Ever wondered how large enterprise scale systems are designed? Before major software development starts, we have to choose a suitable architecture that will provide us with the desired functionality and quality attributes. Hence, we should understand different architectures, before applying them to our design.
What is an Architectural Pattern?
According to Wikipedia,
An architectural pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem in software architecture within a given context. Architectural patterns are similar to software design pattern but have a broader scope.
In this article, I will be briefly explaining the following 10 common architectural patterns with their usage, pros and cons.
- Layered pattern
- Client-server pattern
- Master-slave pattern
- Pipe-filter pattern
- Broker pattern
- Peer-to-peer pattern
- Event-bus pattern
- Model-view-controller pattern
- Blackboard pattern
- Interpreter pattern
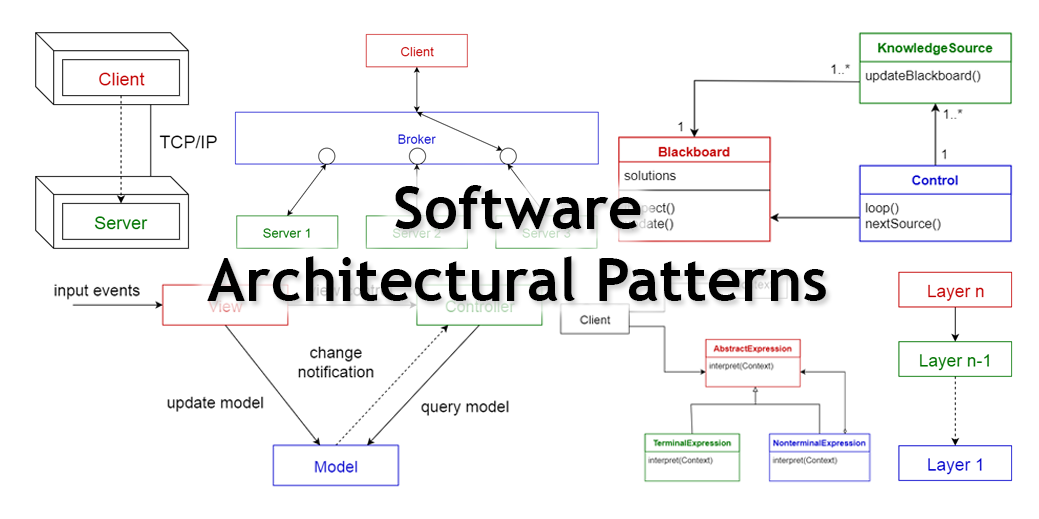
1. Layered pattern
This pattern can be used to structure programs that can be decomposed into groups of subtasks, each of which is at a particular level of abstraction. Each layer provides services to the next higher layer.
The most commonly found 4 layers of a general information system are as follows.
- Presentation layer (also known as UI layer)
- Application layer (also known as service layer)
- Business logic layer (also known as domain layer)
- Data access layer (also known as persistence layer)
Usage
- General desktop applications.
- E commerce web applications.
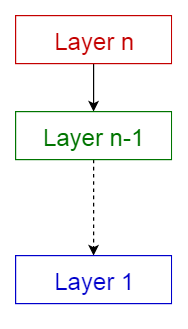
2. Client-server pattern
This pattern consists of two parties; a server and multiple clients. The server component will provide services to multiple client components. Clients request services from the server and the server provides relevant services to those clients. Furthermore, the server continues to listen to client requests.
Usage
- Online applications such as email, document sharing and banking.
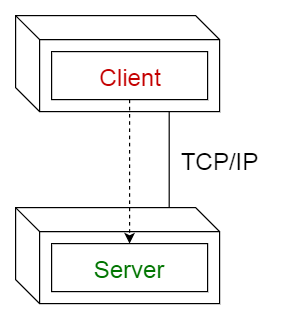
3. Master-slave pattern
This pattern consists of two parties; master and slaves. The master component distributes the work among identical slave components, and computes a final result from the results which the slaves return.
Usage
- In database replication, the master database is regarded as the authoritative source, and the slave databases are synchronized to it.
- Peripherals connected to a bus in a computer system (master and slave drives).
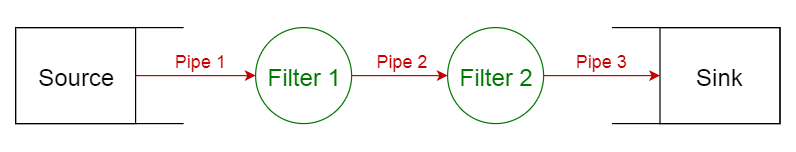
4. Pipe-filter pattern
This pattern can be used to structure systems which produce and process a stream of data. Each processing step is enclosed within a filter component. Data to be processed is passed through pipes. These pipes can be used for buffering or for synchronization purposes.
Usage
- Compilers. The consecutive filters perform lexical analysis, parsing, semantic analysis, and code generation.
- Workflows in bioinformatics.
5. Broker pattern
This pattern is used to structure distributed systems with decoupled components. These components can interact with each other by remote service invocations. A broker component is responsible for the coordination of communication among components.
Servers publish their capabilities (services and characteristics) to a broker. Clients request a service from the broker, and the broker then redirects the client to a suitable service from its registry.
Usage
- Message broker software such as Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka, RabbitMQ and JBoss Messaging.

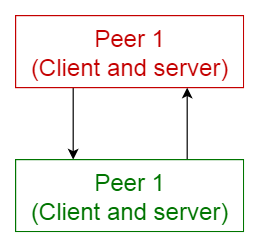
6. Peer-to-peer pattern
In this pattern, individual components are known as peers. Peers may function both as a client, requesting services from other peers, and as a server, providing services to other peers. A peer may act as a client or as a server or as both, and it can change its role dynamically with time.
Usage
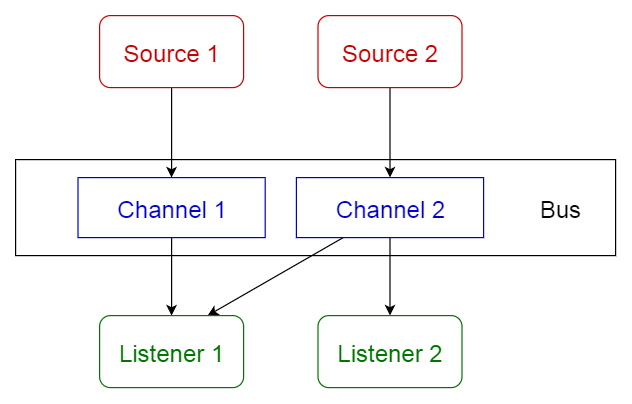
7. Event-bus pattern
This pattern primarily deals with events and has 4 major components; event source, event listener, channel and event bus. Sources publish messages to particular channels on an event bus. Listeners subscribe to particular channels. Listeners are notified of messages that are published to a channel to which they have subscribed before.
Usage
- Android development
- Notification services
8. Model-view-controller pattern
This pattern, also known as MVC pattern, divides an interactive application in to 3 parts as,
- model — contains the core functionality and data
- view — displays the information to the user (more than one view may be defined)
- controller — handles the input from the user
This is done to separate internal representations of information from the ways information is presented to, and accepted from, the user. It decouples components and allows efficient code reuse.
Usage
- Architecture for World Wide Web applications in major programming languages.
- Web frameworks such as Django and Rails.

9. Blackboard pattern
This pattern is useful for problems for which no deterministic solution strategies are known. The blackboard pattern consists of 3 main components.
- blackboard — a structured global memory containing objects from the solution space
- knowledge source — specialized modules with their own representation
- control component — selects, configures and executes modules.
All the components have access to the blackboard. Components may produce new data objects that are added to the blackboard. Components look for particular kinds of data on the blackboard, and may find these by pattern matching with the existing knowledge source.
Usage
- Speech recognition
- Vehicle identification and tracking
- Protein structure identification
- Sonar signals interpretation.

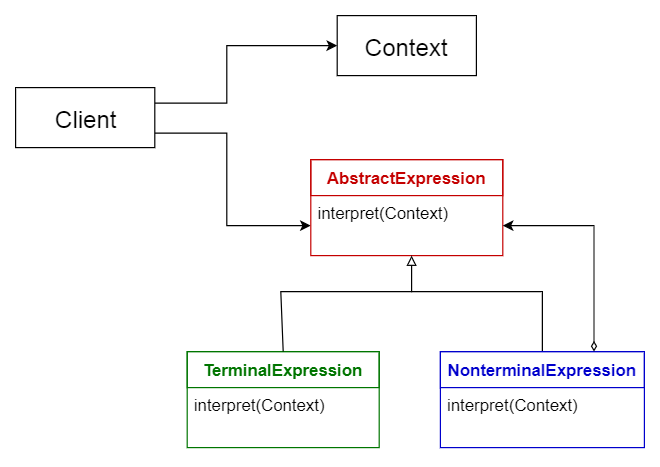
10. Interpreter pattern
This pattern is used for designing a component that interprets programs written in a dedicated language. It mainly specifies how to evaluate lines of programs, known as sentences or expressions written in a particular language. The basic idea is to have a class for each symbol of the language.
Usage
- Database query languages such as SQL.
- Languages used to describe communication protocols.
Comparison of Architectural Patterns
The table given below summarizes the pros and cons of each architectural pattern.

Hope you found this article useful. I would love to hear your thoughts.
























 535
535

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








