name);
this.setAge(age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
先将list集合中的内容写入文件
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//序列化
Student s1=new Student("zhangsan",23);
Student s2=new Student("lisi",24);
Student s3=new Student("wangwu",25);
//利用集合将对象存放在集合中
ArrayList<Student> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
//创建序列化对象
ObjectOutputStream os=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c.txt"));
os.writeObject(list);
os.close();
}
}
package test02;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class read {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//读取
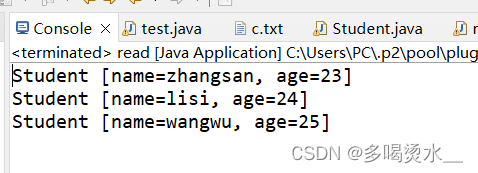
ObjectInputStream oi=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("c.txt"));
ArrayList<Student> s=(ArrayList<Student>)oi.readObject();
for(Student student:s) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}





















 1107
1107

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








