文章目录
堆
计算机科学中,堆是一种基于树的数据结构,通常用完全二叉树实现。堆的特性如下
- 在大顶堆中,任意节点 C 与它的父节点 P 符合 P . v a l u e ≥ C . v a l u e P.value \geq C.value P.value≥C.value
- 而小顶堆中,任意节点 C 与它的父节点 P 符合 P . v a l u e ≤ C . v a l u e P.value \leq C.value P.value≤C.value
- 最顶层的节点(没有父亲)称之为 root 根节点
In computer science, a heap is a specialized tree-based data structure which is essentially an almost complete tree that satisfies the heap property: in a max heap, for any given node C, if P is a parent node of C, then the key (the value) of P is greater than or equal to the key of C. In a min heap, the key of P is less than or equal to the key of C. The node at the “top” of the heap (with no parents) is called the root node
例1 - 满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)特点:每一层都是填满的
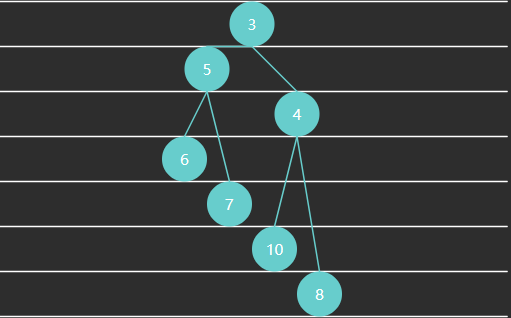
例2 - 完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)特点:最后一层可能未填满,靠左对齐
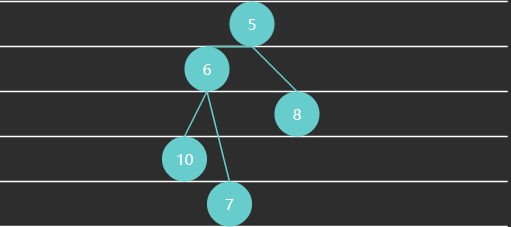
例3 - 大顶堆
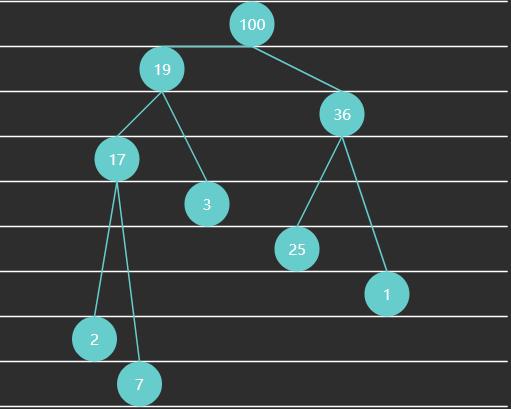
例4 - 小顶堆
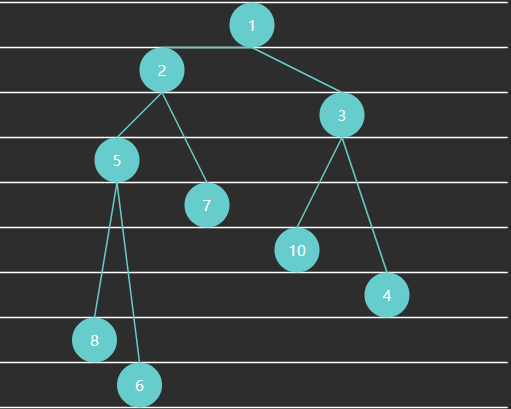
完全二叉树可以使用数组来表示
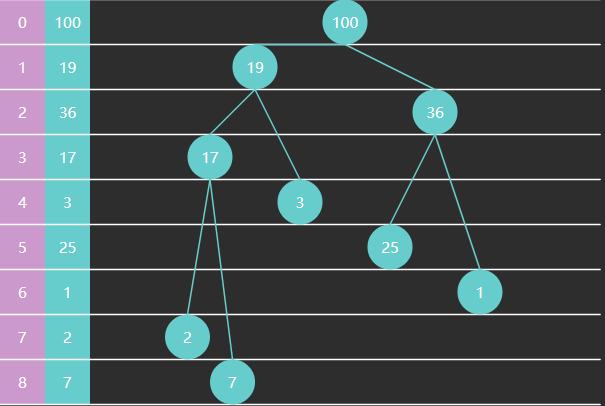
特征
- 如果从索引 0 开始存储节点数据
- 节点 i i i 的父节点为 f l o o r ( ( i − 1 ) / 2 ) floor((i-1)/2) floor((i−1)/2),当 i > 0 i>0 i>0 时
- 节点 i i i 的左子节点为 2 i + 1 2i+1 2i+1,右子节点为 2 i + 2 2i+2 2i+2,当然它们得 < s i z e < size <size
- 如果从索引 1 开始存储节点数据
- 节点 i i i 的父节点为 f l o o r ( i / 2 ) floor(i/2) floor(i/2),当 i > 1 i > 1 i>1 时
- 节点 i i i 的左子节点为 2 i 2i 2i,右子节点为 2 i + 1 2i+1 2i+1,同样得 < s i z e < size <size
Floyd 建堆算法
- 找到最后一个非叶子节点
- 从后向前,对每个节点执行下潜
一些规律
- 一棵满二叉树节点个数为 2 h − 1 2^h-1 2h−1,如下例中高度 h = 3 h=3 h=3 节点数是 2 3 − 1 = 7 2^3-1=7 23−1=7
- 非叶子节点范围为 [ 0 , s i z e / 2 − 1 ] [0, size/2-1] [0,size/2−1]
算法时间复杂度分析
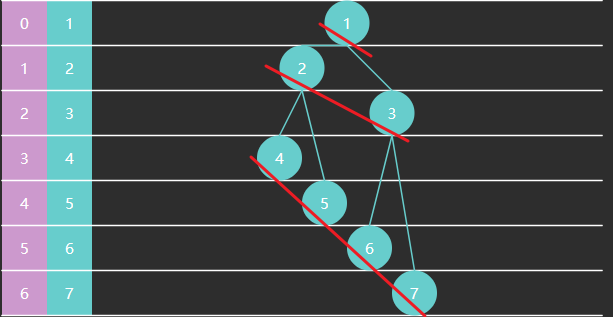
下面看交换次数的推导:设节点高度为 3
| 本层节点数 | 高度 | 下潜最多交换次数(高度-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4567 这层 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| 23这层 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 1这层 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
每一层的交换次数为:
节点个数
∗
此节点交换次数
节点个数*此节点交换次数
节点个数∗此节点交换次数,总的交换次数为
$$
\begin{aligned}
& 4 * 0 + 2 * 1 + 1 * 2 \
& \frac{8}{2}*0 + \frac{8}{4}*1 + \frac{8}{8}*2 \
& \frac{8}{2^1}*0 + \frac{8}{2^2}*1 + \frac{8}{2^3}*2\
\end{aligned}
即
即
即
\sum_{i=1}{h}(\frac{2h}{2^i}*(i-1))
$$
在 https://www.wolframalpha.com/ 输入
Sum[\(40)Divide[Power[2,x],Power[2,i]]*\(40)i-1\(41)\(41),{i,1,x}]
推导出
2
h
−
h
−
1
2^h -h -1
2h−h−1
其中
2
h
≈
n
2^h \approx n
2h≈n,
h
≈
log
2
n
h \approx \log_2{n}
h≈log2n,因此有时间复杂度
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n)
堆实现
public class MaxHeap {
// 存储堆中元素的数组
int[] array;
// 堆中当前元素的数量
int size;
// 构造函数,传入容量初始化堆数组
public MaxHeap(int capacity) {
// 创建一个指定容量的整数数组来存储堆中的元素
this.array = new int[capacity];
}
/**
* 获取堆顶元素
*
* @return 堆顶元素
*/
public int peek() {
// 返回数组中的第一个元素,即堆顶元素,因为在大顶堆中堆顶元素是最大的
return array[0];
}
/**
* 删除堆顶元素
*
* @return 堆顶元素
*/
public int poll() {
int top = array[0];
// 将堆顶元素与最后一个元素交换,这样可以方便地删除堆顶元素
swap(0, size - 1);
// 堆中元素数量减一,表示删除了一个元素
size--;
// 对新的堆顶元素进行下潜操作,以调整堆结构,保持大顶堆的性质
down(0);
// 返回原来的堆顶元素
return top;
}
/**
* 删除指定索引处元素
*
* @param index 索引
* @return 被删除元素
*/
public int poll(int index) {
int deleted = array[index];
// 将指定索引处的元素替换为极大值(Integer.MAX_VALUE),然后进行上浮操作,
// 这样在后续的操作中会将这个极大值移动到堆顶,然后再通过常规的删除堆顶元素的操作来删除该元素
up(Integer.MAX_VALUE, index);
// 删除堆顶元素(此时极大值已在堆顶)
poll();
// 返回被删除的元素
return deleted;
}
/**
* 替换堆顶元素
*
* @param replaced 新元素
*/
public void replace(int replaced) {
// 将新元素赋值给堆顶
array[0] = replaced;
// 对新的堆顶元素进行下潜操作,调整堆结构,确保新的堆顶元素在正确的位置上
down(0);
}
/**
* 堆的尾部添加元素
*
* @param offered 新元素
* @return 是否添加成功
*/
public boolean offer(int offered) {
if (size == array.length) {
// 如果堆已满,即当前元素数量等于数组的长度,返回 false,表示添加失败
return false;
}
// 将新元素进行上浮操作,调整堆结构,找到新元素在堆中的正确位置
up(offered, size);
// 堆中元素数量加一,表示成功添加了一个元素
size++;
// 返回添加成功
return true;
}
// 将 offered 元素上浮: 直至 offered 小于父元素或到堆顶
private void up(int offered, int index) {
int child = index;
// 当 child 大于 0 时,表示还没有到达堆顶
while (child > 0) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// 如果新元素大于父元素
if (offered > array[parent]) {
// 将父元素下移到子节点位置
array[child] = array[parent];
} else {
// 新元素小于等于父元素,停止上浮
break;
}
// 更新子节点索引为父节点索引,继续向上检查
child = parent;
}
// 将新元素放置在正确位置
array[child] = offered;
}
public MaxHeap(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
this.size = array.length;
// 建堆操作
heapify();
}
// 建堆
private void heapify() {
// 找到最后一个非叶子节点的索引,对于一个有 n 个元素的堆,最后一个非叶子节点的索引为 n/2 - 1
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 对每个非叶子节点进行下潜操作,构建堆
down(i);
}
}
// 将 parent 索引处的元素下潜: 与两个孩子较大者交换, 直至没孩子或孩子没它大
private void down(int parent) {
int left = parent * 2 + 1;
int right = left + 1;
int max = parent;
// 如果左子节点存在且大于当前最大元素
if (left < size && array[left] > array[max]) {
max = left;
}
// 如果右子节点存在且大于当前最大元素
if (right < size && array[right] > array[max]) {
max = right;
}
if (max!= parent) { // 找到了更大的孩子
// 交换最大子节点和父节点的元素
swap(max, parent);
// 继续对新的父节点进行下潜操作
down(max);
}
}
// 交换两个索引处的元素
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int t = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {2, 3, 1, 7, 6, 4, 5};
MaxHeap heap = new MaxHeap(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(heap.array));
while (heap.size > 1) {
heap.swap(0, heap.size - 1);
heap.size--;
heap.down(0);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(heap.array));
}
}























 118
118

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








