1、图像点的运算
1.1 线性灰度变换
假定原图像A(x,y)的灰度变换范围为[a,b],处理后的图像B(x,y)的灰度扩展为[c,d],利用imadjust()函数。
close all;clear all;clc;
gamma=0.5;
I=imread("YW.jpg");
R=I;
R(:,:,2)=0;
R(:,:,3)=0;
R1=imadjust(R,[0.5 0.8],[0 1],gamma);
G=I;
G(:,:,1)=0;
G(:,:,3)=0;
G1=imadjust(G,[0 0.3],[0 1],gamma);
B=I;
B(:,:,1)=0;
B(:,:,2)=0;
B1=imadjust(B,[0 0.3],[0 1],gamma);
I1=B1+G1+R1;
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(R);
subplot(122),imshow(R1);
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(G);
subplot(122),imshow(G1);
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(B);
subplot(122),imshow(B1);
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(I);
subplot(122),imshow(I1);
结果:
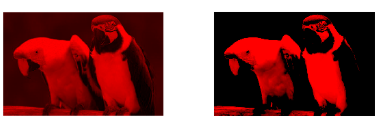

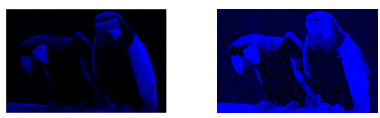

针对图像,分别获得R、G、B图像,然后通过imadjust()中参数gamma对图像进行线性灰度变换,比较三个通道变换。
1.2分段线性灰度变换
首先将彩色图像变为灰度图像,寻找灰度值小于35的像素点,将原图的灰度值扩大10倍。再找到灰度值再35-75的像素点 H(x,y)=(10/7)*[J(x,y)-5]+50。最后大于75的像素点 H(x,y)=(105/180)*[J(x,y)-75]+150。
close all;clear all;clc;
R=imread("YW.jpg");
J=rgb2gray(R);
[M,N]=size(J);
x=1;
y=1;
for x=1:M
for y=1:N
if(J(x,y)<=35);
H(x,y)=J(x,y)*10;
elseif (J(x,y)>35&J(x,y)<=75);
H(x,y)=(10/7)*[J(x,y)-5]+50;
else (J(x,y)>75);
H(x,y)=(105/180)*[J(x,y)-75]+150;
end
end
end
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(J);
subplot(122),imshow(H);
1.3非线性灰度变换
当输出图像的像素点灰度值和输入图像的像素点灰度值不满足线性关系时,这种灰度变换都成为非线性灰度变换 。
eg:基于对数变换的非线性灰度变换:g(x,y)=a+ln[f(x,y)+1]/(b*lnc)
其中a、b、c是为了调整曲线的位置和形状而引入的参数。图像通过对数变换可扩展低灰度值、压缩高灰度值。
对图像进行分段式灰度变换具体代码如下:
close all;clear all;clc;
I=imread("YW.jpg");
G=rgb2gray(I);
J=double(G);
H=(log(J+1))/10;
figure;
imshow(I);
figure;
imshow(G);
figure;
imshow(H);2、图像代数运算
将两幅图进行加减乘除得到输出图像的方法称为图像代数运算。
具体代数表达式如下:
注意!!!
由于MATLAB中图像的数据类型时unit8,当进行迭代时可能会产生属性溢出,所以应当在进行图像代数运算之前首先将数据类型转换成double,从而保证结果准确性。
I=double(G);具体代码实现如下:
2.1 图像叠加
close all;clear all;clc;
i=imread("rice.png");
j=imread("cameraman.tif");
I=double(i);
J=double(j);
K=imadd(i,j);
figure,
subplot(131);imshow(i);
subplot(132);imshow(j);
subplot(133);imshow(K);结果:

2.2 加常数,改变亮度
close all;clear all;clc;
I=imread('flower.tif');
J=imadd(I,30);
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(I);
subplot(122),imshow(J);结果:

注意!!! 图像加法的重要应用是降噪!!
通过同一图像叠加取平均,消除原图像中的附加噪声,其基本原理为巴拉巴拉~(自行百度啦~)
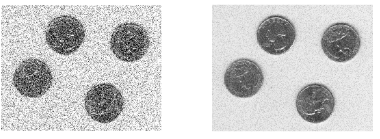
函数:J=imnoise(I,type,parameters):该函数是对图像I添加典型噪声后生成的有噪图像,结果返回J。其中I为原始图像,type为添加的噪声类型,取值可以是高斯噪声Gaussian等。
具体代码如下:
close all;clear all;clc;
RGB=imread('eight.tif');
A=imnoise(RGB,'gaussian',0,0.05);
I=A;
M=3;
I=im2double(I);
RGB=im2double(RGB);
for i=1:M
I=imadd(I,RGB);
end
avg_A=I/(M+1);
figure,
subplot(121);imshow(A);
subplot(122);imshow(avg_A);结果:
函数版本:
Denoise.m
function [BW]=Dennoise(RGB,M)
A=imnoise(RGB,'gaussian',0,0.05);
I=A;
I=im2double(I);
RGB=im2double(RGB);
for i=1:M
I=imadd(I,RGB);
end;
avg_A=I/(M+1);
BW=avg_A;主函数:
close all;clear all;clc;
RGB=imread('eight.tif');
M1=3;
[BW1]=Dennoise(RGB,4);
[BW2]=Dennoise(RGB,9);
figure;
imshow(RGB);
figure;
disp('叠加四次结果:\n');
imshow(BW1);
figure;
disp('叠加九次结果:\n');
imshow(BW2);结果:

2.2 图像的减法运算
利用减法实现DSA减影,具体代码如下:
close all;clear all;clc;
A=imread('cameraman.tif');
B=imread('testpat1.png');
C=imsubtract(A,B);
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(A);
subplot(122),imshow(B);
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(C);
subplot(122),imshow(255-C);




















 3185
3185











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








