目录
- 常见算法
- 简单认识算法
- 排序算法
- 查找算法
- 正则表达式
- 概述、初体验
- 书写规则
- 应用案例
- 用于查找信息
- 用于搜索替换,分割内容
- 异常
- 认识异常
- 自定义异常
- 异常的处理
什么是算法
解决某个实际问题的过程和方法
排序算法
- 冒泡排序
- 选择排序
冒泡排序:每次从数组中找出最大值放在数组的后面去
/**
* 掌握冒泡排序算法
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、准备好一个数组
int[] arr = {7,23,79,81,103,127,131,147};
// 2、确定总共需要比较几轮 : 数组的长度 -1
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < arr.length -i -1; j++) {
// 每轮比较几次 :数组长度-i-1
if(arr[i]>arr[j]){
// 当前位置大于后一个位置,则交换位置
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [7, 23, 79, 81, 103, 127, 131, 147]
}
}
选择排序:每轮选择当前位置,开始找出后面的较小值与该位置交换
/**
* 掌握选择排序算法
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、准备好一个数组
int[] arr = {7,23,79,81,103,127,131,147};
// 2、确定总共需要几轮 :数组长度 -1
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < arr.length; j++) {
// 3、控制每轮以当前位置为基准,与后面的元素选择几次
if (arr[minIndex] > arr[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if(minIndex != i){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [7, 23, 79, 81, 103, 127, 131, 147]
}
}
查找算法
- 二分查找(折半查找)
前提条件:数组中的数据必须是有序的
核心思想:每次排除一半的数据,查询数据的性能明显提高很多
条件:二分查找正常的折半条件是 开始位置 left <= 结束位置 right
/**
* 掌握二分查找算法
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、准备好一个数组
int[] arr = {7,23,79,81,103,127,131,147};
int index = binarySearch(arr, 81);
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有找到该数据!请确认!");
} else {
System.out.println("您要找的数据的位置为:" + (index+1));
}
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr,int data) {
// 1、定义两个变量,一个在最左边,一个在最右边
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
// 定义一个循环控制折半
while (left <= right) {
// 3、每次折半,都算出中间位置处的索引
int middle = (left+right)/2;
// 4、判断当前要找的元素,与中间位置处的元素值的大小情况
if(data > arr[middle]) {
left = middle + 1;
} else if(data < arr[middle]) {
right = middle - 1;
} else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1; // -1特殊结果,就代表没有找到数据,数组中不存在该数据!
}
}
正则表达式
就是由一些特定的字符组成,代表的是一个规则
-
作用一:用来校验数据格式是否合法
- 电话
- 邮箱
- QQ号
-
在一段文本中查找满足要求的内容
书写规则
String提供了一个匹配正则表达式的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Public boolean matches(String regex) | 判断字符串是否匹配正则表达式,匹配返回true,不匹配返回false |
正则表达式的书写规则
字符类(只匹配单个字符)
-
[ abc ] : 只能是 a,b或c
-
[ ^abc ] : 除了a,b,c之外的任何字符
-
[ a-zA-z ] :a到z A到Z,包括(范围)
-
[ a-d [ m-p ] ] : a到d,或m到p
-
[a-z && [ sdf ] ] : s,d,f(取交集)
-
[a-z && [ ^bc ] ] : a到z,除了b和c(相当于[ad-z])
-
[a-z && [ ^m-p] ] : a到z,除了m到p(等同于[ a-lq-z])
预定义字符(只匹配单个字符)
- . 任何字符
- \d 一个数字 :[ 0-9 ]
- \D 非数字 :[ ^0-9 ]
- \s 一个空白字符 :[ \s ]
- \S 非空白字符 :[ ^\S ]
- \w 字母数字下划线 :[ a-zA-Z_0-9]
- \W 非字母数字下划线 :[ ^\W ]
数量词
- x?:x,一次或0次
- x* :x,零次或多次
- x+ :x,一次或多次
- x{ n } :x,正好n次
- x{ n, } :x,至少n次
- x{ n,m } : x,至少n次,但不超过m次
其他几个常用符号:(?!) 忽略大小写、或 | 、分组( )
| 符号 | 含义 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| [ ] | 里面的内容出现一次 | [abc] |
| ^ | 取反 | [^abc] |
| && | 交集,不能写单个的& | [ a-z&&m-p] |
| . | 任意字符 | \n回车符号不匹配 |
| \ | 转义字符 | \\d |
| \\d | 0-9 | \\d+ |
| \\D | 非0-9 | \\D+ |
| \\s | 空白字符 | |
| \\S | 非空白字符 | [ ^\s ] |
| \\w | 单词字符 | [ a-zA-z_0-9] |
| \\W | 非单词字符 | [ ^\w ] |
| ( ) | 分组 | a(bc)+ |
| | | 写在方括号外面表示并集 | ab|AB |
| 符号 | 含义 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| ? | 0次或1次 | \\d? |
| * | 0次或多次 | \\d* (abc)* |
| + | 1次或多次 | \\d+ (abc)+ |
| 1{ } | 具体次数 | a{7} \\d{7,19} |
| (?i) | 忽略后面字符的大小写 | (?i)abc |
| a((?i)b)c | 只忽略b的大小写 | a((?i)b)c |
案例1:请使用正则表达式完成如下需求
需求:校验用户输入的电话、邮箱、时间是否合法
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
checkPhone();
checkEmail();
}
public static void checkPhone() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请您输入您的电话号码(手机|座机)");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String phone = sc.nextLine();
// 18827314036 010-2382483284 010832432843
if(phone.matches("(1[3-9]\\d{9})|(0\\d{2,7}-?[1-9]\\d{4,19})")) {
System.out.println("您输入的号码格式正确");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的号码格式错误");
}
}
}
public static void checkEmail() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请您输入您的邮箱:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String email = sc.nextLine();
/**
* dlei0009@163.com
* 22437242@qq.com
* dhjshe@dhwdf.com.cn
*/
if(email.matches("\\w{2,}@\\w{2,20}(\\.\\w{2,10}){1,2}")) {
System.out.println("您输入的邮箱格式正确");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的邮箱格式错误");
}
}
}
}
案例2:使用正则表达式查找一段文本中的内容
需求:请把下面文本中的电话、邮箱、座机号码、热线都爬取出来
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
}
// 需求:从一下内容中爬取处,手机,邮箱,座机,400电话等信息
public static void method1() {
String data = "电话:18738273493,27384938293\n" +
"或者练习邮箱:boniu@qq.com.cn,\n" +
"座机电话:01037732834,010-83243787\n" +
"邮箱:bozai@itcast.com.cn,\n" +
"邮箱:dlei@163.com,\n" +
"热线电话:400-618-9090 , 400-618-4000, 4006184000,4006189090";
// 1、定义爬取规则
String regex = "(1[3-9]\\\\d{9})|(0\\\\d{2,7}-?[1-9]\\\\d{4,19})|(\\w{2,}@\\w{2,20}(\\.\\w{2,10}){1,2})" + "|400-?\\d{3,7}-?\\d{3,7}";
// 2、把正则表达式封装成一个Pattern对象
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
// 3、通过Pattern对象去获取查找内容的匹配器对象
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(data);
// 4、定义一个循环开始爬取信息
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println(matcher.group()); // 获取到了找到的内容(并输出)
}
}
}
案例3:从以下内容中把邮箱里的用户名爬取出来
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
}
// 需求:从以下内容中把邮箱里的用户名爬取出来
public static void method1() {
String data = "电话:18738273493,27384938293\n" +
"或者练习邮箱:boniu@qq.com.cn,\n" +
"座机电话:01037732834,010-83243787\n" +
"邮箱:bozai@itcast.com.cn,\n" +
"邮箱:dlei@163.com,\n" +
"热线电话:400-618-9090 , 400-618-4000, 4006184000,4006189090";
// 1、定义爬取规则
String regex = "\\w*@";
// 2、把正则表达式封装成一个Pattern对象
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
// 3、通过Pattern对象去获取查找内容的匹配器对象
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(data);
// 4、定义一个循环开始爬取信息
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println(matcher.group()); // 获取到了找到的内容(并输出)
}
}
}
正则表达式用于搜索替换,分割内容,需要结合String提供的如下方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Public String replaceAll(String regex,String newstr) | 按照正则表达式匹配的内容进行替换 |
| Public String[] split(String regex) | 按照正则表达式匹配的内容进行分割字符串,返回一个字符串数组 |
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求1:请把张三ai888李四9966aa王五abc_f6波妞,中间的非中文字符替换成"-"
String s1 = "张三ai888李四9966aa王五abc_f6波妞";
System.out.println(s1.replaceAll("\\w+","-")); // 张三-李四-王五-波妞
// 需求2:某语音系统,收到一个口吃的人说:"我我喜欢编编编程程!",需要识别"我喜欢编程"
String s2 = "我我喜欢编编编程程!";
System.out.println(s2.replaceAll("(.)\\1+", "$1")); // 我喜欢编程!
// 需求3:请把张三ai888李四9966aa王五abc_f6波妞中的人名取出来
String s3 = "张三ai888李四9966aa王五abc_f6波妞";
String[] names = s3.split("\\w+");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names)); // [张三, 李四, 王五, 波妞]
}
}
认识异常
异常:异常就是代表程序出现的问题
异常的体系
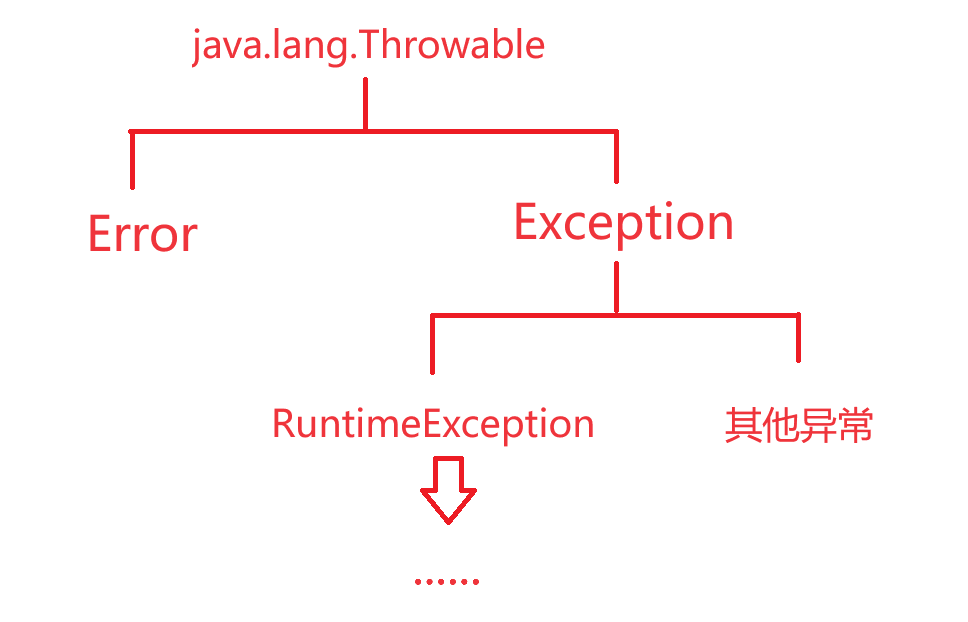
Error:代表系统级别的错误(属于严重问题,也就是说系统一旦出现问题,Sun公司会把这些问题封装成Error对象给出来,Error是给Sun公司自己用的,不是给程序员用的,因此开发人员不用管)
Exception:异常,它代表的才是程序可能出现的问题,所以程序员通常会用Exception以及它的子类来封装出现的问题
- 运行时异常:RuntimeException及其子类,编译阶段不会出现错误提醒,运行时出现的异常(如:数组索引越界异常)
- 编译时异常:编译阶段就会出现错误提醒(如:日期解析异常)
编译时异常的两种处理方法
-
抛出异常(throws)
-
在方法上使用throws关键字,可以将方法内部出现的问题抛出去给调用者处理
方法 throws 异常1,异常2,异常3 ... { ... }
-
-
捕获异常 (try - catch)
-
直接捕获程序出现的异常
try { // 监视可能出现异常的代码1 } catch(异常类型1 变量) { // 处理异常 } catch(异常类型2 变量) { // 处理异常 }
-
自定义异常
- java无法为这个世界上全部的问题都提供异常类来代替,如果企业自己的某种问题,想通过异常来表示,以便用异常来管理该问题,那就需要自己来定义异常类
自定义异常的种类
-
自定义运行时异常
- 定义一个异常类继承RuntimeException
- 重写构造器
- 通过throw new 异常类(xxx)来创建异常对象并抛出
注意:编译阶段不报错,提醒不强烈,运行时才可能出现异常!
public class AgeIllegalRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeIllegalRuntimeException() {
}
public AgeIllegalRuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class ExceptionTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:保存一个合法的年龄
try {
savaAge(18);
System.out.println("底层执行成功!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("底层出现了bug");
}
}
public static void savaAge(int age) {
if(age >0 && age <150) {
System.out.println("年龄合法,成功保存" + age);
} else {
// 用一个异常对象封装这个问题
// throw 抛出去这个异常对象
throw new AgeIllegalRuntimeException("/age is illegal!");
}
}
}
-
自定义编译时异常
- 定义一个异常类来继承Exception
- 重写构造器
- 通过throw new 异常类(xxx)来创建异常对象并抛出
注意:编译阶段就报错,提醒更加强烈
public class AgeIllegalException extends Exception {
public AgeIllegalException() {
}
public AgeIllegalException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class ExceptionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:保存一个合法的年龄
try {
savaAge2(23);
System.out.println("savaAge2底层执行成功!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("savaAge2底层出现了bug");
}
}
public static void savaAge2(int age) throws AgeIllegalException{
if(age >0 && age <150) {
System.out.println("年龄合法,成功保存" + age);
} else {
// 用一个异常对象封装这个问题
// throw 抛出去这个异常对象
// throws 用在方法上,抛出方法内部的异常
throw new AgeIllegalException("/age is illegal!");
}
}
}
异常有什么作用
- 异常是用来查询系统Bug的关键参考信息!
- 异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便通知上层调用者底层的执行情况
异常的处理
代码层面上的处理:1. throws ,2. try - catch
开发中对于异常的常见处理方式
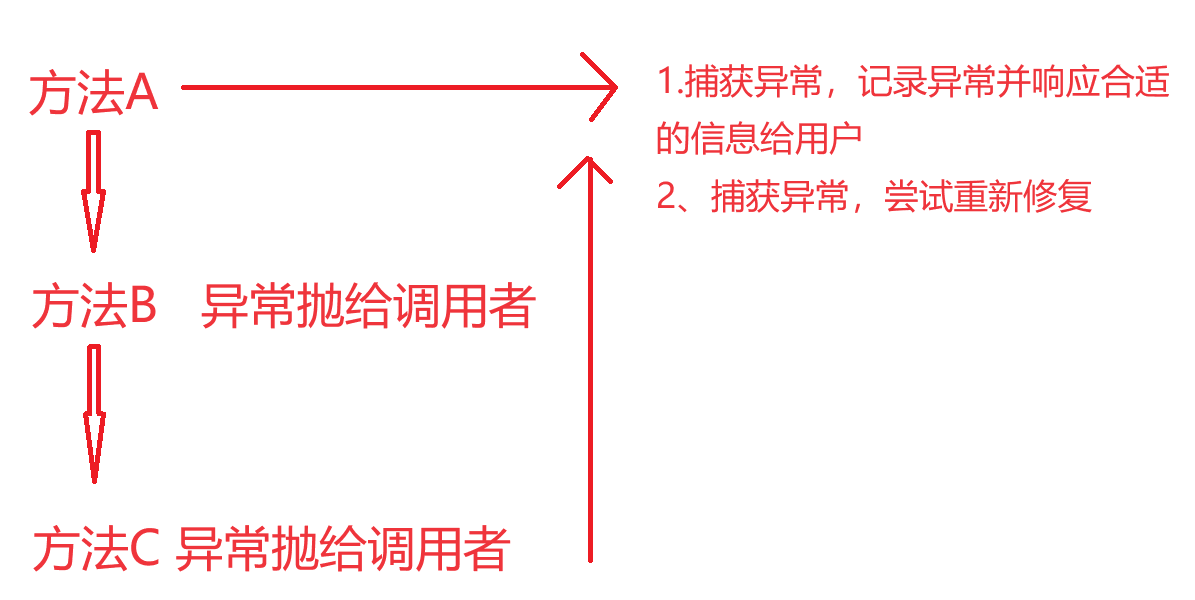
/**
* 处理异常方案一:捕获异常并响应合适的信息给用户
*/
public class ExceptionTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test1();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // 文件找不到异常
System.out.println("您要找的文件不存在!!");
e.printStackTrace(); // 打印出这个异常对象的信息,记录下来
} catch (ParseException e) { // 解析异常
System.out.println("您要解析的时间有问题!!");
e.printStackTrace(); // 打印出这个异常对象的信息,记录下来
}
}
public static void test1() throws FileNotFoundException, ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
Date d = sdf.parse("2025-5-20 10:24");
System.out.println(d);
test2();
}
public static void test2() throws FileNotFoundException {
// 读取文件
InputStream isr = new FileInputStream("D:/picture.png");
}
}
/**
* 处理异常方案二:捕获异常,尝试重新修复
*/
public class ExceptionTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:调用一个方法,让用户输入一个合适的价格返回为止
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println(getMoney()); // 只有输入合法的数字,while循环才会结束
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 捕获到异常,会提醒用户重新输入合法的数字
System.out.println("请您输入合法的数字!");
}
}
}
public static double getMoney() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入合适的价格:");
double money = sc.nextDouble(); // 如果用户不输入数字,就会有异常
if(money >= 0) {
return money;
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的价格是不合适的!");
}
}
}
}
抛出异常(throws)
- 在方法上使用throws关键字,可以将方法内部出现的异常,抛出去,给调用者处理
方法 throws 异常1,异常2,异常3... {
...
}
- // 推荐方法
方法 throws Exception {
...
} // Exception代表可以捕获一切异常
捕获异常(try - catch)
- 直接捕获程序出现的异常
try {
// 监视可能出现异常的代码!
} catch(异常类型1,变量) {
// 处理异常
} catch(异常类型2,变量) {
// 处理异常
}
- 推荐方法
try {
// 可能出现异常的代码
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Exception 代表可以捕获一切异常
处理异常写法上的优化
/**
* 处理异常写法上的优化
*/
public class ExceptionTest3_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test1();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("您当前操作有问题!!");
e.printStackTrace(); // 打印出这个异常对象的信息,记录下来
}
}
public static void test1() throws Exception{
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
Date d = sdf.parse("2025-5-20 10:24");
System.out.println(d);
test2();
}
public static void test2() throws Exception {
// 读取文件
InputStream isr = new FileInputStream("D:/picture.png");
}
}





















 301
301

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








