前言:
在使用map<string,vector<string>> 的对象时。与关键字的内容一致,map.find 却找不到关键字。
结论:
不可使用string.reserve 或者其他方法先为string申请空间,然后通过string.c_str()获取指针为string的内存空间赋值。会导致两个string内容一样时,但是string.compare的结果不正确。
ps:不是直接通过理解STL::String::Compare的方法来定位问题,可能理解有错误。 后续,有时间补充compare的实现,找出更强有力的证据。
问题由来:
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>string source;
string des;
G_WS2S(originWord,source);
map<string,vector<string>>::iterator it=str.find(source);
string cc="编辑\n开胶点";
int a = str.count(source);
int b = str.count("编辑\n开胶点");
int c = str.count(cc);
int d = source.compare(cc);
if(it == str.end())
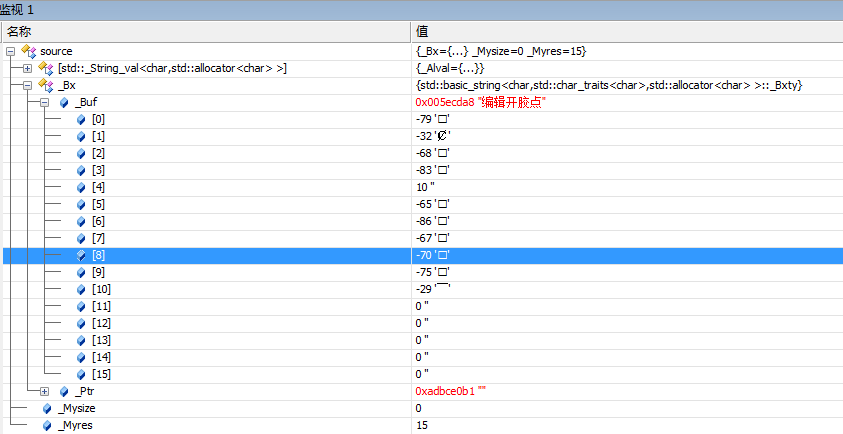
return FALSE;source 中的值
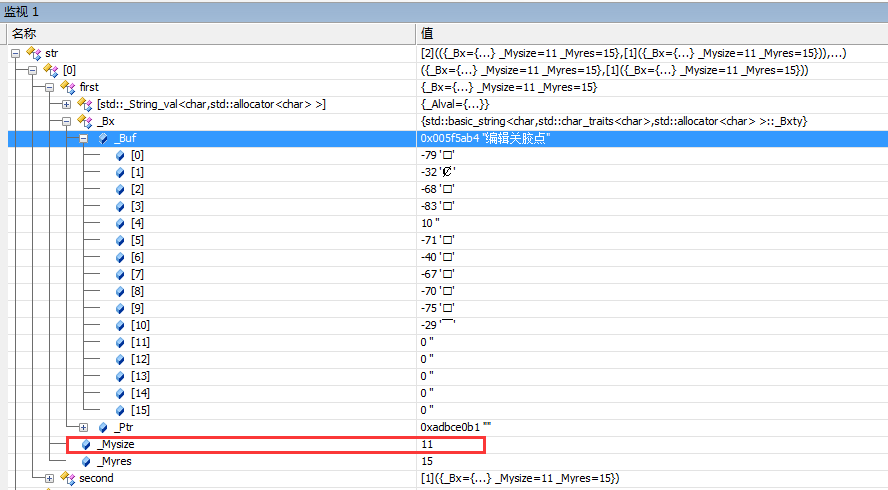
str 变量中的值
代码中,a,b,c,d的值
由此可见 map 中关键字是包含字符串“编辑\n开胶点”了
于是怀疑source 有问题,对比了以下发现 成员变量 _Mysize 和关键字不一样。source._Mysize = 0; 而关键字是11.
由从cc看出字符串“编辑\n开胶点” 并没有特殊性,直接初始化的时候,可正确使用。于是查source 的赋值。
G_WS2S 中对source 的赋值如下,强行的向str的buf 中copy了该字符串,导致string 类的成员变量没有跟新。
std::string& G_WS2S(const std::wstring &wstr,std::string &str)
{
int nLen = (int)wstr.length()*sizeof(wchar_t);
if(nLen == 0) return str;
nLen =WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,0,(LPCWSTR)wstr.c_str(),-1,NULL,0,NULL,NULL);
str.reserve(nLen);
char *tmp =new char[nLen+1];
int nResult = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,0,(LPCWSTR)wstr.c_str(),-1,(LPSTR)str.c_str(),nLen,NULL,NULL);
if (nResult == 0)
{
str.clear();
delete[] tmp;
return str;
}
// str = tmp;
delete[] tmp;
return str;
}最后将代码中的str.c_str() 替换为tmp ,问题得到解决。
修改后的代码如下
std::string& G_WS2S(const std::wstring &wstr,std::string &str)
{
int nLen = (int)wstr.length()*sizeof(wchar_t);
if(nLen == 0) return str;
nLen =WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,0,(LPCWSTR)wstr.c_str(),-1,NULL,0,NULL,NULL);
str.reserve(nLen);
char *tmp =new char[nLen+1];
int nResult = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,0,(LPCWSTR)wstr.c_str(),-1,tmp,nLen,NULL,NULL);
if (nResult == 0)
{
str.clear();
delete[] tmp;
return str;
}
str = tmp;
delete[] tmp;
return str;
}

























 575
575

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








