1. The difference between Angular and JQuery
AngularJS is a very popular JS frameworks. The main difference between Angular and JQuery is that Angular is skilled at data update, and JQuery is more about DOM manipulation. So we can say that JQuery is a library.
Library: a collection of functions which are useful. Your code is in charge.
Frameworks: a particular implementation of a web application, where your code fills in the details. The framework is in charge.
Angular: declarative programming.
JQuery: imperative (procedural) programming
2. What is Angular
Structural framework for dynamic web applications:
- HTML only does static documents
Angular fills in the gap to support dynamic app
Angular is designed with CRUD applications(data-driven) via declarative approach
The basic properties of Angular are as follow:
Two-way Data Binding, Modules, Controller, Templates, Factory, Service, Provider. etc.
I will go details about these properties in the next sections.
3. Getting started using Angular
Include the Angular JS code
<script src="scripts/angular.min.js"></script>Add ng-app directive to the html tag. “ng-app” directive will tell the server that this page will be under the control of AngularJS. And the server will analyze this page based on angular syntax. (you can also attach this directive to other tag, only the scope will be different)
Angular expressions is evaluated against an angular scope object. There is no conditionals, loops or exceptions. All expressions enclosed in {{expression}}
4. Some Angular Built-in Directives
The directive programming in action, declaratively call JavaScript functions. Just like the data-* attributes in Bootstrap/JQuery. (you don’t need to write a single row of JS code to build dynamic web application)
ng-init Directive
This is used to “evaluate an expression” and “initialize a JS variable”
This directive is not very common. we have a better way to initialize variables. (By using scope, we can easily bind the variable in controller to the model)ng-model Directive
The ng-model binds the input value (which in the html tag property) to a variable within the scope (which in the controllerjs. And we can use {{object.var}} to recall it in the controller and display it in the page). So when any of them is changed, the other will be changed accordingly.Example:
<div>
...
<p>{{dish.description}}</p>
<p>comment:{{dish.comment}}</p>
<p>Type your comment:
<input type="text" ng-model="dish.comment"></p>
<!-- This dish is an object in the controller, and when we type something in the input, the text will be displayed in above -->
</div>Note: this div code block is called a template, All the service, controller, factory are based on one template. These components can manage the business logic of its corresponding template.
When Angular starts your application, it parses and processes the new makeup from template using compiler.
The makeup can be seen as the new features of AngularJS, like the directives, {{expression}} .
- ng-repeat Directive
The ng-repeat directive is a looping construct.
-Loops over items in a collection.
-Instantiates a template for each item
<div class="col-xs-9 col-xs-offset-1">
<label>Customer Comments</label><span style="color:#777777; font-size:13px; margin-left: 25px;">Sort by:</span><input type="text" ng-model="orderText">
<!-- if there are 4 comment in the comments object, here there will be 4 <blockquote> in this div-->
<blockquote ng-repeat="comment in dishDetailCtrl.dish.comments | orderBy:orderText">
<p>{{comment.rating}} Stars</p>
<p>{{comment.comment}}</p>
<footer>{{comment.author}}, {{comment.date | date: 'mediumDate'}}</footer>
</blockquote>
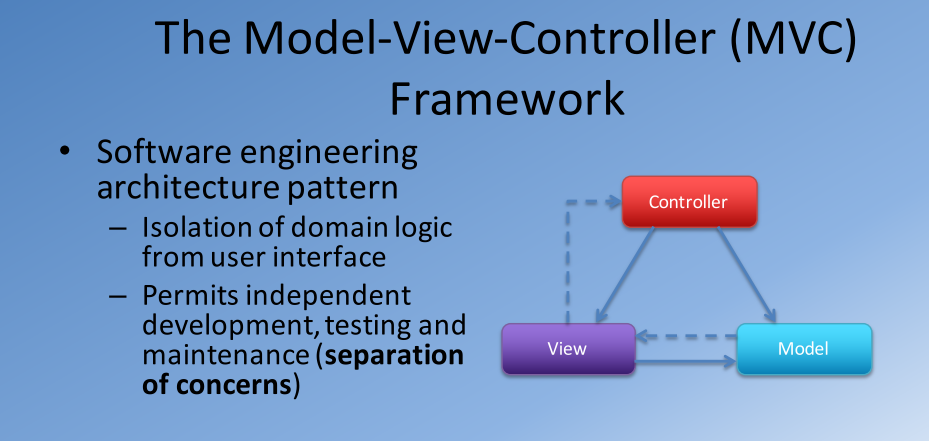
</div>5. Angular framework architecture - MVC
Model:
- manages the behavior and data
- responds to requests from view (get data) or from controller (change data)
- In event-driven systems, the model notifies views when the data changes so that they can react
View
- Renders the model(data) into a form for interaction
- Multiple views can exist for a single model
Controller
- receive user input and initiates a response by recalling on model object
- accept input from user and instruct the model and view to perform actions based on the input
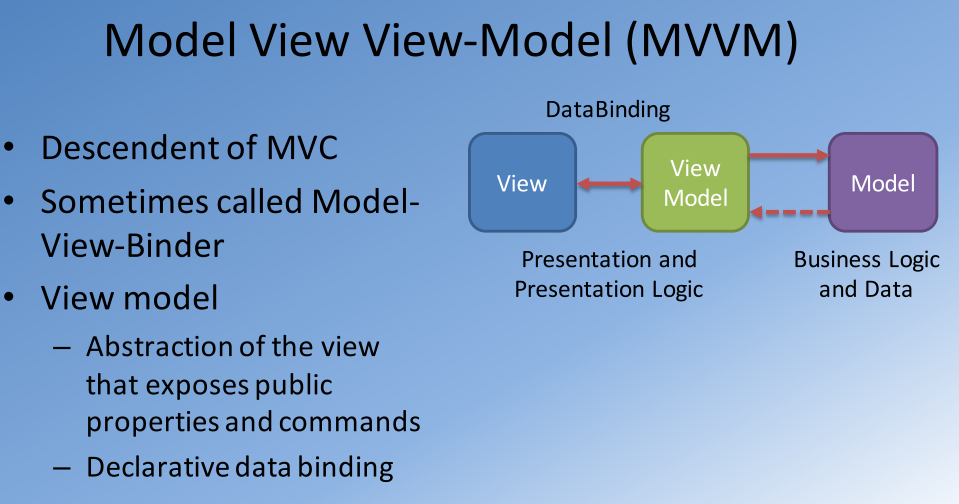
Another descendent of MVC (MVVM)
6. Angular Modules and Controllers
Note: here Module is not model. model is the data shown to the user in the view. Module is a container for the different parts of an app including controllers, services, filters, directives which configures the injector.
- Module
Angular Module is declared by the ng-app directive in html page. Like:
<!-- "confusionApp" is the name of this module -->
<html ng-app="confusionApp">
...
<script>
var app=angular.module('confusionApp', []);
// get this module (container) by this method
</script>
</html>- Controller
Controller defined using a ng-controller dircetive on an HTML element. Like:
<div class="row row-content" ng-controller="menuController">
... this div and its children element will be controlled by "menuController"
</div>But how to use this controller?
First, we need to add this controller into our Module (Container), like
<script>
var app = angular.module('confusionApp',[]).controller('menuController', function(){
//....
});
/*This is chain format, we can add as many controllers as we expected. Different controllers manage different part of the html page. Every controller has a constructor function that creates the actual controller instance.*/
</script>The purpose of controllers is to expose variables and functionality to expressions and directives.
Here is an example from official website:
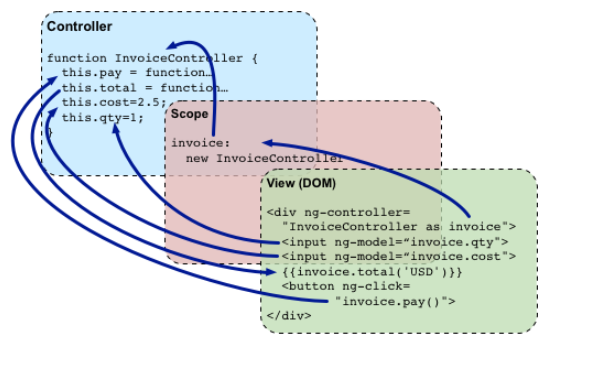
Conceptual Overview
angular.module('invoice1', [])
.controller('InvoiceController', function() {
//we can see controller as a class, which contain //functions and attributes
this.qty = 1;
this.cost = 2;
this.inCurr = 'EUR';
this.currencies = ['USD', 'EUR', 'CNY'];
this.usdToForeignRates = {
USD: 1,
EUR: 0.74,
CNY: 6.09
};
this.total = function total(outCurr) {
return this.convertCurrency(this.qty * this.cost, this.inCurr, outCurr);
};
this.convertCurrency = function convertCurrency(amount, inCurr, outCurr) {
return amount * this.usdToForeignRates[outCurr] / this.usdToForeignRates[inCurr];
};
this.pay = function pay() {
window.alert("Thanks!");
};
});So we can use its functions and attributes in the html page:
<div ng-app="invoice1" ng-controller="InvoiceController as invoice">
<b>Invoice:</b>
<div>
Quantity: <input type="number" min="0" ng-model="invoice.qty" required >
</div>
<div>
Costs: <input type="number" min="0" ng-model="invoice.cost" required >
<select ng-model="invoice.inCurr">
<option ng-repeat="c in invoice.currencies">{{c}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<div>
<b>Total:</b>
<span ng-repeat="c in invoice.currencies">
{{invoice.total(c) | currency:c}}
</span>
<button class="btn" ng-click="invoice.pay()">Pay</button>
</div>
</div>7. Angular Filter
A filter allows us to format the value of an expression for display to end user. They do not modify the underlying data.
There are some built-in filters:
- The format of filters in view templates
{{expression | filter}} eg. {{ 12 | currency }}; display $12.00
lt can be applied to the result of another filter:
{{expression | filter1 | filter2 | ... }} // filter chaining
if we want to add arguments for the filter. The syntax is
{{ expression | filter:argument1:argument2:... }} - Filters in controllers, services and directives
For this, inject a dependency with the name (filterName)Filter into your controller/service/directive. E.g. a filter called number is injected by using the dependency numberFilter. The injected argument is a function that takes the value to format as first argument, and filter parameters starting with the second argument.
angular.module('FilterInControllerModule', []).
controller('FilterController', ['filterFilter', function(filterFilter) {
this.array = [
{name: 'Tobias'},
{name: 'Jeff'},
{name: 'Brian'},
{name: 'Igor'},
{name: 'James'},
{name: 'Brad'}
]; //this 'filterFilter' is the name of FILTER, which has been injected to this controller.
this.filteredArray = filterFilter(this.array, 'a');
}]);
Additional Resources for Filtere:Filter components in ng
A very good example for combining filter and ng-click:
<div class="row row-content"
ng-controller="menuController as menuCtrl">
<div class="col-xs-12">
<!-- ul is navigation bar -->
<ul class="nav nav-tabs" role="tablist">
<li role="presentation"
ng-class="{active:menuCtrl.isSelected(1)}">
<a ng-click="menuCtrl.select(1)"
aria-controls="all menu"
role="tab">The Menus</a></li>
<li role="presentation" ng-class="{active:menuCtrl.isSelected(2)}">
<a ng-click="menuCtrl.select(2)"
aria-controls="appetizers"
role="tab">Appetizers</a></li>
<li role="presentation" ng-class="{active:menuCtrl.isSelected(3)}">
<a ng-click="menuCtrl.select(3)"
aria-controls="mains"
role="tab">Mains</a></li>
<li role="presentation" ng-class="{active:menuCtrl.isSelected(4)}">
<a ng-click="menuCtrl.select(4)"
aria-controls="desserts"
role="tab">Desserts</a></li>
</ul>
<div class="tab-content">
<ul class="media-list">
<li class="media" ng-repeat="dish in menuCtrl.dishes | filter:menuCtrl.filtText">
<div class="media-left media-middle">
<a href="#">
<img class="media-object img-thumbnail"
ng-src={{dish.image}} alt="Uthappizza">
</a>
</div>
<div class="media-body">
<h2 class="media-heading">{{dish.name}}
<span class="label label-danger">{{dish.label}}</span>
<span class="badge">{{dish.price | currency}}</span></h2>
<!--<p>{{dish.description}}</p>
<p>Comment: {{dish.comment}}</p>
<p>Type your comment:
<input type="text" ng-model="dish.comment"></p>-->
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Note: ng-class can dynamically add a class according to its argument
ng-class=”{active:menuCtrl.isSelected(3)}”; “active” which a class name will be add to its tag when “menuCtrl.isSelected(3)” is ture.
8. Angular Factory and Service
- Angular Services
a. Substitutable objects wired together using DI(dependency Injection);
b. Allows organizing and sharing code across an app;
c. Lazily instantiated;
d. Singletons;
Note: Angular has some built-in services, start with $ , like scope, http, rootScope, location, parse, animate, injector, Inject them using DI. More Built-in Services
How to Creating Services:
Service(), factory(), provider(), constant(), value(). these five functions declare services.
Angular Service Example:
angular.module('confusionApp')
.constant("baseURL", "http://localhost:3000/")
.service('menuFactory', ['$http', '$resource', 'baseURL', function ($http, $resource, baseURL) {
/* we define this service name - "menuFactory", and inject $http, $resource to this service */
this.getDishes = function () {
return $resource(baseURL + "dishes/:id", null, {'update': {method: 'PUT'}});
};
this.getDish = function (index) {
return $http.get(baseURL + "dishes/" + index);
};
// implement a function named getPromotion
// that returns a selected promotion.
this.getPromotions = function () {
//return $http.get(baseURL + "promotions/" + index);
return $resource(baseURL + "promotions/:id", null, {'update': {method: 'PUT'}});
};
this.getPromotion = function (index) {
return $http.get(baseURL + "promotions/" + index);
};
}])Angular Factory Example:
angular.module('confusionApp')
.factory('feedbackFactory', ['$resource', 'baseURL', function ($resource, baseURL) {
// here, 'feedbackFactory' is the name of the factory
var feedbackfac = {};
feedbackfac.getfeedback = function () {
return $resource(baseURL + "feedback/:id", null, {'update': {method: 'put'}})
};
return feedbackfac;
}])NOTE: Except using service instance to register a service, factory function that will create this instance when called. (Above is an example). But when we use factory, we need declare an object to represent a factory, and add some variables or functions which you need. At last, don’t forget to return it.
Summary for service: From the above explain, we can see service as a class, which contain some useful variables and functions, which can be used in other component (controller, service, filter or directive) that specifies a dependency on the service
Services: (return function itself)
Syntax: module.service( ‘serviceName’, function ); Result:
When declaring serviceName as an injectable argument you will be
provided with an instance of the function. In other words new
FunctionYouPassedToService().Factory: (return the function’s return value)
Syntax: module.factory( ‘factoryName’, function ); Result:
When declaring factoryName as an injectable argument you will be
provided with the value that is returned by invoking the function
reference passed to module.factory.Providers:(return the function’s $get() function value)
Syntax: module.provider( ‘providerName’, function );
Result: When declaring providerName as an injectable argument you will
be provided with (new ProviderFunction()). get(). The constructor
function is instantiated before the get method is called -
ProviderFunction is the function reference passed to module.provider.Providers have the advantage that they can be configured during the
module configuration phase.
9. Dependency Injection in Angularjs
Software design patten that implements iversion of control for resolving dependencies.
- Dependency: an object or a class that can be used (a service that has some useful function)
- Injection: passing of a dependency to a dependent object so that it can use it. The client does need to build the object.
So the dependency and injection are both objects. But injection is referencing to dependency. (we can image that dependency will be a class which is declared in injection. So the injection can use any propeties in the dependency).
There are three ways for a component to get hold of its dependencies
1. Create dependency using new operator
2. Look up dependency using a global variable
3. Have dependency passed to it where needed
The third option is most flexible.
Dependency Injection involves four roles: the service, the client, the interfaces, the injector.
Controllers can be injected with the components such as services, directives, filters and animations
Example: (the first method is most common used)
First example: (not good)
class MovieLister{
private MovieFinder finer; // the dependency (the service)
.... // some logic business
public MovieList(){
//this is strong coupled, combine AMovieFinder and MovieLister
finder = new AMovieFinder("movies");
}Second Example (good)
class MovieLister{
private MovieFinder finer; // the dependency (the service)
.... // some logic business
public MovieList(MovieFinder finder){
//this is loose coupled, we can use constructor to inject the service
this.finder = finder;
}






















 448
448











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








