前几天学习了HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、WeakHashMap,今天开始学习TreeMap。
TreeMap是Map接口基于红黑树的实现,键值对是有序的。本文主要讲解关于红黑树实现的部分。
部分顶部注释
A Red-Black tree based NavigableMap implementation. The map is sorted according to the Comparable natural ordering of its keys, or by a Comparator provided at map creation time, depending on which constructor is used.
TreeMap是基于NavigableMap的红黑树实现。TreeMap根据键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建map时提供的Comparator进行排序,使用哪种取决于使用的哪个构造方法。
This implementation provides guaranteed log(n) time cost for the containsKey,get, put and remove operations. Algorithms are adaptations of those in Cormen, Leiserson, and Rivest’s Introduction to Algorithms.
TreeMap提供时间复杂度为log(n)的containsKey,get,put ,remove操作。
下面的注释主要讲TreeMap是非同步的,它的迭代器是fail-fastl的。还有很多,不翻译了。
类层次结构图
先来看看TreeMap的定义:
public class TreeMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
从中我们可以了解到:
- TreeMap<K,V>:TreeMap是以key-value形式存储数据的。
- extends AbstractMap<K,V>:继承了AbstractMap,实现Map接口时需要实现的工作量大大减少了。
- implements NavigableMap:实现了NavigableMap,可以返回特定条件最近匹配的导航方法。
- implements Cloneable:表明其可以调用clone()方法来返回实例的field-for-field拷贝。
- implements Serializable:表明该类是可以序列化的。
下图是TreeMap的类结构层次图。
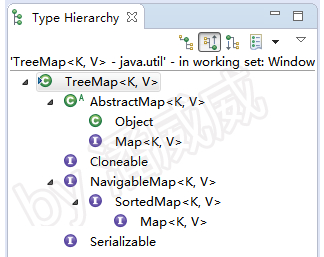
如何查看类层次结构图可以参考我写过的一篇文章:
域
/**
* treeMap的排序规则,如果为null,则根据键的自然顺序进行排序
*
* @serial
*/
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
/**
* 红黑数的根节点
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
/**
* 红黑树节点的个数
*/
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* treeMap的结构性修改次数。实现fast-fail机制的关键。
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;构造函数
TreeMap有四种构造方法:
- TreeMap():使用key的自然排序来构造一个空的treeMap。
- TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator):使用给定的比较器来构造一个空的treeMap。
- TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m):使用key的自然排序来构造一个treeMap,treeMap包含给定map中所有的键值对。
- TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m):使用指定的sortedMap来构造treeMap。treeMap中含有sortedMap中所有的键值对,键值对顺序和sortedMap中相同。
TreeMap()
/**
*
* 使用key的自然排序来构造一个空的treeMap
*/
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator)
/**
* 使用给定的比较器来构造一个空的treeMap
*
* @param 给定的比较器
*/
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)
/**
* 使用key的自然排序来构造一个treeMap,treeMap包含给定map中所有的键值对
*
* @param m 给定map
* @throws ClassCastException 如果map中的key不是Comparable或者不是相互可比较的
* @throws NullPointerException 如果参数map为null
*/
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
关于putAll()方法的讲解请往下看。
putAll( Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
/**
* 将参数map中的所有键值对映射插入到hashMap中,如果有碰撞,则覆盖value。
*
* @param map 参数map
* @throws ClassCastException
* @throws NullPointerException 参数map为null或者参数map中含有值为null的key且treeMap不允许有值为null的key
*/
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {
int mapSize = map.size();
//如果treeMap大小为0且参数map大小不为0且参数map是有序的
if (size==0 && mapSize!=0 && map instanceof SortedMap) {
//取出参数map的比较器
Comparator<?> c = ((SortedMap<?,?>)map).comparator();
//如果参数map的比较器等于treeMap的比较器
if (c == comparator || (c != null && c.equals(comparator))) {
//结构性修改次数+1
++modCount;
try {
//根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap。该方法将map中的元素逐个添加到TreeMap中,并返回map的中间元素作为根节点。
buildFromSorted(mapSize, map.entrySet().iterator(),null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
return;
}
}
//如果执行到了这一步,其实是按照map的entrySet的迭代器的顺序将参数map中所有键值对复制到treeMap中的
super.putAll(map);
}TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m)
/**
* 使用指定的sortedMap来构造treeMap。treeMap中含有sortedMap中所有的键值对,键值对顺序和sortedMap中相同。该方法时间复杂度是线性的。
*
* @param m 指定的sortedMap
* @throws NullPointerException 如果指定的sortedMap为null
*/
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}该构造函数不同于上一个构造函数TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m),在上一个构造函数中传入的参数是Map,Map不一定有序的。而本构造函数的参数是SortedMap类型,是有序的。
关于buildFromSorted方法的讲解请往下看。
查询操作
size()
/**
* 返回treeMap中键值对映射的个数
*
* @return 返回treeMap中键值对映射的个数
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}containsKey( Object key)
/**
* 如果map中含有key为指定参数key的键值对,返回true
*
* @param key 指定参数key
* @return 如果map中含有key为指定参数key的键值对,返回true
* @throws ClassCastException 如果指定参数key不能和map中的key比较
* @throws NullPointerException 如果指定参数key为null而且map使用自然排序,或者比较器不允许key为null
*/
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
}getEntry方法的实现请往下看。
containsValue( Object value)
/**
* 如果hashMap中的键值对有一对或多对的value等于参数value,返回true.
* 判断是否相等的条件为value==null ? v==null : value.equals(v))
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @param value 参数value
* @return 如果hashMap中的键值对有一对或多对的value为参数value,返回true,否则返回false
* @since 1.2
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
//遍历treeMap中所有节点
for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
//判断是否相等的条件为value==null ? v==null : value.equals(v))
if (valEquals(value, e.value))
return true;
return false;
}get(Object key)
/**
* 返回指定的key对应的value,如果value为null,则返回null
*
* @throws ClassCastException 如果参数key和treeMap中的key不可比较
* @throws NullPointerException 如果参数key为null而且treeMap使用自然排序或者比较器不允许key为null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}Comparator<? super K> comparator()
/**
* 返回comparator
*/
public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
return comparator;
}firstKey()
/**
* 返回treeMap中的第一个节点的key
* @throws 如果第一个节点为null,抛出NoSuchElementException
*/
public K firstKey() {
return key(getFirstEntry());
}lastKey()
/**
* 返回treeMap中的第一个节点的key
* @throws 如果第一个节点为null,抛出NoSuchElementException
*/
public K lastKey() {
return key(getLastEntry());
}putAll( Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
putAll()在构造方法TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)处就已经详细讲解了。
getEntry( Object key)
/**
* 返回参数key对应的节点
*
* @return 返回节点,如果没有则返回null
* @throws ClassCastException 如果参数key和treeMap中的key无法比较
* @throws NullPointerException 如果参数key为null而且treeMap使用自然排序或者比较器不允许key为null
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
//如果比较器为不为null
if (comparator != null)
//通过比较器来获取结果。下个介绍的方法就是getEntryUsingComparator
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
//如果key为null,抛出NullPointerException
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//按照二叉树搜索的方式进行搜索,搜到返回
while (p != null) {
//比较节点的key和参数key
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
//如果节点的key小于参数key
if (cmp < 0)
//向左遍历
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)//如果节点的key大于参数key
//向左遍历
p = p.right;
else//如果节点的key等于参数key
return p;
}
//如果遍历完依然没有找到对应的节点,返回null
return null;
}getEntryUsingComparator( Object key)
/**
* 使用comparator获取节点。
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//按照二叉树搜索的方式进行搜索,搜到返回
while (p != null) {
//比较节点的key和参数key
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
//如果节点的key小于参数key
if (cmp < 0)
//向左遍历
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)//如果节点的key大于参数key
//向左遍历
p = p.right;
else//如果节点的key等于参数key
return p;
}
}
return null;
}getCeilingEntry( K key)
/**
* 获取TreeMap中大于/等于key的最小的节点,若不存在,就返回null
*/
final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
//比较参数key和节点p的key
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
// 若节点p的key > 参数key。
// 若 p 存在左孩子,则设 p=p的左孩子;否则,返回p
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp > 0) {// 若节点p的key < key
if (p.right != null) {//若 p 存在右孩子,则设 p=p的右孩子
p = p.right;
} else {//若 p 不存在右孩子,则找出 p 的后继节点,并返回
//这里返回的p的后继节点有2种可能性:第一,null;第二,TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点。
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else//若p的key = key。
return p;
}
return null;
}getFloorEntry( K key)
/**
* 获取TreeMap中小于/等于key的最大的节点,若不存在,就返回null
*/
final Entry<K,V> getFloorEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
//比较参数key和节点p的key
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
// 若节点p的key < 参数key。
// 若 p 存在右孩子,则设 p=p的右孩子;否则,返回p
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp < 0) {// 若节点p的key < key
if (p.left != null) {//若 p 存在左孩子,则设 p=p的左孩子
p = p.left;
} else {//若 p 不存在左孩子,则找出 p 的后继节点,并返回
//这里返回的p的后继节点有2种可能性:第一,null;第二,TreeMap中小于key的最大的节点。
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else//若p的key = key。
return p;
}
return null;
}getHigherEntry( K key)
/**
* 获取TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点,若不存在,返回null
*/
final Entry<K,V> getHigherEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else {
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}getLowerEntry( K key)
/**
* 获取TreeMap中小于key的最大的节点,若不存在,就返回null
*/
final Entry<K,V> getLowerEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else {
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}put( K key, V value)
/**
* 将指定参数key和指定参数value插入map中,如果key已经存在,那就替换key对应的value
*
* @param key 参数key
* @param value 参数value
*
* @return 如果value被替换,则返回旧的value,否则返回null。当然,可能key对应的value就是null。
* @throws ClassCastException 如果指定参数key不能和map中的key比较
* @throws NullPointerException 如果指定参数key为null而且map使用自然排序,或者比较器不允许key为null
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
//如果根节点为空
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // 对key是否为null进行检查type
//创建一个根节点,返回null
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
//记录比较结果
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
//如果comparator不为null
if (cpr != null) {
//循环查找key要插入的位置
do {
//记录上次循环的节点t
parent = t;
//比较节点t的key和参数key的大小
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
//如果节点t的key > 参数key
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)//如果节点t的key < 参数key
t = t.right;
else//如果节点t的key = 参数key,替换value,返回旧value
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);//t为null,没有要比较的节点,代表已经找到新节点要插入的位置
}
else {如果comparator为null,,则使用key作为比较器进行比较,并且key必须实现Comparable接口
//如果key为null,抛出NullPointerException
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {//循环查找key要插入的位置
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
// 找到新节点的父节点后,创建节点对象
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
//如果新节点key的值小于父节点key的值,则插在父节点的左侧
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else//否则插在父节点的左侧
parent.right = e;
//插入新的节点后,为了保持红黑树平衡,对红黑树进行调整
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
//这种情况下没有替换旧value,返回努力了
return null;
}remove( Object key)
/**
* 如果key在treeMap中存在,删除对应的节点,返回旧value,否则返回null
*
* @param key 参数key
* @return 如果节点被删除,返回节点的value,否则返回null。当然,可能key对应的value就是null
* @throws ClassCastException 如果指定参数key为null而且map使用自然排序,或者比较器不允许key为null
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
//获取key对应的节点
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
//如果节点为null,返回null
if (p == null)
return null;
//记录旧value
V oldValue = p.value;
//删除节点
deleteEntry(p);
//返回旧value
return oldValue;
}clear()
/**
*
* 删除map中所有的键值对
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
size = 0;
root = null;
}clone()
/**
* 浅克隆一个TreeMap对象并返回。
*
* @return 浅克隆的TreeMap对象
*/
public Object clone() {
TreeMap<?,?> clone;
try {
clone = (TreeMap<?,?>) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
// Put clone into "virgin" state (except for comparator)
clone.root = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
clone.entrySet = null;
clone.navigableKeySet = null;
clone.descendingMap = null;
// Initialize clone with our mappings
try {
clone.buildFromSorted(size, entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
return clone;
}到这里对TreeMap的讲解就结束了。下面最TreeMap作简单的总结
总结
TreeMap与HashMap比较
不同点
| 不同点 | HashMap | TreeMap |
|---|---|---|
| 数据结构 | 数组+链表+红黑树 | 红黑树 |
| 是否有序 | 否 | 是 |
| 是否实现NavigableMap | 否 | 是 |
| 是否允许key为null | 是 | 否 |
| 增删改查操作的时间复杂度 | O(1) | log(n) |
相同点
- 都以键值对的形式存储数据。
- 都继承了AbstractMap,实现了Map、Cloneable、Serializable。
- 都是非同步的。
本文已收录于Java8容器源码札记专栏。
























 1333
1333

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








