提前说明一下
代码中使用的InputReader类是我仿照其他大佬写的输入类
代码如下
对题目有更好解法的,可以评论中指出,提前感谢
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class InputReader {
BufferedReader br;
//构造函数
public InputReader(InputStream stream) {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream));
}
//获取下一个int类型整数
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
//读取下一个字符的ascii,返回
int c = br.read();
//当读取到的字符为空,不断循环读取
while (c <= 32) {
c = br.read();
}
//negative用于判定正负
boolean negative = false;
//当读取到的第一个字符为‘-’号,negative为true,读取下一个字符
if (c == '-') {
negative = true;
c = br.read();
}
//声明一个x变量
int x = 0;
//当读取到的字符不为空,则继续循环
while (c > 32) {
//c减去0的ascii码的差值就是c对应的值
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
//读取下一个字符
c = br.read();
}
//三元运算符,当negative为负返回负数,否则返回正数
return negative ? -x : x;
}
//获取下一个long类型整数
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
int c = br.read();
while (c <= 32) {
c = br.read();
}
boolean negative = false;
if (c == '-') {
negative = true;
c = br.read();
}
long x = 0;
while (c > 32) {
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
c = br.read();
}
return negative ? -x : x;
}
//获取下一个字符串
public String next() throws IOException {
int c = br.read();
while (c <= 32) {
c = br.read();
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (c > 32) {
sb.append((char) c);
c = br.read();
}
return sb.toString();
}
//获取下一个浮点数
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
int c = br.read();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (c != 10 && c != 13){
sb.append((char)c);
c = br.read();
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
A - 车厢重组
在一个旧式的火车站旁边有一座桥,其桥面可以绕河中心的桥墩水平旋转。
一个车站的职工发现桥的长度最多能容纳两节车厢,如果将桥旋转 180
度,则可以把相邻两节车厢的位置交换,用这种方法可以重新排列车厢的顺
序。于是他就负责用这座桥将进站的车厢按车厢号从小到大排列。他退休
后,火车站决定将这一工作自动化,其中一项重要的工作是编一个程序,输
入初始的车厢顺序,计算最少用多少步就能将车厢排序。
输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数 n (1≤n≤10000)。表示火车的车厢个数。
第二行是 nnn 个不同的数表示初始的车厢顺序。
输出格式
最少的旋转次数。
Sample Input
4
4 3 2 1
Sample Output
6
JAVA代码
//冒泡排序的时候记下数就好
public class carriage_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int num = in.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
arr[i] = in.nextInt();
}
int t = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < num-i-1;j++){
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
t = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = t;
count++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
B - 6084问题
任意给出一个四位数,把它重新组成一个四位的最大数和一个最小数,算出两者间的差。
例如:3721 这个数,
可以重组成:7321 和 1237,
差值为 7321−1237。
输入格式
一个四位数。
输出格式
题目中所说的差值。
Sample Input
3721
Sample Output
6084
JAVA代码
//提一下解题思路
//这一题主要就是要理解如何组合数字获得最大,如何组合数值就是最小
//获得最大的数就要把四个数中最大的数放在千位,然后百位十位个位
//最小同理
//知道怎么获取数值后,然后就很简单了,把获取到的数值拆分到数组中
//然后排序
//最后组合出最大最小,相减
public class problem6084_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int num = in.nextInt();
int max_num = 0;
int min_num = 0;
int[] arr = new int[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
arr[i] = num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4;i++){
for (int j = 0; j < 4-i-1; j++){
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
t =arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = t;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++){
max_num += (int)(arr[i] * Math.pow(10, i));
min_num += (int)(arr[4-i-1] * Math.pow(10, i));
}
System.out.println(max_num - min_num);
}
}
C - 绝对值排序
输入 3 个整数,按绝对值从小到大排序。
输入格式
输入包含 3个int范围内的整数,用空格隔开。
输出格式
输出一行,包含三个数,用空格隔开。
若两个数字的绝对值一样,则比较两个数字的大小。
Sample Input
1 3 -3
Sample Output
1 -3 3
JAVA代码
//排序的时候稍微注意一下要求就可以了
public class absolute_sort_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
arr[i] = in.nextInt();
}
int t;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3-i-1; j++){
if (abs(arr[j]) > abs(arr[j+1])){
t = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}else if (abs(arr[j+1]) == abs(arr[j]) && arr[j+1] != arr[j]){
if (arr[j+1] < arr[j]){
t = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0;i < 3;i++){
System.out.print(String.valueOf(arr[i]) + " ");
}
}
static int abs(int num){
if (num < 0){return -num;}
else {return num;}
}
}
D - 开灯
小蓝家的灯是线型开关的,拉一次灯开,再拉一次灯关,未拉之前是熄灭状态。
输入一个正整数 M(1<M<100),作为小蓝拉灯的次数,判断拉灯 MMM 次后,灯是点亮状态还是熄灭状态。
输入格式
输入一个正整数 MMM 作为拉灯的次数(1<M<1001 < M < 1001<M<100)
输出格式
入过灯是点亮状态输出整数 111,如果灯是熄灭状态输出整数 000。
Sample Input
5
Sample Output
1
JAVA代码
//最简单的题目
public class light_up_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println(new InputReader(System.in).nextInt()%2);
}
}
蒜头学院开学了,老师要统计班里每个人的生日,并按照出生日期从早到晚排序。
输入格式
第一行一个整数 n (1≤n≤100),班级班级的人数。
接下来 n行,每行包含一个字符串 s 和三个整数 y,m,d,表示姓名为 s 的同学出生日期是 y 年 m 月 d 日。
保证所有日期合法,姓名由小写字母构成,不超过 20 个字符。
输出格式
输出 n 行,每行一个字符串表示姓名。如果有两个同学出生日期相同,输入靠后的同学先输出。
Sample Input
3
qwb 1996 6 30
gyt 1995 7 28
wc 1996 6 30
Sample Output
gyt
wc
qwb
JAVA代码
//C里面标准答案使用结构体,所以我在JAVA里面就用了类来做一下,数组当让也是可以的,可
//能就是数据移来移去有点麻烦。
//本来还是想用平时使用的冒泡,结果发现总是会有两组数据过不去,冒泡排序的过程中似乎会
//打乱原有顺序,这样就达不到靠后同学先输出的要求了,所以就参考朋友的换了一下方法
//感觉应该算是插入排序的一种
public class BS_5_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int num = in.nextInt();
student[] arr = new student[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
arr[i] = new student(in.next(), in.nextInt(), in.nextInt(), in.nextInt());
}
student t;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j <num;j++){
if (arr[i].cmp(arr[j])){
t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
}
}
for (student s:arr){
System.out.println(s.name);
}
}
}
class student{
String name;
int year;
int month;
int day;
public student() {
}
public student(String name, int year, int month, int day) {
this.name = name;
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public Boolean cmp(student other) {
if ((this.year > other.year) || (this.year == other.year && this.month > other.month) || (this.year == other.year && this.month == other.month && this.day >= other.day)){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
F - 打印字符
蒜头君知道每个字符都有一个对应的 ASCII 码。
现在输入一个 ASCII 码,要求你输出对应的字符。
输入格式
一个整数,即字符的 ASCII 码,保证对应的字符为可见字符。
输出格式
一行,包含相应的字符。
Sample Input
65
Sample Output
A
JAVA代码
//副队出的题目真是亚萨西啊
public class print_char_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
System.out.printf("%c\n", in.nextInt());
}
}
G - 最大字符
给你三个 ASCII 字符,找出其中最大的那个
输入格式
输入包含三个字符,之间有一个空格隔开。
输出格式
输出 ASII 码最大的那个字符,占一行。
数据范围
为了降低难度,本题的字母只有数字和大小写字母。
Sample Input
a b c
Sample Output
c
JAVA代码
//比较ascii码后选出最大,然后格式化输出就完了
public class max_char_7{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int max = br.read();
int next = br.read();
while (next <= 32){
next = br.read();
}
if (next > max){max = next;}
next = br.read();
while (next <= 32){
next = br.read();
}
if (next > max){max = next;}
System.out.printf("%c", max);
}
}
H - 输出保留3位小数的浮点数
读入一个浮点数,保留 33 位小数输出这个浮点数。
输入格式
只有一行,一个浮点数 x(-10^5 <= x <= 10^5).
输出格式
也只有一行,保留 3 位小数的浮点数。
Sample Input
12.34521
Sample Output
12.345
JAVA代码
//格式化输出,考语法的
public class retain_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
System.out.printf("%.3f",in.nextDouble());
}
}
I - 字符替换
把一个字符串中特定的字符全部用给定的字符替换,得到一个新的字符串。
输入格式
只有一行,由一个字符串和两个字符组成,中间用单个空格隔开。
字符串是待替换的字符串,字符串长度小于等于 3030 个字符,且不含空格等空白符;
接下来一个字符为需要被替换的特定字符;
接下来一个字符为用于替换的给定字符。
输出格式
一行,即替换后的字符串。
Sample Input
hello-how-are-you o O
Sample Output
hellO-hOw-are-yOu
JAVA代码
//可以直接调函数
//当你也可以通过读取后通过split切分成数组,然后循环替换,输出
public class replace_char_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
String[] s1 = in.nextLine().split(" ");
System.out.println(s1[0].replace(s1[1], s1[2]));
}
}
J - 过滤多余的空格
一个句子中也许有多个连续空格,过滤掉多余的空格,只留下一个空格。
输入格式
一行,一个字符串(长度不超过 200200),句子的头和尾都没有空格。
输出格式
过滤之后的句子。
Sample Input
Hello world.This is c language.
Sample Output
Hello world.This is c language.
JAVA代码
//java调用split函数后可能不像python那么智能,可能会残留有空字符串在数组中,所以循环时
//直接遇到跳过就好了,这里可以选择不用StringBuilder,直接输出
//c语言的话,我不是很清楚有没有这个方法,但应该可以循环字符串时,设置两个变量,一个
//指向下一个字符,一个指向当前字符,当下一个字符不为空格,当前字符为空格,保留空格,
//应该就可以了(纯粹设想,没怎么学过c)
public class redundant_space_10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
String[] s1 = s.split(" ");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String s2 : s1){
if (!s2.equals("")){
sb.append(s2 + " ");
}
}
System.out.printf(sb.toString());
}
}
K - 爬楼梯
树老师爬楼梯,他可以每次走1级或者2级,输入楼梯的级数,求不同的走法数
例如:楼梯一共有3级,他可以每次都走一级,或者第一次走一级,第二次走两级
也可以第一次走两级,第二次走一级,一共3种方法。
Input
输入包含若干行,每行包含一个正整数N,代表楼梯级数,1 <= N <= 30
Output
不同的走法数,每一行输入对应一行输出
Sample Input
5
8
10
Sample Output
8
34
89
JAVA代码
//这里稍微麻烦了一些,我没有用Scanner来写,所以获取数据有点麻烦,Scanner调用
//hasNextInt()就可以进行判断了,不过其他都还好,虽然说是考察递归,不过我用的动态规
//划,可以看一下
public class climb_stairs_11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int x = 0;
int c = br.read();
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//当读取到的字符不为空,则继续循环
while(true){
while (c > 32) {
//c减去0的ascii码的差值就是c对应的值
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
//读取下一个字符
c = br.read();
}
arr.add(x);
x = 0;
c = br.read();
if(c <= 32){break;}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){
System.out.println(fun(arr.get(i)));
}
}
static int fun(int num){
if (num == 0) return 0;
if (num == 1) return 1;
if (num == 2) return 2;
int i = 1;
int j = 2;
int n = 0;
for (int z = 3; z <= num; z++){
n = i + j;
i = j;
j = n;
}
return n;
}
}
//这边贴一份以前写的递归的解法,不过当时写的是可以一步跨三个楼梯,也没啥区别
static int fun1(int num){
if(num == 1){
return 1;
}
if (num == 2){
return 2;
}
if (num == 3){
return 4;
}
return fun1(num-1) + fun1(num-2) + fun1(num-3);
}

//这一题数据和时间要求不高,如果递归继续走下去会变得很慢,因为在这个递归运算过程中会
//计算很多重复值,就会出现超时
//所以这里再给出一份优化版本,讲每次计算的数据存放到数组中,当需要数据时,优先到数组
//中查询
static int climbStairsWithRecursionMemory(int n) {
int[] memoryArray = new int[n + 1];
memoryArray[1] = 1;
if (n >= 2){memoryArray[2] = 2; }
if (n >= 3){memoryArray[3] = 4; }
if (n <= 3){return memoryArray[n];}
return subClimbStairsWithRecursionMemory(n - 1, memoryArray) + subClimbStairsWithRecursionMemory(n - 2, memoryArray) + subClimbStairsWithRecursionMemory(n-3, memoryArray);
}
static int subClimbStairsWithRecursionMemory(int n, int[] memoryArray) {
if (memoryArray[n] > 0) {
return memoryArray[n];
}
memoryArray[n] = subClimbStairsWithRecursionMemory(n - 1, memoryArray) + subClimbStairsWithRecursionMemory(n - 2, memoryArray) + subClimbStairsWithRecursionMemory(n-3, memoryArray);
return memoryArray[n];
}
L - 机器人走方格
M * N的方格,一个机器人从左上走到右下,只能向右或向下走。有多少种不同的走法?
由于方法数量可能很大,只需要输出Mod 10^9 + 7的结果。
Input
第1行,2个数M,N,中间用空格隔开。(2 <= m,n <= 1000)
Output
输出走法的数量。
Sample Input
2 3
Sample Output
3
JAVA代码
//和上一题很相似,没什么好说的,动态规划,或者递归,递归这次必须要用数组存放数据了,不
//然会超时
//动态规划
public class robots {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {arr[i] = 1;}
for (int i = 1;i < m;i++){
for (int j = 1;j < n;j++){
arr[j] += arr[j-1];
if (arr[j] >= 1000000007){arr[j] %= 1000000007;}
}
}
System.out.print(arr[arr.length - 1]);
}
}
//递归
public class robots_11_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
int[][] arr = new int[m][n];
System.out.println(fun1(m-1, n-1, arr));
}
static int fun1(int m, int n, int[][] arr){
if (n == 0 || m == 0){
arr[m][n] = 1;
return 1;
}
if (arr[m][n] != 0){return arr[m][n];}
arr[m][n] = fun1(m-1, n, arr) + fun1(m, n-1, arr);
if (arr[m][n] > 1000000007){arr[m][n] %= 1000000007;}
return arr[m][n];
}
}
M - 数的计算
我们要求找出具有下列性质数的个数(包含输入的自然数 nnn):
先输入一个自然数 n(n≤1000),然后对此自然数按照如下方法进行处理:
不作任何处理;
在它的左边加上一个自然数,但该自然数不能超过原数的一半;
k加上数后,继续按此规则进行处理,直到不能再加自然数为止。
输入格式
1 个自然数 n(n≤1000)。
输出格式
1 个整数,表示具有该性质数的个数。
样例说明
满足条件的数为:
6,16,26,126,36,136。
Sample Input
6
Sample Output
6
解题思路
首先我们要明确一点,他让我们去计算的是满足条件的数的个数
而不是让我们去输出这些满足条件的数
那我们只需要计算个数就可以了,不要去考虑把这些数全部搞出来,让后计算个数,那太麻烦了
不会真的有人会去想把数全都整出来再计算吧,不会吧不会吧,哦,是我啊,那没事了
OK,我们来简单看一下这一题。
获取一个数假定是n,他前面只能放不能超过原数一半的,那么它前面就可以放
n/2,n/2-1,n/2-2, ....... , 1
我们假定f(n)等于n这个数对应的有多少个满足条件的个数,这个时候我们就可以发现其实这一
题的公式就已经出来了f(n) = f(n/2) + f(n/2-1) + .... + f(1) + 1
加1是因为n本身也要计算再内。然后去写一下代码就可以了
其实你再仔细思考一下会发现,当n>=2时,所有奇数的个数都和他的前一位偶数相同,直接拿来用就行了,不用算
当然其实你再仔细想想,当n>2时,所有偶数的个数都等于它前一个偶数的个数加上当前这个偶数的二分之一的那个数值的个数。
有点绕,可以自己写写理解一下
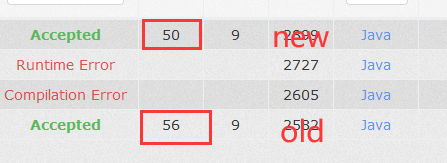
可以看出第新的方法的速度还是蛮快的(指快了6ms,这边应该是因为数据量比较小,当数据量大时,速度的快慢应该就很明显了)。
JAVA代码
//重点还是要理解这一题,抓住这一题的公式
//这边只用了动态规划,没写递归。
public class num_13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int num = in.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[num+1];
arr[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= num; i++) {
arr[i] = 1;
for (int t = i/2;t >= 1;t--){
arr[i] += arr[t];
}
}
System.out.println(arr[num]);
}
}
//new
public class num_13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int num = in.nextInt();
if (num == 1){
System.out.println(1);
return;
}else if (num == 2){
System.out.println(2);
return;
}
int[] arr = new int[num+1];
arr[1] = 1;
arr[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= num; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 1){
arr[i] = arr[i-1];
}else{
arr[i] = arr[i-2] + arr[i/2];
}
}
System.out.println(arr[num]);
}
}
N - 汉诺塔问题(Hanoi)
**一、汉诺塔问题**
有三根杆子A,B,C。A杆上有N个(N>1)穿孔圆盘,盘的尺寸由下到上依次变小。
要求按下列规则将所有圆盘移至C杆: 每次只能移动一个圆盘; 大盘不能叠在小盘上面。
提示:可将圆盘临时置于B杆,也可将从A杆移出的圆盘重新移回A杆,但都必须遵循
上述两条规则。
问:如何移?最少要移动多少次?
二、故事由来
法国数学家爱德华·卢卡斯曾编写过一个印度的古老传说:在世界中心贝拿勒斯(在印度北部)的圣庙里,一块黄铜板上插着三根宝石针。
印度教的主神梵天在创造世界的时候,在其中一根针上从下到上地穿好了由大到小的64片金片,这就是所谓的汉诺塔。不论白天黑夜,
总有一个僧侣在按照下面的法则移动这些金片:一次只移动一片,不管在哪根针上,小片必须在大片上面。僧侣们预言,当所有的金片
都从梵天穿好的那根针上移到另外一根针上时,世界就将在一声霹雳中消灭,而梵塔、庙宇和众生也都将同归于尽。
不管这个传说的可信度有多大,如果考虑一下把64片金片,由一根针上移到另一根针上,并且始终保持上小下大的顺序。这需要多少次移动呢?
这里需要递归的方法。假设有n片,移动次数是f(n).显然f(1)=1,f(2)=3,f(3)=7,且f(k+1)=2*f(k)+1。此后不难证明f(n)=2^n-1。n=64时,
假如每秒钟一次,共需多长时间呢?一个平年365天有31536000 秒,闰年366天有31622400秒,平均每年31556952秒,计算一下:
18446744073709551615秒 这表明移完这些金片需要5845.54亿年以上,而地球存在至今不过45亿年,太阳系的预期寿命据说也就是数百亿年。
真的过了5845.54亿年,不说太阳系和银河系,至少地球上的一切生命,连同梵塔、庙宇等,都早已经灰飞烟灭。
三、解法
解法的基本思想是递归。假设有A、B、C三个塔,A塔有N块盘,目标是把这些盘全部移到C塔。那么先把A塔顶部的N-1块盘移动到B塔,再把A塔剩下
的大盘移到C,最后把B塔的N-1块盘移到C。 每次移动多于一块盘时,则再次使用上述算法来移动。
Input
输入为一个整数后面跟三个单字符字符串。
整数为盘子的数目,后三个字符表示三个杆子的编号。
Output
输出每一步移动盘子的记录。一次移动一行。
每次移动的记录为例如3:a->b 的形式,即把编号为3的盘子从a杆移至b杆。
我们约定圆盘从小到大编号为1, 2, ...n。即最上面那个最小的圆盘编号为1,最下面最大的圆盘编号为n。
Sample Input
3 a b c
Sample Output
1:a->c
2:a->b
1:c->b
3:a->c
1:b->a
2:b->c
1:a->c
解题实录
想象一下,我们现在要移动整个汉诺塔到一根柱子上
那么我们必然要移动下面最大的塔移动到那根柱子上
那么其余的塔必然有序的在另一根柱子上
那么我们就可以得出移动n个汉诺塔到一根柱子上,必须要先移动上面n-1个汉诺塔到另一个柱子上。
JAVA代码
public class Hanoi_14 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
int num = in.nextInt();
String a = in.next();
String b = in.next();
String c = in.next();
fun(num, a, c, b);
}
static void fun(int num, String start, String end, String t){
if (num != 1){
fun(num-1,start, t, end);
System.out.println(num + ":" + start + "->" + end);
fun(num-1, t, end, start);
}else{
System.out.println(num + ":" + start + "->" + end);
}
}
}
O - 全排列
给定一个由不同的小写字母组成的字符串,输出这个字符串的所有全排列。我们假设对于小写
字母有'a'<'b'<...<'y'<'z',而且给定的字符串中的字母已经按照从小到大的顺序排列。
输入格式
输入只有一行,是一个由不同的小写字母组成的字符串,已知字符串的长度在 1到6 之间。
输出格式
输出这个字符串的所有排列方式,每行一个排列。要求字母序比较小的排列在前面。字母序
如下定义:
已知 S=s1s2...sk,T=t1t2...tk,则 S<T 等价于,存在 p(1≤p≤k),使得 s1=t1,s2=t2,...,sp−1=tp−1,sp<tp 成立。
Sample Input
abc
Sample Output
abc
acb
bac
bca
cab
cba
解题思路
这一题说真的我的方法应该比较辣鸡,全排列的题目我一直都没有去看过,之前转专业
之后就里面学习了数据结构(Java),因为自己当时不会Java,虽然最开始听着还行,但
一谈到代码就完全不行了,久而久之这节课就水了,所以全排列,广度,深度什么的都是我
很欠缺的知识,所以这一题做起来有点吃力。
不过好在想到了一种解法,之前做过一次八皇后的题目,发现可以用那一题的思路
把这一题套出来


首先建立一个整形二维数组(布尔或者其他都行),两个长度和字符串长度相同
可以看一下上面那个图,当二维数组一层的下标为i的值为1时,则代表我们当前这个字符串
的第一个元素是字符数组中下标为i的元素。
然后我们去递归数组的每一层,然后在每一层进行循环,在循环每一个元素时进行判断,
如果上面所有层的这个位子不为1,则讲该层的这个位子赋予1,当递归到最后一层并赋予1
后,把数组传到一个输出函数,翻译输出一下就好。
说的不是很好,各位见谅一下,当然这个只是我自己想出的解决方法,一定是会有更好的解
决方法的,各位知道了解的可以在评论中指出,最好有一下代码。
全排列这个东西似乎是一个比较死的东西,可以去了解一下,之后做这种题目应该就不会
这么麻烦了。
JAVA代码
public class full_permutation_15 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
String[] str_arr = in.nextLine().split("");
int[][] arr = new int[str_arr.length][str_arr.length];
fun(arr, 0, str_arr);
}
static void fun(int[][] arr,int c, String[] str_arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if (fun1(c, i, arr)){
arr[c][i] = 1;
if (c != arr.length-1){
fun(arr, c+1, str_arr);
arr[c][i] = 0;
}else {
print(arr,str_arr);
arr[c][i] = 0;
return;
}
}
}
}
static Boolean fun1(int i, int j, int[][] arr){
if (i == 0){return true;}
for (int n = i;n >= 0;n--){
if(arr[n][j] == 1){return false;}
}
return true;
}
static void print(int[][] arr, String[] str_arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] == 1){
System.out.print(str_arr[j]);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
这个题目前面10题是由两位副队出的,最后5题是我出的,他们让我出点感觉可
以压轴的,我个人感觉我还是比较菜的,所以就出了点感觉我自己解决有点麻烦
的题目来压轴。
算法这个东西,我个人感觉吧,就是要多做题,多想,看别人代码不仅要把别人代码吃透
了解他是怎么做的,更要了解他是站在怎么一个角度是怎么想到这个解法的,然后学着去用
他的角度去看待其他问题。
最后,如果各位如果有更好的解法各位可以在评论中提出





















 1018
1018











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








