一、概念
类和结构可以包含比整数类型占用更小空间的成员。 这些成员被指定为位域。
位域是一种特殊的类数据成员(结构体数据成员),用于保存特定的位数。
二、位域的数据类型
位域必须是整型数据类型,可以是signed或者是unsigned。
《C++ Primer》一书中给出:“通常最好将位域设为unsigned类型。存储在signed类型中的位域的行为由实现定义”的建议。
三、位域的定义
通过在成员名后面接一个冒号以及指定位数的常量表达式,指出成员是一个位域。
四、位域的内存布局
1.一般情况
struct Date
{
unsigned short nWeekDay : 3; // 0..7 (3 bits)
unsigned short nMonthDay : 6; // 0..31 (6 bits)
unsigned short nMonth : 5; // 0..12 (5 bits)
unsigned short nYear : 8; // 0..100 (8 bits)
};类型 Date 对象的概念内存布局如下图所示。
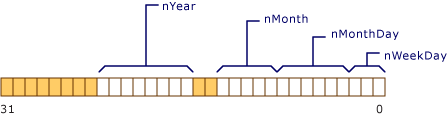
图1 数据对象的内容布局
请注意 nYear 长度为 8 位和溢出该声明的类型的字边界,无符号的 short。因此,它开始于新 unsigned short的开头。所有位域适合该基础类型的一个对象不是必须的:根据在声明里要求的位数,分配存储的新单元。
在Microsoft编译器环境下,声明为位域的数据的排序是从低位到高位,如上面图1所示。
2. 特殊情况——声明包括长度为 0 的一个未命名的字段
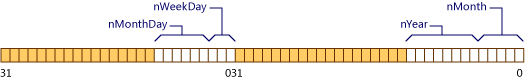
如下面的示例所示,如果结构的声明包括长度为 0 的一个未命名的字段,struct Date
{
unsigned nWeekDay : 3; // 0..7 (3 bits)
unsigned nMonthDay : 6; // 0..31 (6 bits)
unsigned : 0; // Force alignment to next boundary.
unsigned nMonth : 5; // 0..12 (5 bits)
unsigned nYear : 8; // 0..100 (8 bits)
};内存布局如下图中所示。
图2 带有零长度位域的数据对象的布局
五、位域的使用
使用方法与类和结构的其他数据成员的相同方法访问位域。
下面就借用《C++ Primer》里面的例子,来说说位域的使用吧。
typedef unsigned int Bit;
class File {
Bit mode: 2; // mode has 2 bits
Bit modified: 1; // modified has 1 bit
Bit prot_owner: 3; // prot_owner has 3 bits
Bit prot_group: 3; // prot_group has 3 bits
Bit prot_world: 3; // prot_world has 3 bits
// operations and data members of File
public:
enum modes { READ = 01, WRITE = 02, EXECUTE = 03 };
File &open(modes);
void close();
void write();
bool isRead() const;
void setWrite();
};
//从下面的代码可以看出与我们一般看到的数据成员的操作方式是一样的
void File::write()
{
modified = 1;
// . . .
}
void File::close()
{
if (modified)
// . . . save contents
}
//通常使用按位操作符来操作超过一位的位域
File &File::open(File::modes m)
{
mode |= READ; // set the READ bit by default
// other processing
if (m & WRITE) // if opening READ and WRITE
// processing to open the file in read/write mode
return *this;
}
//通过定义一组内联成员函数来测试和设置位域的值
inline bool File::isRead() const { return mode & READ; }
inline void File::setWrite() { mode |= WRITE; }值得注意的是,地址操作符(&)不能应用于位域,所以不可能有引用类位域的指针,位域也不能是类的静态成员。
六、位域的特点
1. 位域总是从字的第一个位开始;
2. 位域不能与整数的边界重叠,也就是说一个结构中所有域的长度之和不能大于字段大小。如果比字段大的话,重叠域将字段作为下一个字的开始。
3. 可以给未命名的域声明大小。例如:unsigned:bit-length,这种域在字段中提供填充值。
4. 字段中可以有未使用的位。
5. 不能使用位域变量的地址(同上面下划线的注意事项),这也意味着不能使用scanf函数将数值读入位域(可以使用中间变量赋值的方法来解决)。
6. 也不能使用位域变量的地址来访问位域。
7. 位域不能数组化。
8. 位域必须进行赋值,而且所赋的值必须在位域的大小范围之内,过大会发生不可预知的错误。
9. 位域定义中的数据类型如果是signed,那么其位数就不能少于两位(因为其中一个是符号位)。
参考文献
[1] MSDN. C++ 位域. http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/ewwyfdbe.aspx,2014-1-8.
[2]Stanley B.Lippman, Josée Lajoie, BarbaraE. Moo. C++ Primer, Fifth Edition[M]. 2012.
[3]陈正冲. C语言深度解剖[M]. 第二版. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社,2012: 41-44.






















 1814
1814

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








