For your understanding, the definition of Radio Link Failure is simply "Physical Layer (especially low PHY) break" and in most case this failure is unintentional.
Firstly the question is "How UE or eNodeB can detect this kind of Radio Link Failure?"
you can refer to 3GPP TR 36.133 and TR 36.213, among the spec of TR 36.133 “Requirements for support of radio resource management” and chapter 7.6 “Radio Link Monitoring”, the standards says,
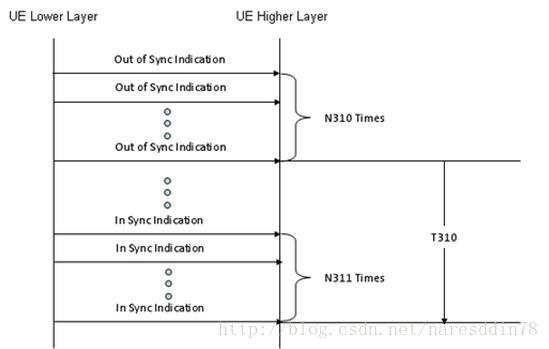
“The UE shall monitor the downlink link quality based on the cell-specific reference signal in order to detect the downlink radio link quality of the PCell as specified in [3]. The UE shall estimate the downlink radio link quality and compare it to the thresholds Qout and Qin for the purpose of monitoring downlink radio link quality of the PCell.
… “
Unfortunately, the detailed detection implementation is up to UE chipset maker and eNodeB maker, but we can think of several guidelines.
UE may assume that Radio Link is broken in the following sections.
- The measured RSRP is too low (under a certain limit)
- It failed to decode PDCCH due to power signal quality (e.g, low RSRP, RSRQ)
- It failed to decode PDSCH due to power signal quality (e.g, low RSRP, RSRQ)
However, detailed mechanism to RLF is up to the chipset implementation.
eNodeB may assume that that Radio Link is broken in the following sections.
- SRS Power (SINR) from UE is much lower than what eNB configured for the UE
- eNodeB couldn't detect (see) any NACK nor ACK from UE for PDSCH.
In most case, this kind of problem should happen for a certain period of time consecutively and a couple of timers and parameters are involved in the criteria setup.
Then the next question is "What UE does when it detects Radio Link Failure ?"
The most typical procedure is to go through RRC Connection Reestablishment procedure.
As the above picture, RACH is used for recovering from radio link failure.
LTE RACH is used to achieve uplink time synchronization for a UE which either has not yet acquired, or has lost, its uplink synchronization. Once uplink synchronization is achieved for a UE, the eNodeB can schedule orthogonal uplink transmission resources for it.
The LTE random access procedure comes in two forms, allowing access to be either contention-based or contention-free.
A UE initiates a contention-based random access procedure for radio link failure. In this procedure, a random access preamble signature is randomly chosen by the UE, with the result that it’s possible for more than one UE simultaneously to transmit the same signature,leading to a need for a subsequent contention resolution process.
for the use-cases, new downlink data and handover, the eNodeB has the option of preventing contention occurring by allocating a dedicated signature to a UE, resulting in contention-free access. This is faster than contention-based access – a factor which is particularly important for the case of handover, which is time-critical.



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








