本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl/article/details/51347818
大家知道,自定义View有三个重要的步骤:measure,layout,draw。而measure处于该链条的首端,占据着极其重要的地位;然而对于measure的理解却不是那么容易,许多问题都是一知半解,比如:为什么父View影响到了子View的MeasureSpec的生成?为什么我们自定义一个View在布局时将其宽或者高指定为wrap_content但是其实际是match_parent的效果?子View的specMode和specSize的生成依据又是什么?
1、MeasureSpec基础知识
系统显示一个View,首先需要通过测量(measure)该View来知晓其长和宽从而确定显示该View时需要多大的空间。在测量的过程中MeasureSpec贯穿全程,发挥着不可或缺的作用。
所以,了解View的测量过程,最合适的切入点就是MeasureSpec。
我们先来瞅瞅官方文档对于MeasureSpec 的介绍:
A MeasureSpec encapsulates the layout requirements passed from parent to child.Each MeasureSpec represents a requirement for either the width or the height.A MeasureSpec is comprised of a size and a mode.请注意这段话所包含的重要信息点:
1 MeasureSpec封装了父布局传递给子View的布局要求。
2 MeasureSpec可以表示宽和高
3 MeasureSpec由size和mode组成
MeasureSpec是一个32位的int数据。其中高2位代表SpecMode即某种测量模式,低30位为SpecSize代表在该模式下的规格大小.
可以通过如下方式分别获取这两个值:
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec)当然,也可以通过这两个值生成新的MeasureSpec
int measureSpec=MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(size, mode);SpecMode一共有三种:
1、MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
官方文档的描述:
The parent has determined an exact size for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless of how big it wants to be.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY模式表示:父容器已经检测出子View所需要的精确大小。
在该模式下,View的测量大小即为SpecSize。
2、MeasureSpec.AT_MOST
官方文档的描述:
The child can be as large as it wants up to the specified size.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST模式表示:父容器未能检测出子View所需要的精确大小,但是指定了一个可用大小即specSize
在该模式下,View的测量大小不能超过SpecSize。
3、MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED
官方文档的描述:
The parent has not imposed any constraint on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.父容器不对子View的大小做限制.
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED这种模式一般用作Android系统内部,或者ListView和ScrollView等滑动控件,在此不做讨论。
看完了这三个SpecMode的含义,我们再从源码里看看它们是怎么形成的。
在ViewGroup中测量子View时会调用到measureChildWithMargins()方法,或者与之类似的方法。源码如下:
/**
* @param child
* 子View
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec
* 父容器(比如LinearLayout)的宽的MeasureSpec
* @param widthUsed
* 父容器(比如LinearLayout)在水平方向已经占用的空间大小
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec
* 父容器(比如LinearLayout)的高的MeasureSpec
* @param heightUsed
* 父容器(比如LinearLayout)在垂直方向已经占用的空间大小
*/
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec =
getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec =
getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}通过这些参数看出来一些端倪,该方法要测量子View传进来的参数却包含了父容器的宽的MeasureSpec,父容器在水平方向已经占用的空间大小,父容器的高的MeasureSpec,父容器在垂直方向已经占用的空间大小等父View相关的信息。这在一定程度体现了:父View影响着子View的MeasureSpec的生成。
该方法主要有四步操作:
第一步:得到子View的LayoutParams,请参见第15行代码。
第二步:得到子View的宽的MeasureSpec,请参见第16-18行代码。
第三步:得到子View的高的MeasureSpec,请参见第19-21行代码。
第四步:测量子View,请参见第22行代码。
第一步,没啥好说的;第二步和第三步都调用到了getChildMeasureSpec( ),在该方法内部又做了哪些操作呢?
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int parentSpec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(parentSpec);
int specSize = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(parentSpec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
case View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}该方法就是确定子View的MeasureSpec的具体实现。
请注意该方法的参数:
parentSpec:
父容器的宽或高的MeasureSpec
padding:
父容器在垂直方向或者水平方向已被占用的空间。
为什么这么说,它的依据在哪里?
请看在measureChildWithMargins()方法里调用getChildMeasureSpec()的地方,传递给getChildMeasureSpec()的第二个参数是如下构成:
比如:mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
其中:
mPaddingLeft和mPaddingRight表示父容器左右两内侧的padding
lp.leftMargin和lp.rightMargin表示子View左右两外侧的margin
这四部分都不可以再利用起来布局子View.所以说这些值的和表示:父容器在水平方向已经被占用的空间
childDimension
通过子View的LayoutParams获取到的子View的宽或高
所以,从getChildMeasureSpec()方法的第一个参数spec和第二个参数padding也可以看出:
父容器(如LinearLayout)的MeasureSpec和子View的LayoutParams共同决定了子View的MeasureSpec!
明白了该方法的参数,我们再来看方法的具体实现步骤。
第一步:
得到父容器的specMode和specSize,请参见第2-3行代码。
第二步:
得到父容器在水平方向或垂直方向可用的最大空间值,请参见第5行代码。
第三步:
确定子View的specMode和specSize,请参见第10-50行代码。
在这里出现了一个很关键的switch语句,该语句的判断条件就是父View的specMode;在此根据父View的specMode的不同来决定子View的specMode和specSize.
情况1:
父容器的specMode为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,请参见第11-22行代码。
也请记住该先决条件,因为以下的讨论都是基于此展开的。
我们首先看到一个if判断if (childDimension >= 0),或许看到这有点懵了:childDimension>=0是啥意思?难道还有小于0的情况?是的,请注意两个系统常量:
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT=-1和LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT=-2
所以在此处的代码:
if (childDimension >= 0)表示子View的宽或高不是match_parent,也不是wrap_content而是一个具体的数值,比如100px。
那么:子View的size就是childDimension,子View的mode也为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,即:
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;看完这个if,我们来看第一个else if
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT)表示子View的宽或高是LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT。
那么:子View的size就是父容器在水平方向或垂直方向可用的最大空间值即size,子View的mode也为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,即:
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;我们来看第二个else if
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)表示子View的宽或高是LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT。
那么:子View的size就是父容器在水平方向或垂直方向可用的最大空间值即size,子View的mode为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,即:
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;后面的情况就不一一列举了。
至此,我们可以清楚地看到: 子View的MeasureSpec由其父容器的MeasureSpec和该子View本身的布局参数LayoutParams共同决定。
在此经过测量得出的子View的MeasureSpec是系统给出的一个期望值(参考值),我们也可摒弃系统的这个测量流程,直接调用setMeasuredDimension( )设置子View的宽和高的测量值。
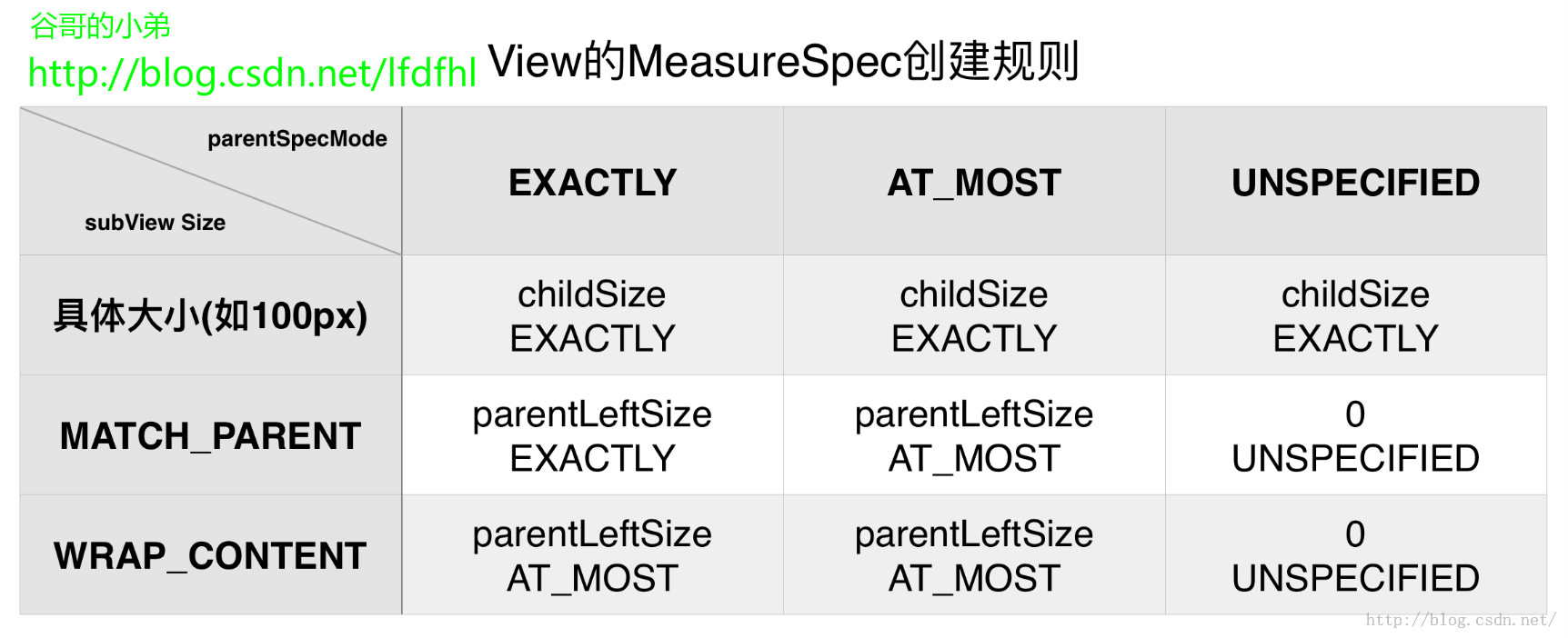
对于以上的分析可用表格来规整各一下MeasureSpec的生成
(1)在哪些具体的情况下子View的SpecMode为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY?
第一种情况:
当子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用具体的值(如100px)时且父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY或者MeasureSpec.AT_MOST或者MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED时:系统返回给该子View的specMode就为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,系统返回给该子View的specSize就为子View自己指定的大小(childSize)。
通俗地理解:
子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用具体的值(如100px)时,那么说明该子View的大小是非常明确的,明确到了令人发指的地址,都已经到了用具体px值指定的地步了。那么此时不管父容器的specMode是什么,系统返回给该子View的specMode总是MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,并且系统返回给该子View的specSize就是子View自己指定的大小(childSize)。
第二种情况:
当子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用match_parent时并且父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY时:系统返回给该子View的specMode就为 MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize)。
通俗地理解:
子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用match_parent并且父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY。这时候说明子View的大小还是挺明确的:就是要和父容器一样大,更加直白地说就是父容器要怎样子View就要怎样。所以,如果父容器MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,那么系统返回给该子View的specMode就为 MeasureSpec.EXACTLY和父容器一样;系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize),即为父容器的剩余大小.
(2)在哪些具体的情况下子View的SpecMode为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST?
第一种情况:
当子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用match_parent并且父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST时:系统返回给该子View的specMode就为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize)
通俗地理解:
子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用match_parent并且父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST。这时候说明子View的大小还是挺明确的:就是要和父容器一样大,直白地说就是父容器要怎样子View就要怎样。但是此时父容器的大小不是很明确其MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,那么系统返回给该子View的specMode就为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST和父容器一样;系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize),即为父容器的剩余大小.
第二种情况:
当子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用wrap_content时并且父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY时:系统返回给该子View的specMode就为 MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize)
通俗地理解:
子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用wrap_content时说明这个子View的宽高不明确,要视content而定。这时如果父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY即父容器是一个精确模式。这种情况概况起来简单地说就是:子View大小是不确定的,但父容器大小是确定的,那么系统返回给该子View的specMode也就是不确定的即为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize)
第三种情况:
当子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用wrap_content时并且父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST时:系统返回给该子View的specMode就为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize)
通俗地理解:
子View的LayoutParams的宽(高)采用wrap_content,即说明这个子View的宽高不明确,要视content而定。这个时候父容器的MeasureSpec为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST。这种情况概况起来简单地说就是:子View的宽高是不确定的,父容器的宽高也是不确定的,那么系统返回给该子View的specMode也就是不确定的即为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,系统返回给该子View的specSize就为该父容器剩余空间的大小(parentLeftSize)
(3)在哪些具体的情况下子View的SpecMode为MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED?
前面也说了该模式在实际开发中极少用到,故在此不做讨论。
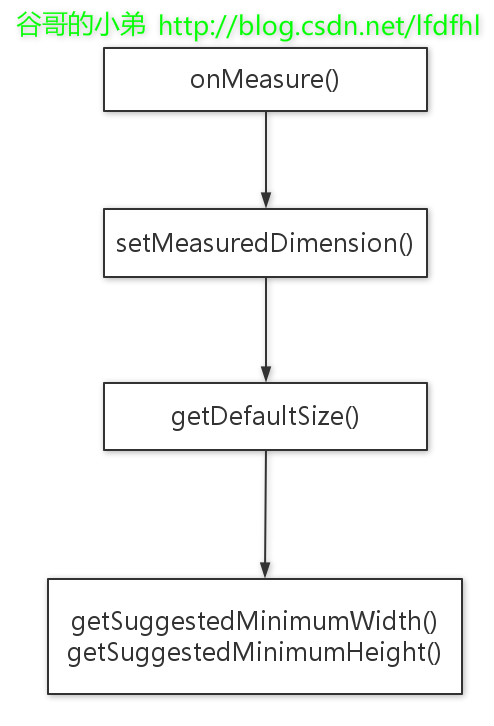
二、onMeasure源码分析
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
} onMeasure( )源码流程如下:
(1) 在onMeasure调用setMeasuredDimension( )设置View的宽和高.
(2) 在setMeasuredDimension()中调用getDefaultSize()获取View的宽和高.
(3) 在getDefaultSize()方法中又会调用到getSuggestedMinimumWidth()或者getSuggestedMinimumHeight()获取到View宽和高的最小值.
即这一系列的方法调用顺序为:
先来看getSuggestedMinimumWidth( )
//Returns the suggested minimum width that the view should use
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}该方法返回View的宽度的最小值MinimumWidth.
在此需要注意该View是否有背景.
(1) 若该View没有背景。
那么该MinimumWidth为View本身的最小宽度即mMinWidth。
有两种方法可以设置该mMinWidth值:
第一种:XML布局文件中定义minWidth
第二种:调用View的setMinimumWidth()方法为该值赋值
(2) 若该View有背景。
那么该MinimumWidth为View本身最小宽度mMinWidth和View背景的最小宽度的最大值
getSuggestedMinimumHeight()方法与此处分析很类似,故不再赘述.
接下来看看getDefaultSize( )的源码
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}该方法用于获取View的宽或者高的大小。
该方法的第一个输入参数size就是调用getSuggestedMinimumWidth()方法获得的View的宽或高的最小值。
从getDefaultSize()的源码里的switch可看出该方法的返回值有两种情况:
(1) measureSpec的specMode为MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED
在此情况下该方法的返回值就是View的宽或者高最小值.
该情况很少见,基本上可忽略
(2) measureSpec的specMode为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST或MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
在此情况下getDefaultSize()的返回值就是该子View的measureSpec中的specSize。
除去第一种情况不考虑以外,可知:
在measure阶段View的宽和高由其measureSpec中的specSize决定!!
最后再来看setMeasuredDimension( )的源码
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}经过了前面的一系列操作,终于得到了View的宽高。
在此调用setMeasuredDimension( )设置View的宽和高的测量值。
三、遗留问题
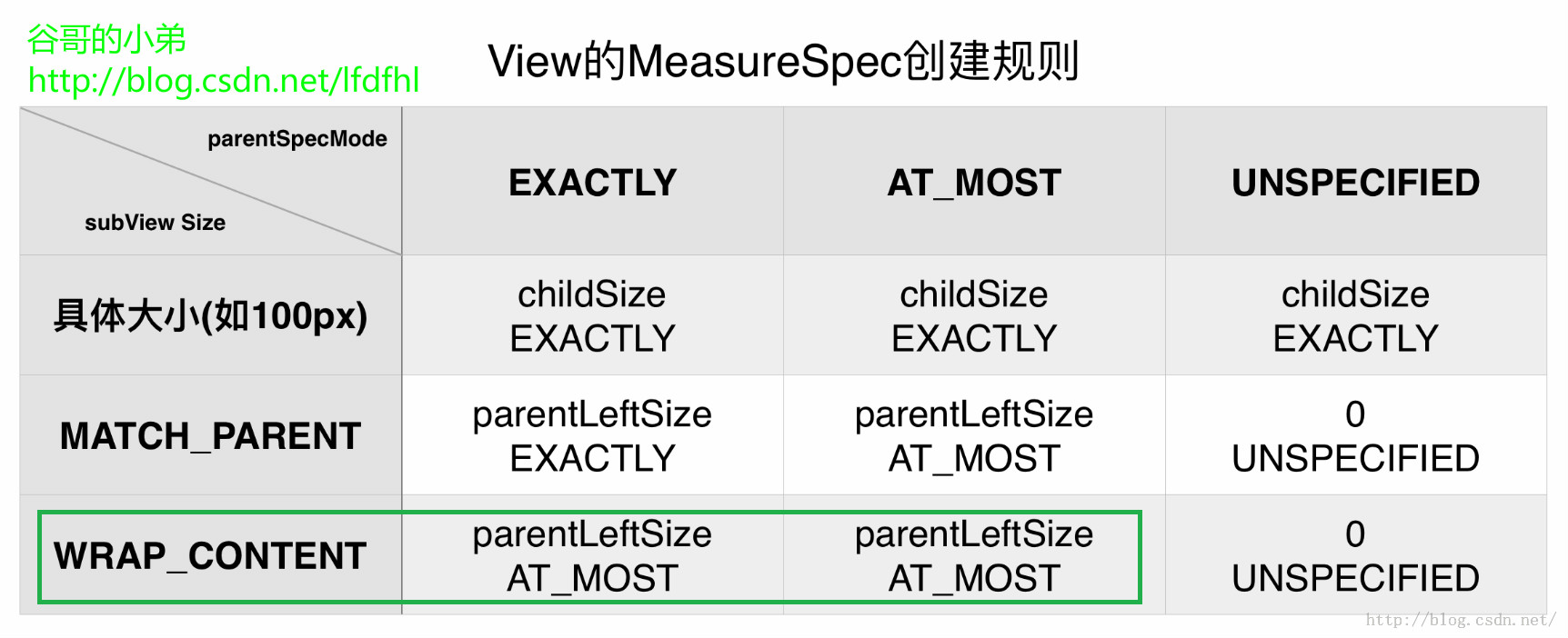
看了这么久的源码,我们终于搞清楚了这个问题;但是刚刚舒展开的眉头又皱起来了。结合刚才的图发现一个问题:在该图的最后一行,如果子View在XML布局文件中对于大小的设置采用wrap_content,那么不管父View的specMode是MeasureSpec.AT_MOST还是MeasureSpec.EXACTLY对于子View而言系统给它设置的specMode都是MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,并且其大小都是parentLeftSize即父View目前剩余的可用空间。这时wrap_content就失去了原本的意义,变成了match_parent一样了.
所以自定义View在重写onMeasure()的过程中应该手动处理View的宽或高为wrap_content的情况。
第一种情况:
如果在xml布局中View的宽和高均用wrap_content.那么需要设置View的宽和高为mWidth和mHeight.
第二种情况:
如果在xml布局中View的宽或高其中一个为wrap_content,那么就将该值设置为默认的宽或高,另外的一个值采用系统测量的specSize即可.
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec , heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpceSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpceSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST&&heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}else if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, heightSpceSize);
}else if(heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpceSize, mHeight);
}
}该部分的处理主要有两步
第一步:
调用super.onMeasure(),请参见第2行代码
第二步:
处理子View的大小为wrap_content的情况,请参见第3-14行代码。
此处涉及到的mWidth和mHeight均为一个默认值;应根据具体情况而设值。
其实,Andorid系统的控件比如TextView等也在onMeasure()中对其大小为wrap_content这一情况作了特殊的处理。
请注意在第二步的代码中用的判断条件:
四、ViewGroup的measure阶段
刚分析完了View的onMeasure()源码,现在接着看ViewGroup的measure阶段的实现
public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent,ViewManager{ }首先,请注意ViewGroup是一个抽象类,它没有重写View的onMeasure( )但它提供了measureChildren( )测量所有的子View。
在measureChildren()方法中调用measureChild( )测量每个子View,在该方法内又会调用到child.measure( )方法,这又回到了前面熟悉的流程。
即ViewGroup中测量子View的流程:
measureChildren( )—>measureChild( )—>child.measure( )
既然ViewGroup继承自View而且它是一个抽象类,那么ViewGroup的子类就应该根据自身的要求和特点重写onMeasure( )方法。
那么这些ViewGroup的子类会怎么测量子View和确定自身的大小呢?
假若ViewGroup知道了每个子View的大小,将它们累加起来是不是就知道了自身的大小呢?
顺着这个猜想,我们选择ViewGroup的子类LinearLayout瞅瞅,就从它的onMeasure( )开始看吧
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}嗯哼,代码里分了水平线性和垂直线性这两种情况进行测量,类似的逻辑在其onLayout( )阶段也会看到的。我们就选measureVertical( )继续往下看
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mTotalLength = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
int alternativeMaxWidth = 0;
int weightedMaxWidth = 0;
boolean allFillParent = true;
float totalWeight = 0;
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
boolean matchWidth = false;
boolean skippedMeasure = false;
final int baselineChildIndex = mBaselineAlignedChildIndex;
final boolean useLargestChild = mUseLargestChild;
int largestChildHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);
continue;
}
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
mTotalLength += mDividerHeight;
}
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
totalWeight += lp.weight;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
skippedMeasure = true;
} else {
int oldHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
oldHeight = 0;
lp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
measureChildBeforeLayout(
child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec,
totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0);
if (oldHeight != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
lp.height = oldHeight;
}
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin +
lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
if (useLargestChild) {
largestChildHeight = Math.max(childHeight, largestChildHeight);
}
}
if ((baselineChildIndex >= 0) && (baselineChildIndex == i + 1)) {
mBaselineChildTop = mTotalLength;
}
if (i < baselineChildIndex && lp.weight > 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Exception");
}
boolean matchWidthLocally = false;
if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
matchWidth = true;
matchWidthLocally = true;
}
final int margin = lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
final int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + margin;
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, measuredWidth);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
allFillParent = allFillParent && lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
if (lp.weight > 0) {
weightedMaxWidth = Math.max(weightedMaxWidth,
matchWidthLocally ? margin : measuredWidth);
} else {
alternativeMaxWidth = Math.max(alternativeMaxWidth,
matchWidthLocally ? margin : measuredWidth);
}
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
}
if (mTotalLength > 0 && hasDividerBeforeChildAt(count)) {
mTotalLength += mDividerHeight;
}
if (useLargestChild &&
(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST || heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)) {
mTotalLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);
continue;
}
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) {
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams)
child.getLayoutParams();
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + largestChildHeight +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
}
}
mTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
int heightSize = mTotalLength;
heightSize = Math.max(heightSize, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
int heightSizeAndState = resolveSizeAndState(heightSize, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
heightSize = heightSizeAndState & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
int delta = heightSize - mTotalLength;
if (skippedMeasure || delta != 0 && totalWeight > 0.0f) {
float weightSum = mWeightSum > 0.0f ? mWeightSum : totalWeight;
mTotalLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
float childExtra = lp.weight;
if (childExtra > 0) {
int share = (int) (childExtra * delta / weightSum);
weightSum -= childExtra;
delta -= share;
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin, lp.width);
if ((lp.height != 0) || (heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)) {
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + share;
if (childHeight < 0) {
childHeight = 0;
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec,
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
} else {
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec,
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(share > 0 ? share : 0,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState()
& (MEASURED_STATE_MASK>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
}
final int margin = lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
final int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + margin;
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, measuredWidth);
boolean matchWidthLocally = widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY &&
lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
alternativeMaxWidth = Math.max(alternativeMaxWidth,
matchWidthLocally ? margin : measuredWidth);
allFillParent = allFillParent && lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + child.getMeasuredHeight() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
}
mTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
} else {
alternativeMaxWidth = Math.max(alternativeMaxWidth,
weightedMaxWidth);
if (useLargestChild && heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null || child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp =
(LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
float childExtra = lp.weight;
if (childExtra > 0) {
child.measure(
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(child.getMeasuredWidth(),
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(largestChildHeight,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
}
}
}
if (!allFillParent && widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
maxWidth = alternativeMaxWidth;
}
maxWidth += mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight;
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
heightSizeAndState);
if (matchWidth) {
forceUniformWidth(count, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}这段代码的主要操作:
1、遍历每个子View,并对每个子View调用measureChildBeforeLayout(),请参见代码第115-133行
在measureChildBeforeLayout()方法内又会调用measureChildWithMargins()从而测量每个子View的大小。在该过程中mTotalLength保存了LinearLayout的高度,所以每当测量完一个子View该值都会发生变化。
2、设置LinearLayout的大小,请参见代码第241
以上就是LinearLayout的onMeasure( )的简要分析。
其余的ViewGroup的子类均有自己各不相同的measure操作,具体实现请参考对应的源码。
五、总结
终于,分析完了和Measure有关的主要代码。
代码稍微有点多,所以就有点小小的犯晕了。
再回过头看刚才讨论过的两个方法:
以下为measureChildWithMargins
/**
* @param child The child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
* @param widthUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
* @param heightUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* vertically (possibly by other children of the parent)
*/
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
}对于参数parentWidthMeasureSpec和parentHeightMeasureSpec注释的描述是:
The width(height) requirements for this view父容器对子View宽(高)的要求(或者说是期望值)。
以下为getChildMeasureSpec
/**
*
* @param spec The requirements for this view
* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and margins, if applicable
* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current dimension
* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child
*/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int parentSpec, int padding, int childDimension) {
}注释对于第一个参数spec的描述也是类似的:
The requirements for this view咦,为什么我们在解读这两个方法的时候说:
parentWidthMeasureSpec和parentHeightMeasureSpec和spec这三个值表示宽或者高的MeasureSpec呢?
我们的表述和注释的说明怎么不一样呢?
难道我们理解错了?非也,非也。
1、子View的MeasureSpec是由父View的MeasureSpec及子View自身的LayoutParam共同决定的。
2、关于“子View自身的LayoutParam”好理解,就是子View的宽或高等条件
3、那“父View的MeasureSpec”又体现在哪里呢?
当然就是这里出现的parentWidthMeasureSpec和parentHeightMeasureSpec以及spec。只不过文档说得委婉些“对于子View的要求(期望)”。
其实,我个人觉得理解成为“要求”更好一些,就是父View对子View的要求。比如,在绝大多数情况下父View要求子View的大小不能超过其大小,这就是一种要求。而父View的大小就封装在父View的MeasureSpec里的。
所以,可以从这个角度来体会文档的描述






















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








