Android GPS源码分析总结
本篇主要包括如下内容:
1. 术语介绍
2. 应用层开发总结
3. framework分析
4. HAL层接口介绍
1. 术语介绍
1.1 GNSS
GNSS为Global Navigation Satellite System的缩写,即全球导航卫星系统。当前应用较广泛的主要有美国的GPS、俄罗斯的GLONASS、欧盟的GALILEO和中国北斗卫星导航系统等4大GNSS系统。
1.2 NMEA-0183
NMEA 0183是美国国家海洋电子协会(National Marine Electronics Association )为海用电子设备制定的标准格式。目前业已成了GPS导航设备统一的RTCM(Radio Technical Commission for Maritime services)标准协议。
NMEA-0183协议采用ASCII码,定义的语句非常多,但是常用的只有$GPGGA、$GPGSA、$GPGSV、$GPRMC、$GPVTG、$GPGLL等。举个例子如下:
$GPGGA,<1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>,<8>,<9>,M,<10>,M,<11>,<12>*hh<CR><LF>
<1> UTC时间,hhmmss(时分秒)格式
<2> 纬度ddmm.mmmm(度分)格式(前面的0也将被传输)
<3> 纬度半球N(北半球)或S(南半球)
<4> 经度dddmm.mmmm(度分)格式(前面的0也将被传输)
<5> 经度半球E(东经)或W(西经)
<6> GPS状态:0=未定位,1=非差分定位,2=差分定位,6=正在估算
<7> 正在使用解算位置的卫星数量(00~12)(前面的0也将被传输)
<8> HDOP水平精度因子(0.5~99.9)
<9> 海拔高度(-9999.9~99999.9)
<10> 地球椭球面相对大地水准面的高度
<11> 差分时间(从最近一次接收到差分信号开始的秒数,如果不是差分定位将为空)
<12> 差分站ID号0000~1023(前面的0也将被传输,如果不是差分定位将为空)
1.3 GIS
地理信息系统(GIS,Geographic Information System)是一门综合性学科,结合地理学与地图学以及遥感和计算机科学,已经广泛的应用在不同的领域,是用于输入、存储、查询、分析和显示地理数据的计算机系统,随着GIS的发展,也有称GIS为“地理信息科学”(Geographic Information Science),近年来,也有称GIS为"地理信息服务"(Geographic Information service)。
1.4 地理编码
地理编码指将地名的详细地址以地理坐标(如经纬度)表示的过程。其中,将地址信息映射为地理坐标的过程称之为地理编码;将地理坐标转换为地址信息的过程称之为逆地理编码。
2. 应用层开发
2.1 AndroidManifest.xml中权限添加
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FIND_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"></uses-permission>
2.2 Interfaces
| GpsStatus.Listener | This interface was deprecated in API level 24. use GnssStatus.Callback instead. |
| GpsStatus.NmeaListener | This interface was deprecated in API level 24. use OnNmeaMessageListener instead. |
| LocationListener | Used for receiving notifications from the LocationManager when the location has changed. |
| OnNmeaMessageListener | Used for receiving NMEA sentences from the GNSS. |
2.3 Classes
| Address | A class representing an Address, i.e, a set of Strings describing a location. |
| Criteria | A class indicating the application criteria for selecting a location provider. |
| Geocoder | A class for handling geocoding and reverse geocoding. |
| GnssClock | A class containing a GPS clock timestamp. |
| GnssMeasurement | A class representing a GNSS satellite measurement, containing raw and computed information. |
| GnssMeasurementsEvent | A class implementing a container for data associated with a measurement event. |
| GnssMeasurementsEvent.Callback | Used for receiving GNSS satellite measurements from the GNSS engine. |
| GnssNavigationMessage | A class containing a GNSS satellite Navigation Message. |
| GnssNavigationMessage.Callback | Used for receiving GNSS satellite Navigation Messages from the GNSS engine. |
| GnssStatus | This class represents the current state of the GNSS engine. |
| GnssStatus.Callback | Used for receiving notifications when GNSS events happen. |
| GpsSatellite | This class was deprecated in API level 24. use GnssStatus and GnssStatus.Callback. |
| GpsStatus | This class was deprecated in API level 24. use GnssStatus and GnssStatus.Callback. |
| Location | A data class representing a geographic location. |
| LocationManager | This class provides access to the system location services. |
| LocationProvider | An abstract superclass for location providers. |
| SettingInjectorService | Dynamically specifies the summary (subtitle) and enabled status of a preference injected into the list of app settings displayed by the system settings app For use only by apps that are included in the system image, for preferences that affect multiple apps. |
2.4 sample code
进行GPS应用开发牵涉到的接口或类位于android.location这个package,使用流程大体如下。

3. framework分析
3.1 类图

说明如下:
1.GPS Framework逻辑设计上可分为GPS Client和GPS Server两部分,两者之间基于接口进行通信(Binder机制):ILocationListner、IGpsStatusListner、ILocationManager等。开发上的依赖关系为:APK -> GPS Client -> GPS Server -> GPS HAL Layer;
2.ILocationManager的Bn端实现为LocationManagerService,供GPS Client端调用;
3.这里的GPS Client并不是绝对的充当Client(客户端)角色,其中的LocationListner、IGpsStatusListner的接口实现类(Bn端)充当Server(服务端)角色,供HAL层间接调用以通知GPS状态信息;
4.蓝色标注的部分为HAL层接口,后面会介绍。
5.GPS Client端的关键类设计意图上面已有介绍,这里摘录GPS Server端几个关键类的设计意图如下:
/**
* System private API for talking with the location service.
*
* @hide
*/
interface ILocationManager{
......
}
/**
* The service class that manages LocationProviders and issues location
* updates and alerts.
*/
public class LocationManagerService extends ILocationManager.Stub {
......
}
/**
* Location Manager's interface for location providers.
* @hide
*/
public interface LocationProviderInterface {
public String getName();
public void enable();
public void disable();
public boolean isEnabled();
public void setRequest(ProviderRequest request, WorkSource source);
public void dump(FileDescriptor fd, PrintWriter pw, String[] args);
// --- deprecated (but still supported) ---
public ProviderProperties getProperties();
public int getStatus(Bundle extras);
public long getStatusUpdateTime();
public boolean sendExtraCommand(String command, Bundle extras);
}
/**
* A GPS implementation of LocationProvider used by LocationManager.
*
* {@hide}
*/
public class GpsLocationProvider implements LocationProviderInterface {
......
}3.2 序列图
3.2.1 GPS Client端初始化

上图主要完成开机后LocationManger的实例创建,App开发人员可以透过context.getSystemService()获取到此实例。
3.2.2 GPS Server端初始化
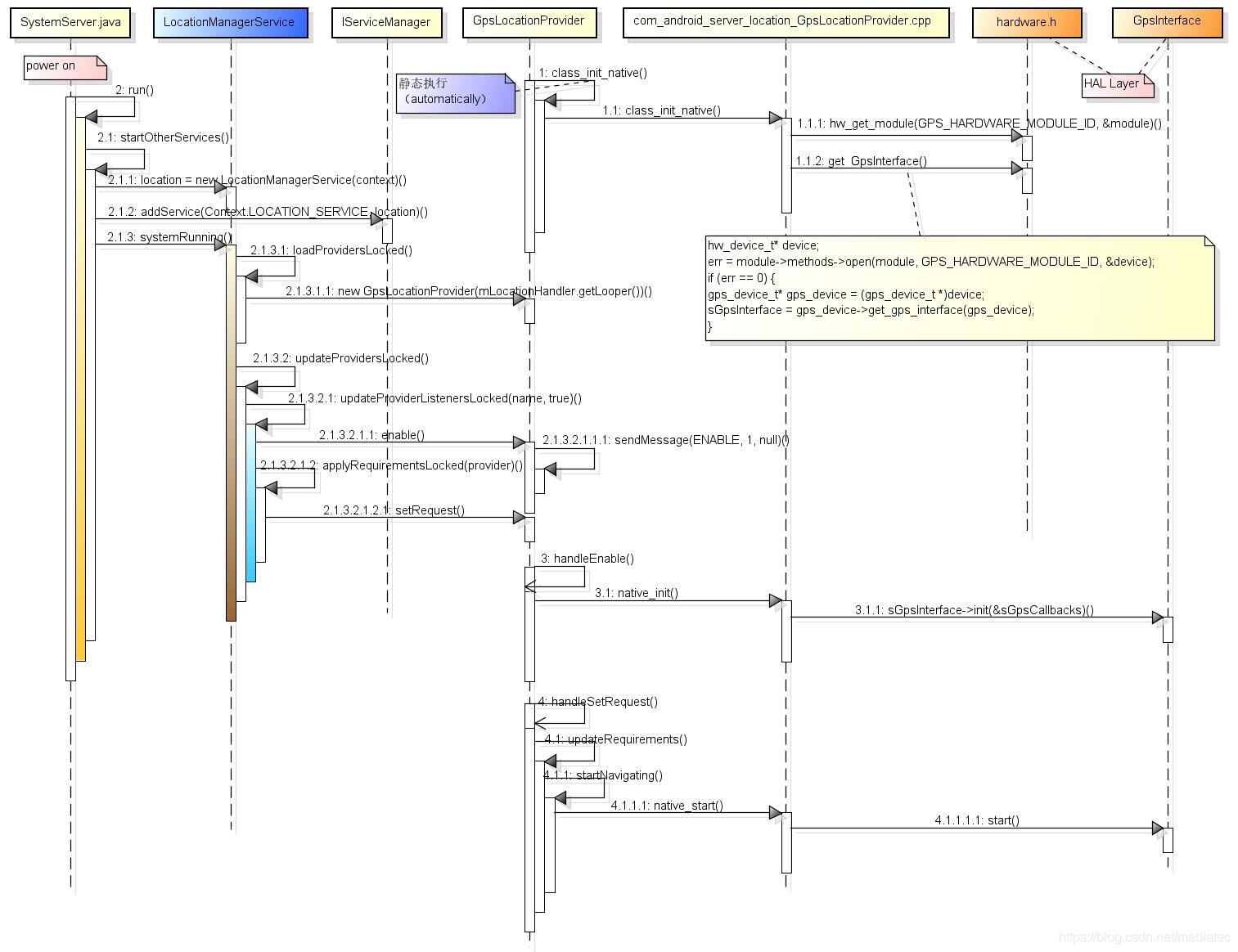
上图主要完成了LocationManagerService的创建、注册以及GPS Module(HAL Layer)的初始化动作,细节请参考源码。
4. HAL层接口介绍
/** Represents a location. */
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(GpsLocation) */
size_t size;
/** Contains GpsLocationFlags bits. */
uint16_t flags;
/** Represents latitude in degrees. */
double latitude;//纬度
/** Represents longitude in degrees. */
double longitude;//经度
/** Represents altitude in meters above the WGS 84 reference
* ellipsoid. */
double altitude;//高度
/** Represents speed in meters per second. */
float speed;//速度
/** Represents heading in degrees. */
float bearing;//方位角
/** Represents expected accuracy in meters. */
float accuracy;
/** Timestamp for the location fix. */
GpsUtcTime timestamp;
} GpsLocation;
/** GPS callback structure. */
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(GpsCallbacks) */
size_t size;
//位置信息
gps_location_callback location_cb;
//GPS状态信息
gps_status_callback status_cb;
//卫星信息
gps_sv_status_callback sv_status_cb;
//NMEA log信息
gps_nmea_callback nmea_cb;
//GPS支持度
gps_set_capabilities set_capabilities_cb;
//This can be used to prevent the CPU from suspending while handling GPS events.
gps_acquire_wakelock acquire_wakelock_cb;
//Callback utility for releasing the GPS wakelock.
gps_release_wakelock release_wakelock_cb;
//Callback for creating a thread that can call into the Java framework code.
gps_create_thread create_thread_cb;
//Callback for requesting NTP time
gps_request_utc_time request_utc_time_cb;
} GpsCallbacks;
/** GPS status event values. */
//GPS状态定义
typedef uint16_t GpsStatusValue;
// IMPORTANT: Note that the following values must match
// constants in GpsLocationProvider.java.
/** GPS status unknown. */
#define GPS_STATUS_NONE 0
/** GPS has begun navigating. */
#define GPS_STATUS_SESSION_BEGIN 1
/** GPS has stopped navigating. */
#define GPS_STATUS_SESSION_END 2
/** GPS has powered on but is not navigating. */
#define GPS_STATUS_ENGINE_ON 3
/** GPS is powered off. */
#define GPS_STATUS_ENGINE_OFF 4
/** Represents the status. */
//状态信息
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(GpsStatus) */
size_t size;
GpsStatusValue status;
} GpsStatus;
/** Represents SV information. */
//卫星信息
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(GpsSvInfo) */
size_t size;
/** Pseudo-random number for the SV. */
int prn;//卫星编号
/** Signal to noise ratio. */
float snr;//信号强度
/** Elevation of SV in degrees. */
float elevation;//仰望角
/** Azimuth of SV in degrees. */
float azimuth;//方位角
} GpsSvInfo;
/** Represents the standard GPS interface. */
typedef struct {
/**
* Opens the interface and provides the callback routines
* to the implementation of this interface.
*/
// 注册callback
int (*init)( GpsCallbacks* callbacks );
/** Starts navigating. */
// 启动定位
int (*start)( void );
/** Stops navigating. */
// 取消定位
int (*stop)( void );
/** Closes the interface. */
// 关闭GPS
void (*cleanup)( void );
......
} GpsInterface;参考:
1,https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/android/location/package-summary.html
2,https://baike.baidu.com/item/NMEA-0183/1810482?fr=aladdin
3,http://www.cnblogs.com/ljf181275034/articles/3238087.html
3,android 6.0源码






















 716
716











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








