比赛中,不建议自己编写高精度算法,
只建议在int,unsigned int,long long,unsigned long long,__int128,中进行选择,
有人说,拿不到比较高的分数怎么办,
我说,就成功率而言,在int,unsigned int,long long,unsigned long long,__int128,中进行选择远远大于自己编写高精度算法,而且省时,可以将有限的精力集中于问题的其它部分解决。
特别推荐:六、__int128回避输入与输出函数的用法
一、加
1.int 数据范围 -2^31---2^31-1 即 -2147483648---2147483647 也即 -2.1*10^9---2.1*10^9

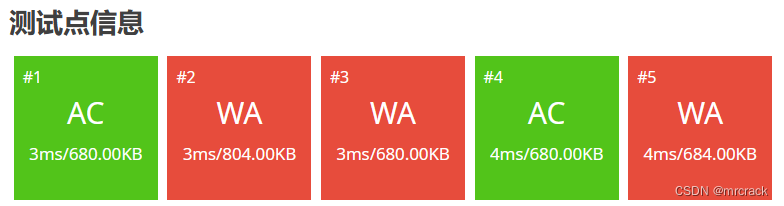
40分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
c=a+b;
printf("%d\n",c);
return 0;
} 2.unsigned int 数据范围 0---2^32-1 即 0---4294967295 也即 0---4.29*10^9

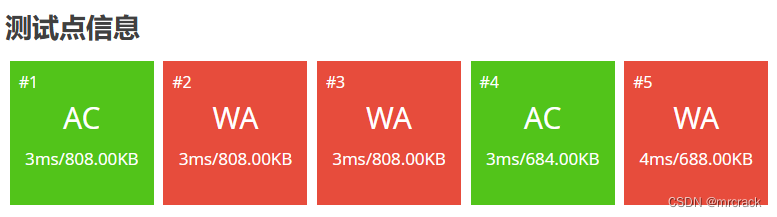
40分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unsigned int a,b,c;
scanf("%u%u",&a,&b);
c=a+b;
printf("%u\n",c);
return 0;
} 3.long long 数据范围 -2^63---2^63-1 即 -9223372036854775808---9223372036854775807 也即 -9.2*10^18---9.2*10^18

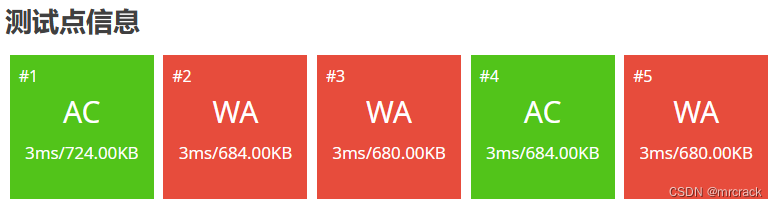
40分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long a,b,c;
scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b);
c=a+b;
printf("%lld\n",c);
return 0;
} 4.unsigned long long 数据范围0 ---2^64-1 即 0---18446744073709551615 也即 0---1.8*10^19
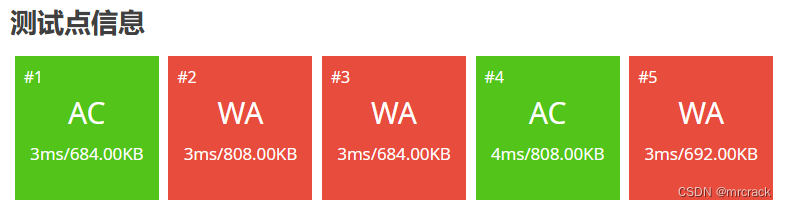 40分代码如下:
40分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unsigned long long a,b,c;
scanf("%llu%llu",&a,&b);
c=a+b;
printf("%llu\n",c);
return 0;
} 5.__int128 数据范围 -2^127---2^127-1 即 -1.7014118346046923173168730371588e+38---2^127 也即 1.7*10^38---1.7*10^38

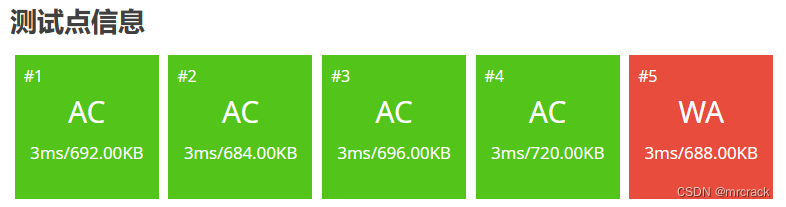
80分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline __int128 read(){//int128读取
__int128 x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){//读取非数字字符
if(ch=='-')f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(__int128 x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x){
print(x/10);//递归写法
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
}
int main(){
__int128 a,b,c;
a=read();
b=read();
c=a+b;
if(c==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(c);
return 0;
} 二、减
3.long long 数据范围 -2^63---2^63-1 即 -9223372036854775808---9223372036854775807 也即 -9.2*10^18---9.2*10^18
 30分代码如下:
30分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long a,b,c;
scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b);
c=a-b;
printf("%lld\n",c);
return 0;
} 5.__int128 数据范围 -2^127---2^127-1 即 -1.7014118346046923173168730371588e+38---2^127 也即 1.7*10^38---1.7*10^38
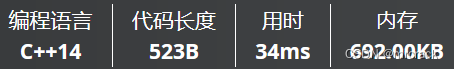
30分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline __int128 read(){//int128读取
__int128 x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){//读取非数字字符
if(ch=='-')f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(__int128 x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x){
print(x/10);//递归写法
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
}
int main(){
__int128 a,b,c;
a=read();
b=read();
c=a-b;
if(c==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(c);
return 0;
} 三、乘
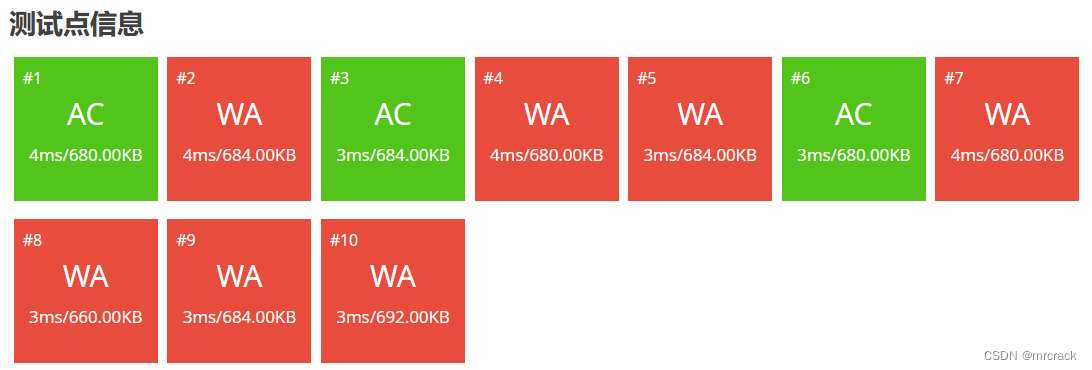
4.unsigned long long 数据范围0 ---2^64-1 即 0---18446744073709551615 也即 0---1.8*10^19

 40分代码如下:
40分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unsigned long long a,b,c;
scanf("%llu%llu",&a,&b);
c=a*b;
printf("%llu\n",c);
return 0;
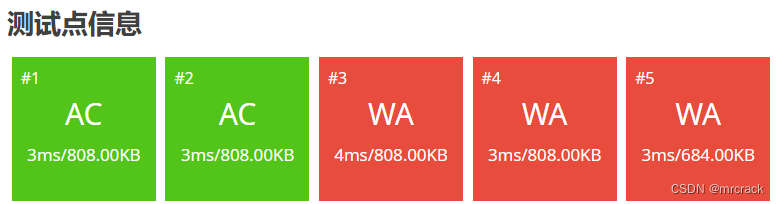
} 5.__int128 数据范围 -2^127---2^127-1 即 -1.7014118346046923173168730371588e+38---2^127 也即 1.7*10^38---1.7*10^38

 60分代码如下:
60分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline __int128 read(){//int128读取
__int128 x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){//读取非数字字符
if(ch=='-')f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(__int128 x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x){
print(x/10);//递归写法
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
}
int main(){
__int128 a,b,c;
a=read();
b=read();
c=a*b;
if(c==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(c);
return 0;
} 四、除
4.unsigned long long 数据范围0 ---2^64-1 即 0---18446744073709551615 也即 0---1.8*10^19

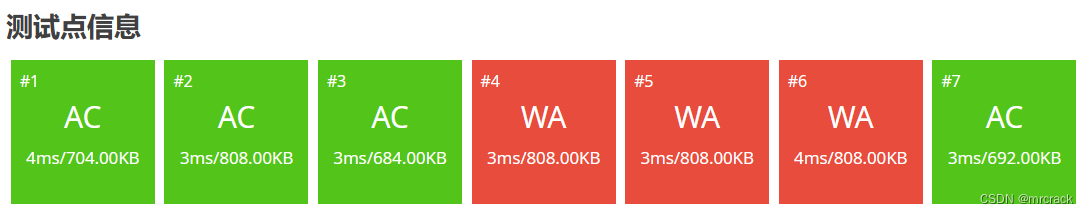 52分代码如下:
52分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unsigned long long a,b,c;
scanf("%llu%llu",&a,&b);
c=a/b;
printf("%llu\n",c);
return 0;
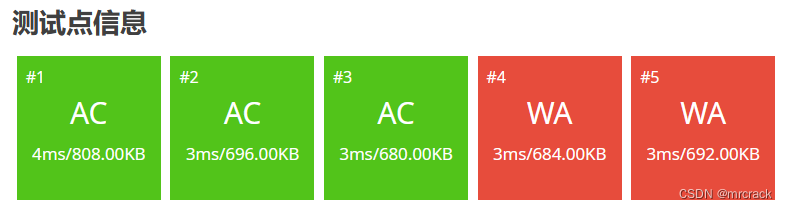
} 5.__int128 数据范围 -2^127---2^127-1 即 -1.7014118346046923173168730371588e+38---2^127 也即 1.7*10^38---1.7*10^38

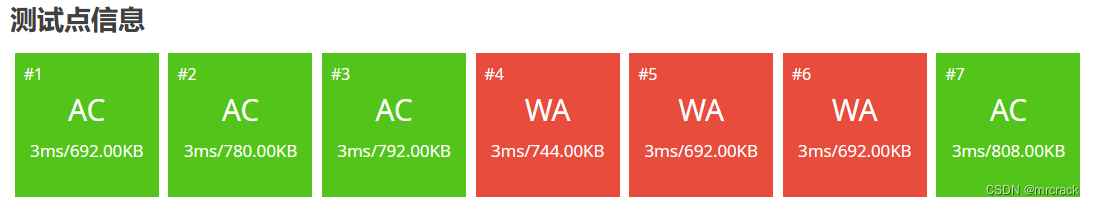 52分代码如下:
52分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline __int128 read(){//int128读取
__int128 x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){//读取非数字字符
if(ch=='-')f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(__int128 x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x){
print(x/10);//递归写法
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
}
int main(){
__int128 a,b,c;
a=read();
b=read();
c=a/b;
if(c==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(c);
return 0;
} 五、模
洛谷 P1932 A+B A-B A*B A/B A%B Problem
3.long long 数据范围 -2^63---2^63-1 即 -9223372036854775808---9223372036854775807 也即 -9.2*10^18---9.2*10^18

 10分代码如下:
10分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long a,b,c,d,e,f,g;
scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b);
c=a+b;
d=a-b;
e=a*b;
f=a/b;
g=a%b;
printf("%lld\n",c);
printf("%lld\n",d);
printf("%lld\n",e);
printf("%lld\n",f);
printf("%lld\n",g);
return 0;
} 5.__int128 数据范围 -2^127---2^127-1 即 -1.7014118346046923173168730371588e+38---2^127 也即 1.7*10^38---1.7*10^38

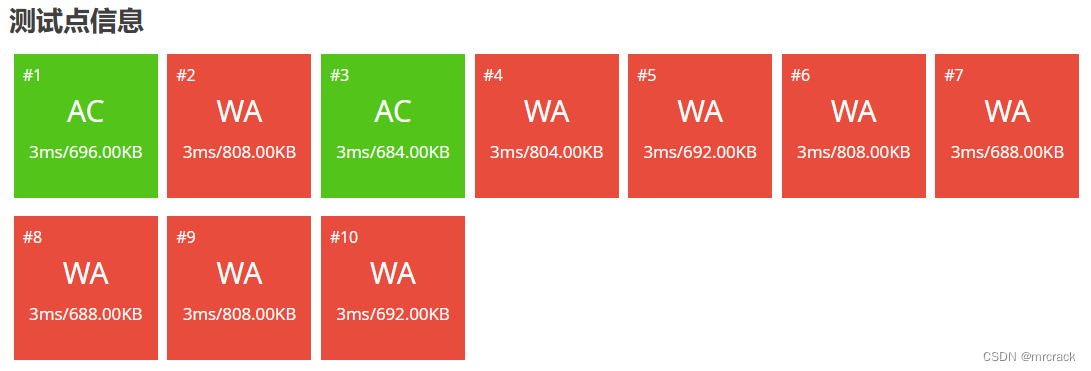 20分代码如下:
20分代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline __int128 read(){//int128读取
__int128 x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){//读取非数字字符
if(ch=='-')f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(__int128 x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x){
print(x/10);//递归写法
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
}
int main(){
__int128 a,b,c,d,e,f,g;
a=read();
b=read();
c=a+b;
d=a-b;
e=a*b;
f=a/b;
g=a%b;
if(c==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(c);
printf("\n");
if(d==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(d);
printf("\n");
if(e==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(e);
printf("\n");
if(f==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(f);
printf("\n");
if(g==0)putchar('0');//补上了int128输出是0的漏洞
else print(g);
printf("\n");
return 0;
} 六、__int128回避输入与输出函数的用法
__int128更进一步的用法,可以不考虑读取,输出函数的编写,如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
__int128 a,b,e;
int c,d;
scanf("%d%d",&c,&d);
a=c;
b=d;
e=a*b;
if(e==c*d){
printf("y\n");
}else{
printf("n\n");
}
return 0;
}上述程序
输入:
2 3
输出:
y
























 778
778











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








