A 并查集
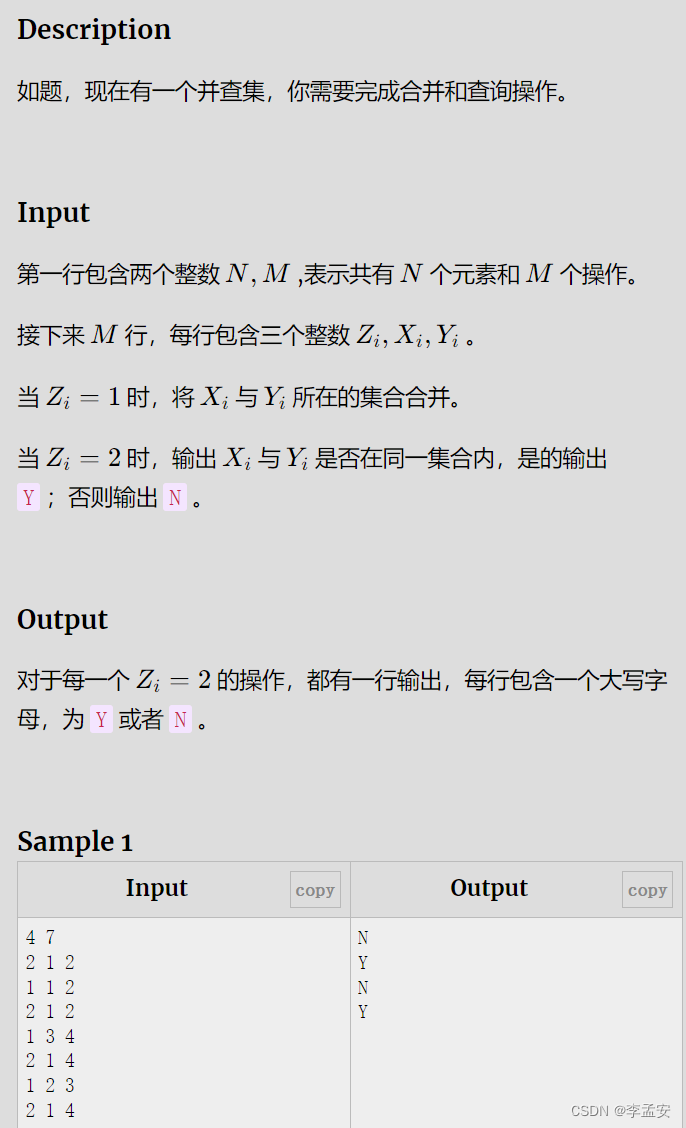
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int f[100086];
int n, m;
int find(int x){
if(f[x] == x) return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy) f[fy] = fx;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0);
while(cin>>n>>m){
int z, x, y;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
f[i] = i;
for(int i = 0;i < m; i++){
cin>>z>>x>>y;
if(z == 1) merge(x, y);
if(z == 2){
int a = find(x), b = find(y);
if(a == b) cout<<"Y"<<endl;
else cout<<"N"<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
B - 修复公路

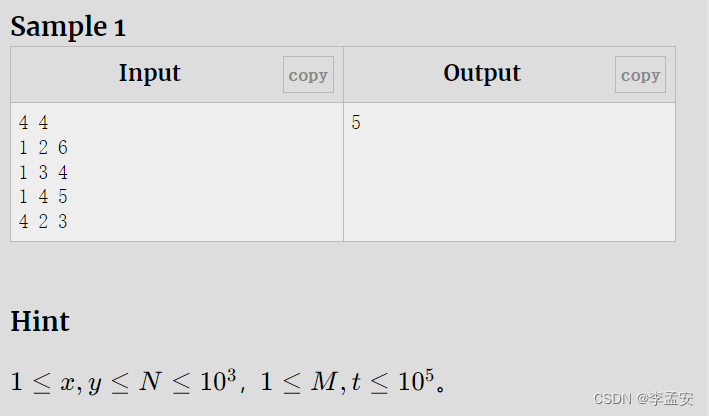
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int f[1005];
struct road
{
int x, y, t;
} rd[100860];
bool cmp(road x, road y)
{
return x.t < y.t;
}
int find(int x)
{
if (f[x] == x)
return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
if (x != y)
f[y] = x;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int cnt = 0, flg = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
f[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
cin >> rd[i].x >> rd[i].y >> rd[i].t;
sort(rd + 1, rd + m + 1, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int xx = find(rd[i].x), yy = find(rd[i].y);
if (xx != yy)
{ // 祖先不同则为两点不连通
merge(xx, yy);
cnt++;
}
if (cnt == n - 1)
{ // 本质是求最小生成树,当边 = n - 1时结束
flg = 1;
cout << rd[i].t << endl;
break;
}
}
if (!flg)
cout << "-1" << endl;
return 0;
}
C - 亲戚

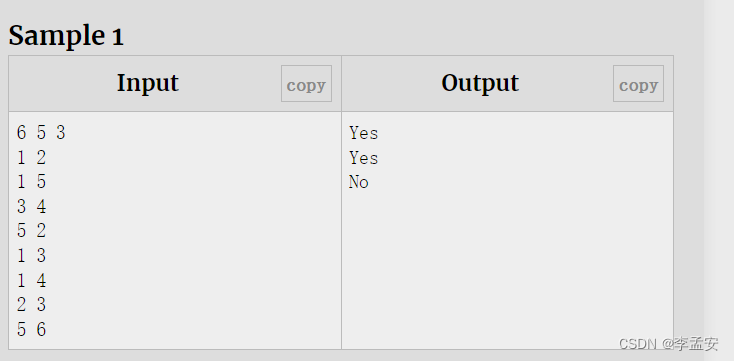
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int f[5003];
int find(int x){
if(f[x] == x) return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy) f[fy] = fx;
}
int main(){
int n, m, p;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>p;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
f[i] = i;
for(int i = 0;i < m; i++){
int x, y; cin>>x>>y;
merge(x, y);
}
for(int i = 0;i < p; i++){
int x, y; cin>>x>>y;
if(find(x) == find(y)) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
D - 一中校运会之百米跑

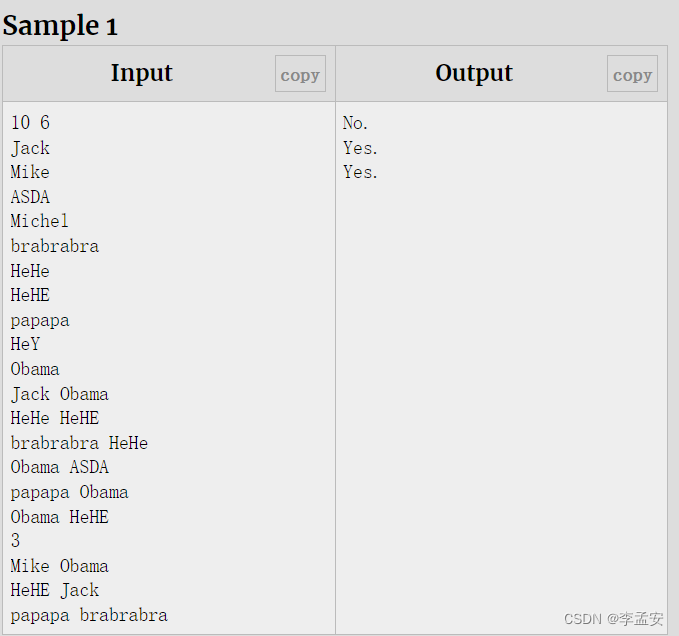
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int f[20086];
int find(int x){
if(x == f[x]) return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy) f[fy] = fx;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
map <string, int> mp;
int n, m; cin>>n>>m;
string x, y;
string name;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
f[i] = i;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
cin>>name;
mp[name] = i;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++){
cin>>x>>y;
merge(mp[x], mp[y]);
}
int k;cin>>k;
while(k--){
cin>>x>>y;
if(find(mp[x]) != find(mp[y])) cout<<"No."<<endl;
else cout<<"Yes."<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
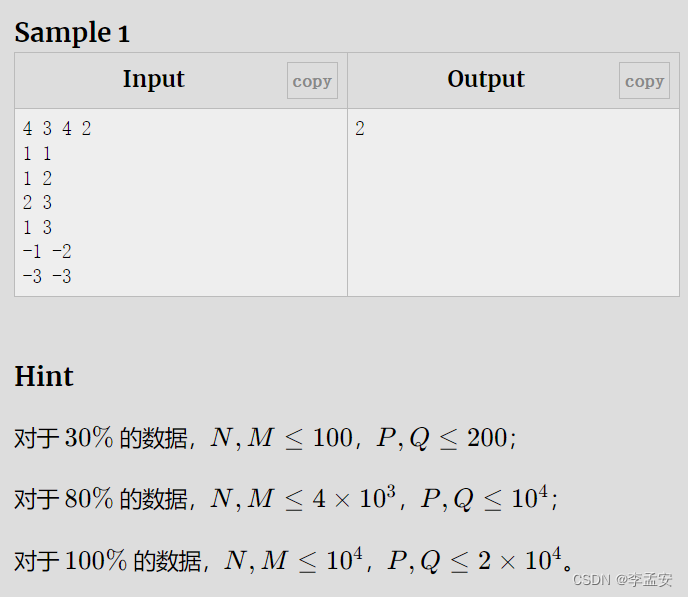
E - 朋友

代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fA[10086], fB[10086];
int findA(int x){
if(x == fA[x]) return x;
return fA[x] = findA(fA[x]);
}
int findB(int x){
if(x == fB[x]) return x;
return fB[x] = findB(fB[x]);
}
void mergeA(int x, int y){
int fx = findA(x),fy = findA(y);
if(fx != fy) fA[fy] = fx;
}
void mergeB(int x, int y){
int fx = findB(x),fy = findB(y);
if(fx != fy) fB[fy] = fx;
}
int main(){
int n, m, p, q;
cin>>n>>m>>p>>q;
int x, y;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
fA[i] = i;
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++)
fB[i] = i;
while(p--){
cin>>x>>y;
mergeA(x, y);
}
while(q--){
cin>>x>>y;
x *= -1;y *= -1;
mergeB(x, y);
}
x = y = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
if(findA(i) == findA(1))
x++;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++){
if(findB(i) == findB(1))
y++;
}
cout<<min(x, y)<<endl;
return 0;
}
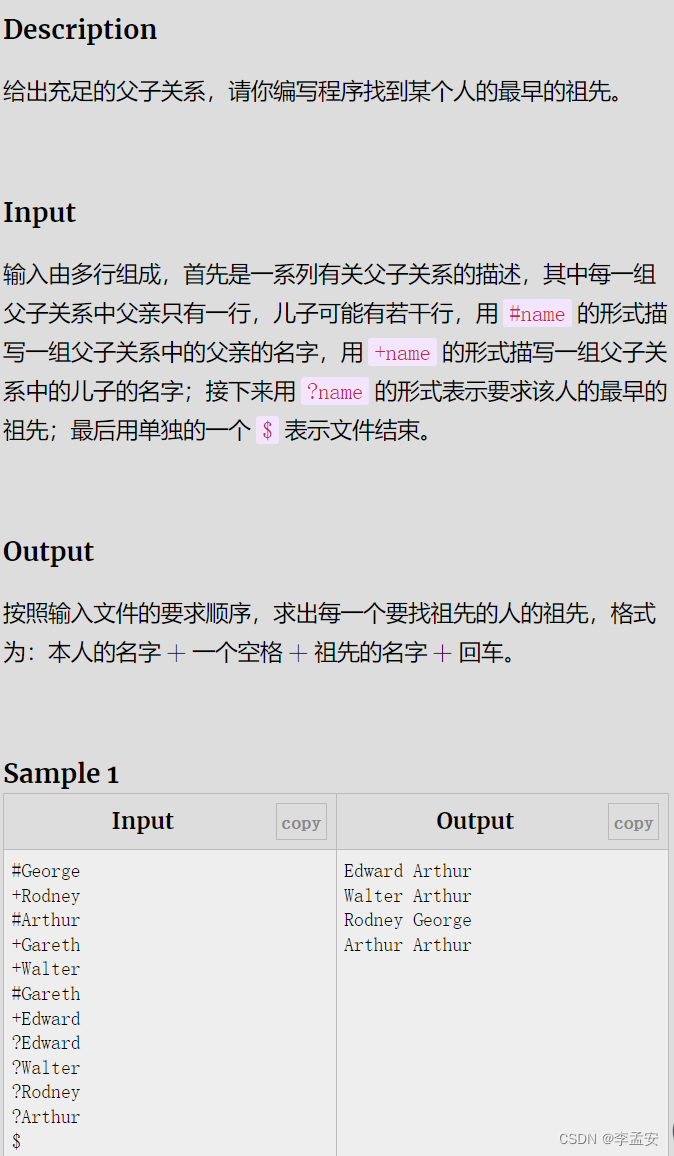
F - 家谱
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
map<string, string> f;
string find(string x){
if(x == f[x]) return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
int main(){
char c;
string father, son;
while(cin>>c && c != '$'){
if(c == '#'){
cin>>father;
if(!f.count(father))
f[father] = father;
}
if(c == '+'){
cin>>son;
f[son] = father;
}
if(c == '?'){
cin>>son;
cout<<son<<' '<<find(son)<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}





















 728
728











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








