MongoDB学习01:MongoDB的安装及其CRUD操作
MongoDB的官方文档The MongoDB 4.0 Manual — MongoDB Manual,阅读官方文档永远是最好的学习方法.
MongoDB的安装与使用
下载安装MongoDB并将其目录加入到Path
MongoDB社区版的下载地址:MongoDB社区版下载.下载并安装好之后可以MongoDB的/bin目录加入到系统路径Path中.
启动MongoDB
-
启动MongoDB前,要先创建好MongoDB的工作目录,其目录结构如下:
C: └─db ├─data └─log其中
db/data目录保存数据库中的数据,db/log目录保存日志.
MongoDB的默认工作目录在C:盘下,可以在启动时添加--dbpath 目录参数修改其工作目录. -
在控制台输入
mongod,开启MongoDB服务端 -
在控制台输入
mongo,开启MongoDB客户端,此即为Mongo shell,可以在里面运行js代码对MongoDB进行操作.
将MongoDB服务端加入系统服务
我们可以将MongoDB服务端加入系统服务,开机自动启动,步骤如下:
-
在MongoDB的安装目录下创建配置文件
mongod.cfg,其内容如下.systemLog: destination: file path: c:\data\log\mongod.log storage: dbPath: c:\data\db -
添加服务: 在控制台输入命令如下,将MongoDB服务端添加进系统服务
其中binPath属性为MongoDB服务端的全路径,config属性为该配置文件的路径.sc.exe create MongoDB binPath= "\"D:\MongoDB\Server\3.2\bin\mongod.exe\" --service --config=\"C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.2\mongod.cfg\"" DisplayName= "MongoDB" start= "auto"若提示
[SC] OpenSCManager FAILED 5:错误,证明权限不足,可以以管理员身份打开控制台执行上面语句. -
在任务管理器中将MongoDB服务设为开机自启动.
-
若上述过程中出现错误,可在控制台中输入
sc delete MongoDB删除MongoDB服务,并重复上述步骤.
MongoDB基本CRUD操作
MongoDB的基本概念
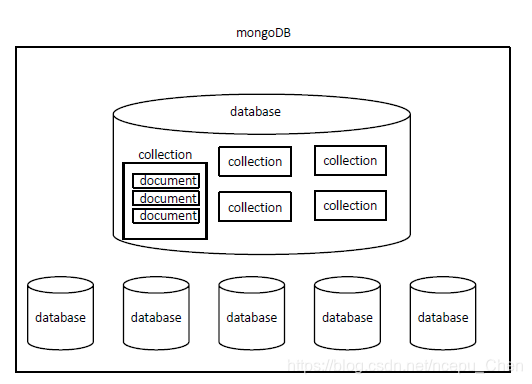
在MongoDB中数据库database表示一个数据库,集合collection相当于关系型数据库的表,文档document相当于关系型数据库的一行记录.
文档document是以二进制json的形式存储在数据库中的,是我们直接操作的对象.
基于Mongo Shell的数据库管理操作
数据库管理语法
| 操作 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| 查看所有数据库 | show dbs;或show databases; |
| 查看当前数据库 | db; |
| 切换到某数据库(若数据库不存在则创建数据库) | use <数据库名>; |
| 删除当前数据库 | db.dropDatabase(); |
集合管理语法
| 操作 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| 查看所有集合 | show collections; |
| 创建集合 | db.createCollection("集合名"); |
| 删除集合 | db.<集合名>.drop() |
基于Mongo Shell的CRUD操作
在Mongo Shell中,通过javascript语句,可以与数据库进行交互.
增加操作
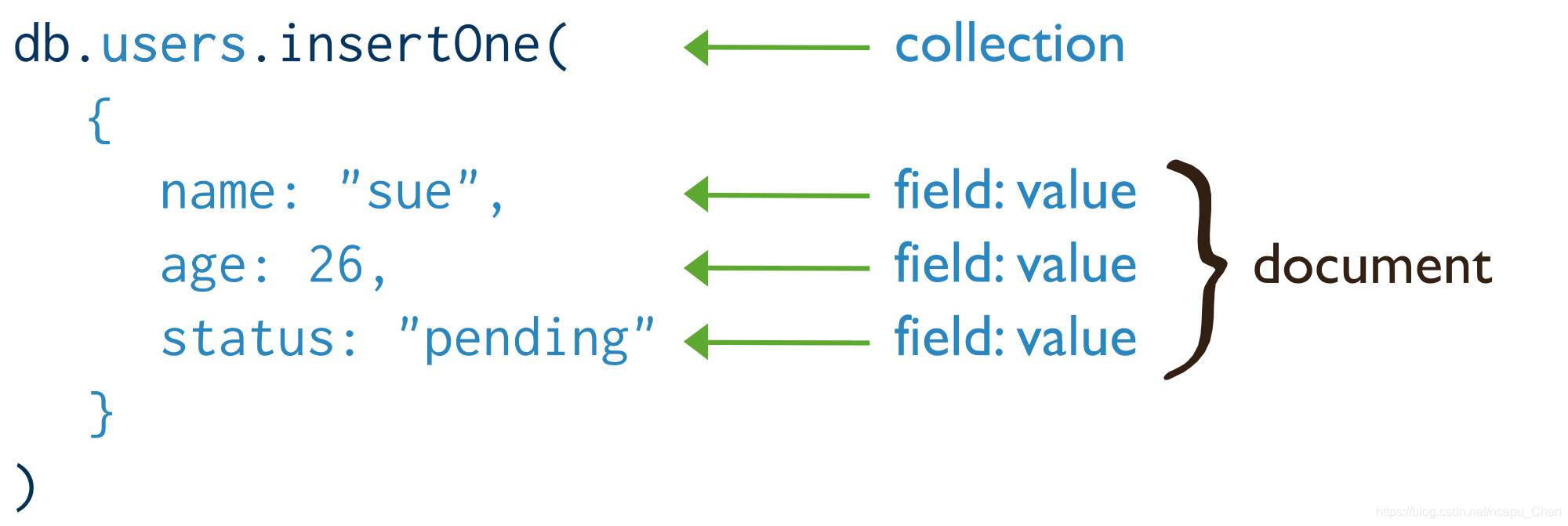
- 使用
db.集合名.insertOne()向集合中添加一个文档,参数一个json格式的文档 - 使用
db.集合名.insertMany()向集合中添加多个文档,参数为json文档数组
// 向inventory集合中添加一个文档
db.inventory.insertOne(
{ item: "canvas", qty: 100, tags: ["cotton"], size: { h: 28, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" } }
)
// 向inventory集合中添加多个文档
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, tags: ["blank", "red"], size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mat", qty: 85, tags: ["gray"], size: { h: 27.9, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mousepad", qty: 25, tags: ["gel", "blue"], size: { h: 19, w: 22.85, uom: "cm" } }
])
查询操作
基本查询
使用db.集合名.find(<filter>, <options>)方法对集合进行查询,接受一个json格式的查询条件
db.inventory.find( { status: "D" } )

-
可以使用
$in操作符表示范围查询db.inventory.find( { status: { $in: [ "A", "D" ] } } ) -
多个查询条件用逗号分隔,表示
AND的关系db.inventory.find( { status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } } )等价于下面sql语句
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" AND qty < 30 -
使用
$or操作符表示后边数组中的条件是OR的关系db.inventory.find( { $or: [ { status: "A" }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] } )等价于下面sql语句
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" OR qty < 30 -
联合使用
AND和OR的查询语句db.inventory.find( { status: "A", $or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ] } )
对数组进行查询
向集合中添加含有数组属性的文档如下
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, tags: ["blank", "red"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, tags: ["red", "blank"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, tags: ["red", "blank", "plain"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, tags: ["blank", "red"], dim_cm: [ 22.85, 30 ] },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, tags: ["blue"], dim_cm: [ 10, 15.25 ] }
]);
-
匹配整个数组
在查询条件中指定一个数组,表示匹配文档的该数组属性有且只有该条件数组的所有元素-
默认情况下匹配会要求顺序.下面查询语句要求匹配文档的
tags属性正好有"red","blank"两个元素且按照该顺序排列.db.inventory.find( { tags: ["red", "blank"] } ) -
使用
$all操作符表示取消匹配顺序.下面查询语句要求匹配文档的tags属性正好有"red","blank"两个元素并可以按任意顺序排列.db.inventory.find( { tags: { $all: ["red", "blank"] } } )
-
-
多条件查询数组
-
默认情况下,多条件查询一个数组,要求匹配文档对应数组属性中所有元素的任意组合匹配所有条件.既可以数组中一个元素满足所有条件,也可以数组中每个元素只满足一部分条件但加起来满足了所有条件
db.inventory.find( { dim_cm: { $gt: 15, $lt: 20 } } ) -
使用
$elemMatch操作符表示要求数组中至少一个元素满足所有条件db.inventory.find( { dim_cm: { $elemMatch: { $gt: 22, $lt: 30 } } } ) -
使用
数组属性名.下标指定数组某一位要满足的条件,下标从0开始db.inventory.find( { "dim_cm.0": { $gt: 25 } } )使用
.时json的属性名必须用为字符串 -
使用
$size表示根据要求数组长度满足某条件db.inventory.find( { tags: { $size: 3 } } )
-
对内联文档数组进行查询
当文档的某属性为文档,则称之为内联文档. 向集合中添加含有内联文档数组属性的文档如下:
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ item: "journal", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 5 }, { warehouse: "C", qty: 15 } ] },
{ item: "notebook", instock: [ { warehouse: "C", qty: 5 } ] },
{ item: "paper", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 60 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 15 } ] },
{ item: "planner", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 40 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 5 } ] },
{ item: "postcard", instock: [ { warehouse: "B", qty: 15 }, { warehouse: "C", qty: 35 } ] }
]);
-
直接查询一个内联文档
可以通过直接指定查询一个元素的方式对内联文档数组进行查询:db.inventory.find( { "instock": { warehouse: "A", qty: 5 } } )该方式需要注意所指定的内联文档的属性及顺序要与数组中的元素完全匹配,更改顺序或缺少属性都不能匹配到数组.
// 属性顺序不匹配 db.inventory.find( { "instock": { qty: 5, warehouse: "A" } } ) // 属性不全 db.inventory.find( { "instock": { warehouse: "A"} } ) -
通过内联文档属性进行查询
我们可以通过内联文档属性进行查询,会返回数组中至少有一个元素满足匹配的文档.db.inventory.find( { 'instock.qty': { $lte: 20 } } )也可以指定要求数组中某位置的元素属性满足的条件
db.inventory.find( { 'instock.0.qty': { $lte: 20 } } ) -
指定多条件查询
-
对内联文档数组指定多条件查询时,只要求数组中所有元素的任意匹配满足所有条件,而不必有一个元素满足所有条件.
db.inventory.find( { "instock.qty": { $gt: 10, $lte: 20 } } ) db.inventory.find( { "instock.qty": 5, "instock.warehouse": "A" } ) -
可以使用
$elemMatch要求数组中至少存在一个元素满足所有条件.db.inventory.find( { "instock": { $elemMatch: { qty: { $gt: 10, $lte: 20 } } } } ) db.inventory.find( { "instock": { $elemMatch: { qty: 5, warehouse: "A" } } } )
-
修改操作
- 使用
db.集合名.updateOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)方法修改一个匹配<filter>条件的文档 - 使用
db.集合名.updateMany(<filter>, <update>, <options>)方法修改所有匹配<filter>条件的文档 - 使用
db.集合名.replaceOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)方法替换一个匹配<filter>条件的文档
其中<filter>参数与查询方法中的条件参数完全一致.

下面演示修改操作:向集合中添加文档如下:
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ item: "canvas", qty: 100, size: { h: 28, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "mat", qty: 85, size: { h: 27.9, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "mousepad", qty: 25, size: { h: 19, w: 22.85, uom: "cm" }, status: "P" },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "P" },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "sketchbook", qty: 80, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "sketch pad", qty: 95, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30.5, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }
] );
db.集合名.updateOne()和db.集合名.updateMany()方法接收的<update>参数的格式如下:
{
<update operator>: { <field1>: <value1>, ... },
<update operator>: { <field2>: <value2>, ... },
...
}
其中最常用的修改操作符即为$set和$unset,分别表示赋值和取消赋值.
db.inventory.updateOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "cm", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)
db.inventory.updateMany(
{ qty: { $lt: 50 } },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "in", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)
db.集合名.replaceOne()方法替换除_id属性外的所有属性,其<update>参数应为一个全新的文档.
db.inventory.replaceOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{ item: "paper", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 60 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 40 } ] }
)
删除操作
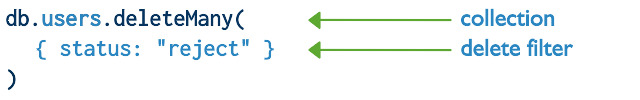
- 使用
db.collection.deleteMany()方法删除一个匹配的文档. - 使用
db.collection.deleteOne()方法删除所有匹配的文档.
db.inventory.deleteMany( { qty : { $lt : 50 } } )
基于Java的CRUD操作
在Java程序中操作MongoDB数据库的方式与Mongo Shell中操作MongoDB数据库的方式类似.
在Java中,文档被抽象成了Document对象,其parse()方法可以将字符串解析为文本对象.MongoDB的操作符也大多可以在Java中找到对应的函数.
增加操作
collection.insertMany(Arrays.asList(
Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }")
));
查询操作
查询操作返回一个FindIterable<Document>对象,它是一个Iterable对象,可以调用其forEach()方法对结果集进行操作
collection.insertMany(Arrays.asList(
Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }")
));
FindIterable<Document> findIterable = collection.find(new Document());
findIterable = collection.find(eq("status", "D"));
findIterable = collection.find(in("status", "A", "D"));
findIterable = collection.find(and(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)));
findIterable = collection.find(or(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)));
findIterable = collection.find(and(eq("status", "A"), or(lt("qty", 30), regex("item", "^p"))));
修改操作
collection.updateOne(eq("item", "paper"),
combine(set("size.uom", "cm"), set("status", "P"),
currentDate("lastModified")));
collection.updateMany(lt("qty", 50),
combine(set("size.uom", "in"), set("status", "P"),
currentDate("lastModified")));
collection.replaceOne(eq("item", "paper"),
Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', instock: [ { warehouse: 'A', qty: 60 }, { warehouse: 'B', qty: 40 } ] }"));
删除操作
collection.deleteMany(new Document());
collection.deleteMany(eq("status", "A"));
collection.deleteOne(eq("status", "D"));










 本文详细介绍MongoDB的安装步骤,包括配置环境变量、启动服务和加入系统服务的方法。同时,深入讲解MongoDB的CRUD操作,涵盖增删改查的基础语法和高级查询技巧,如数组和内联文档的查询,以及基于Java的CRUD操作实现。
本文详细介绍MongoDB的安装步骤,包括配置环境变量、启动服务和加入系统服务的方法。同时,深入讲解MongoDB的CRUD操作,涵盖增删改查的基础语法和高级查询技巧,如数组和内联文档的查询,以及基于Java的CRUD操作实现。
















 1916
1916

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








