目录
一 . 什么是树
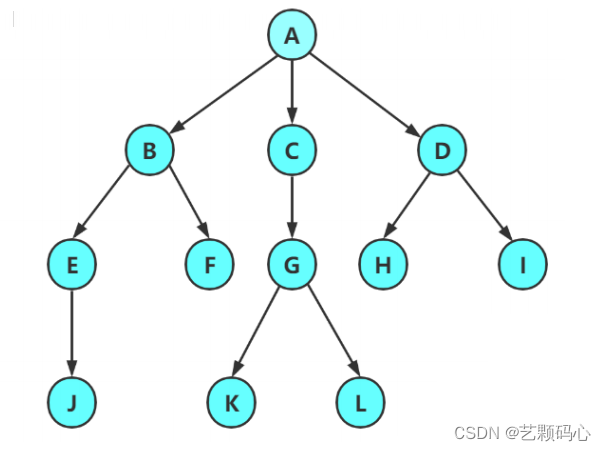
注意 :
1.子树是不相交的.

2.除了根节点以外,每个节点有且仅有一个父节点
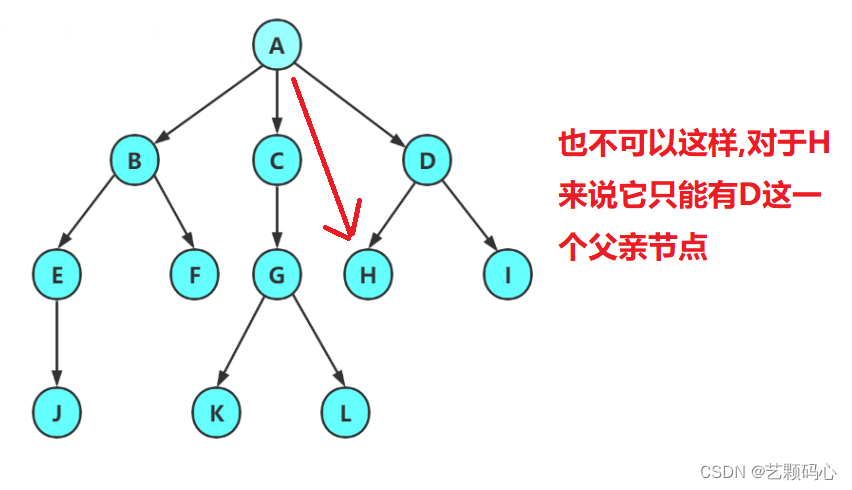
3,一棵N个节点的树有N-1条边.
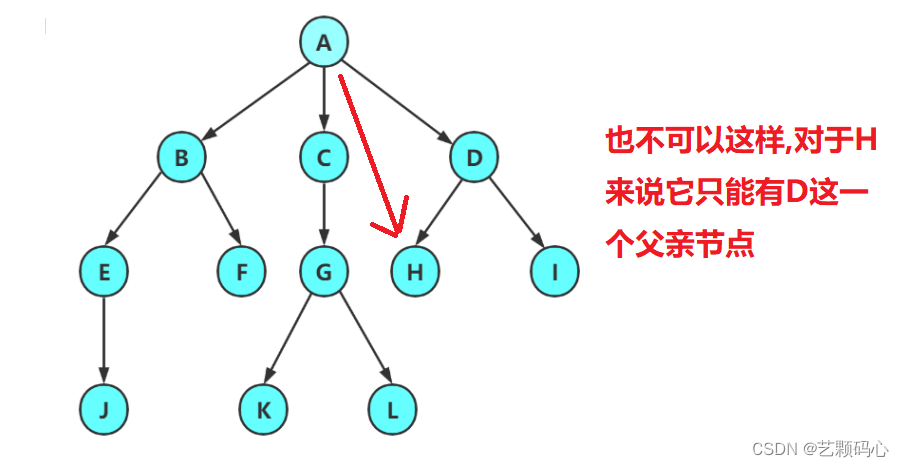
树的概念
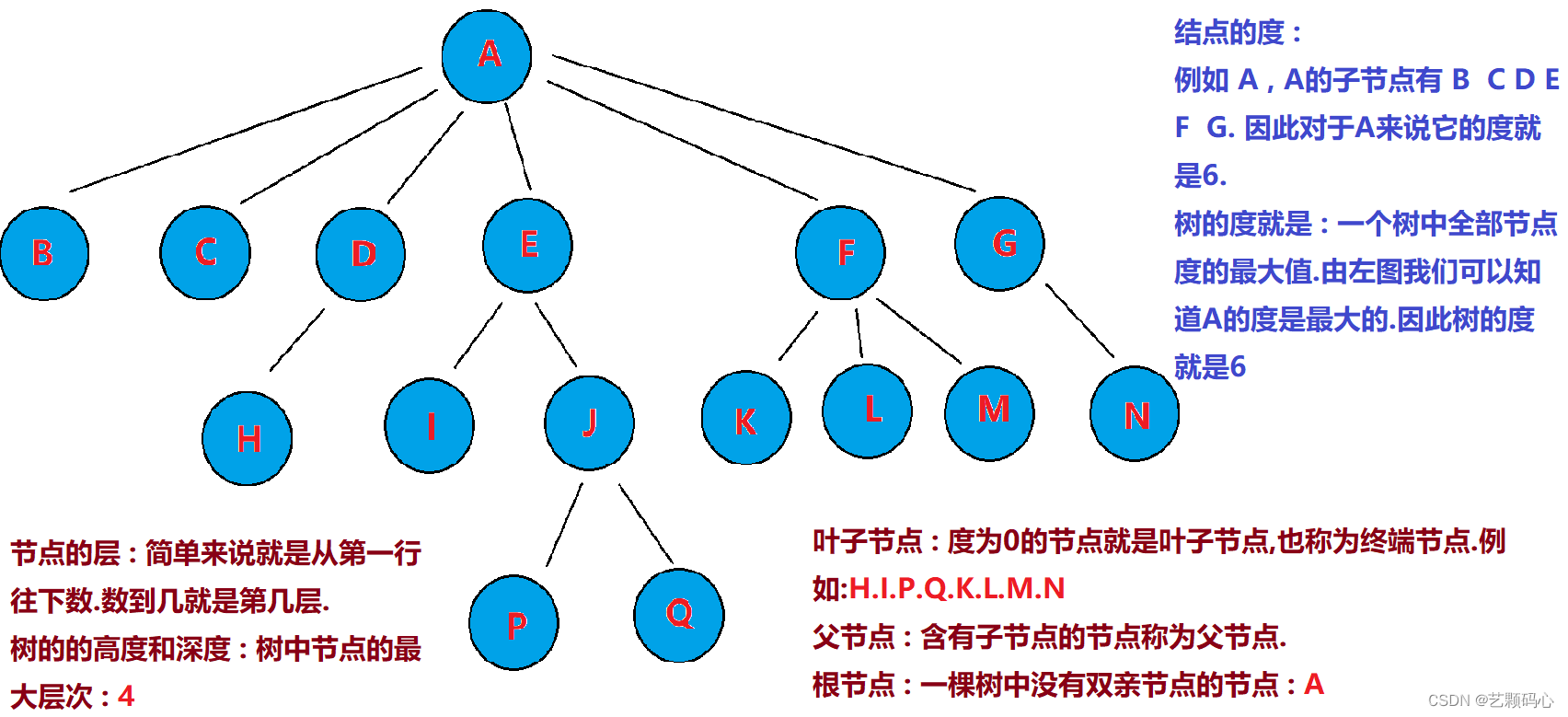
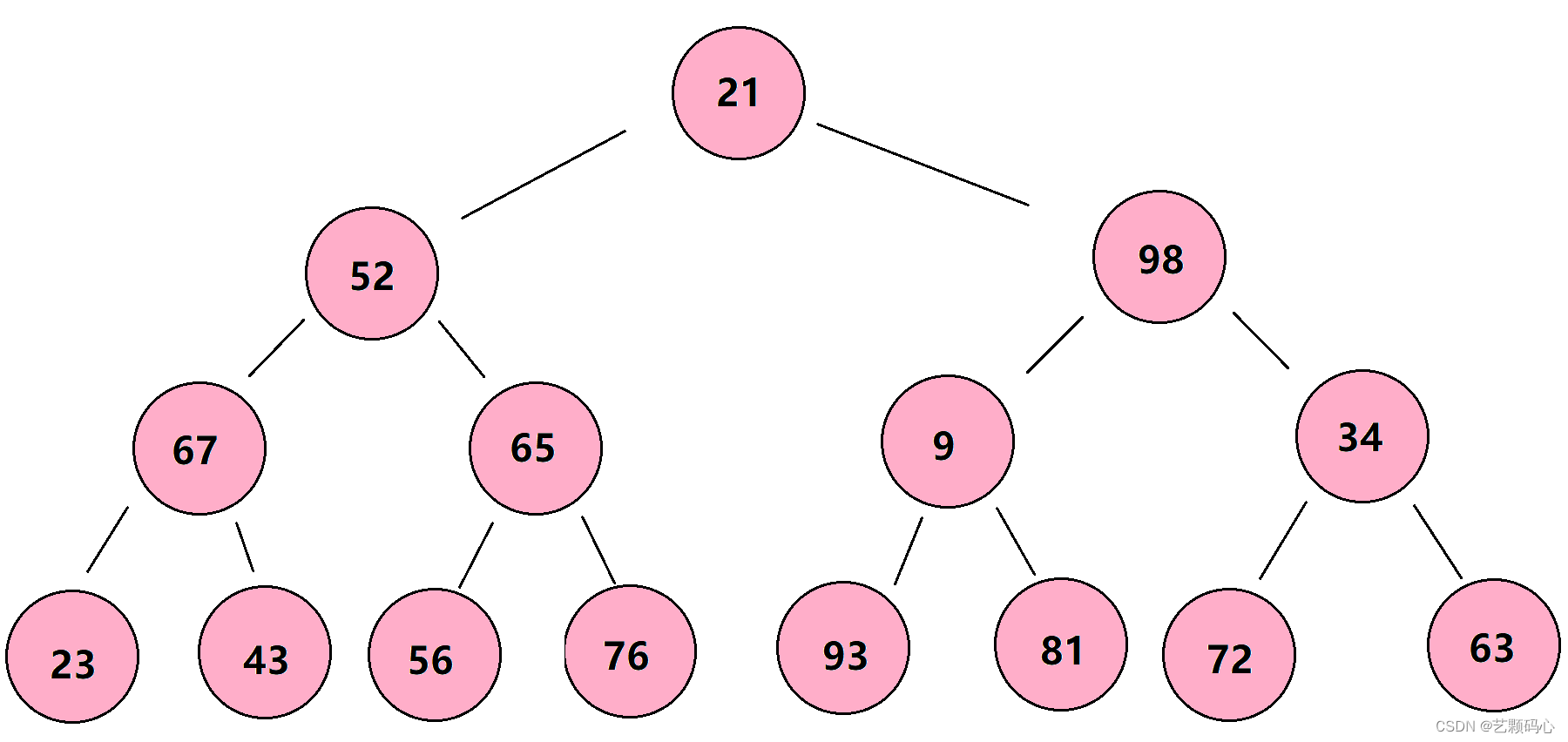
1. 结点的度:一个结点含有子树的个数称为该结点的度; 如上图:A的度为6
2. 树的度:一棵树中,所有结点度的最大值称为树的度; 如上图:树的度为6
8. 树的高度或深度:树中结点的最大层次; 如上图:树的高度为4
树的表示形式
树的表示方式有很多 , 如 : 双亲表示法,孩子表示法,孩子双亲表示法,孩子兄弟表示法.
我们采用最常用的孩子兄弟表示法.
比较简单 : 就像我们之前学的链表一样.
对于二叉树来说 : 有三个值域 : 分别存储 : 值, 左孩子节点地址, 右孩子节点地址
public class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}二. 二叉树
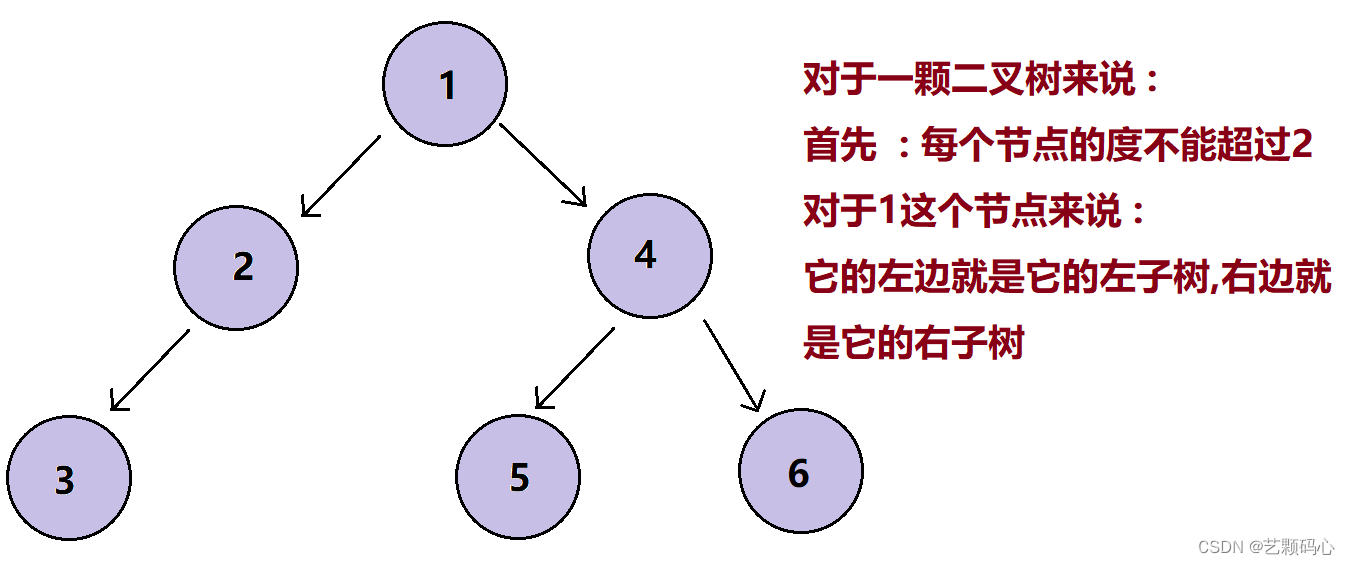
1. 概念 :
二叉树的每个节点的度不能超过2.
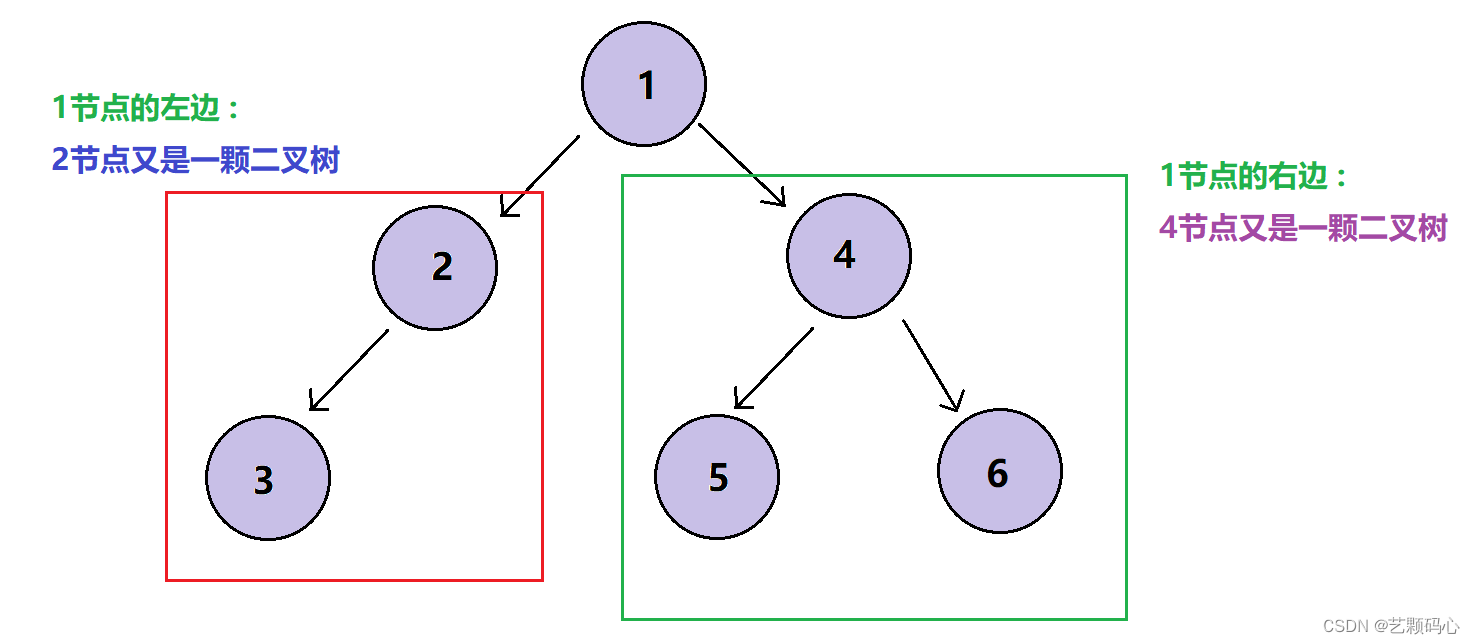
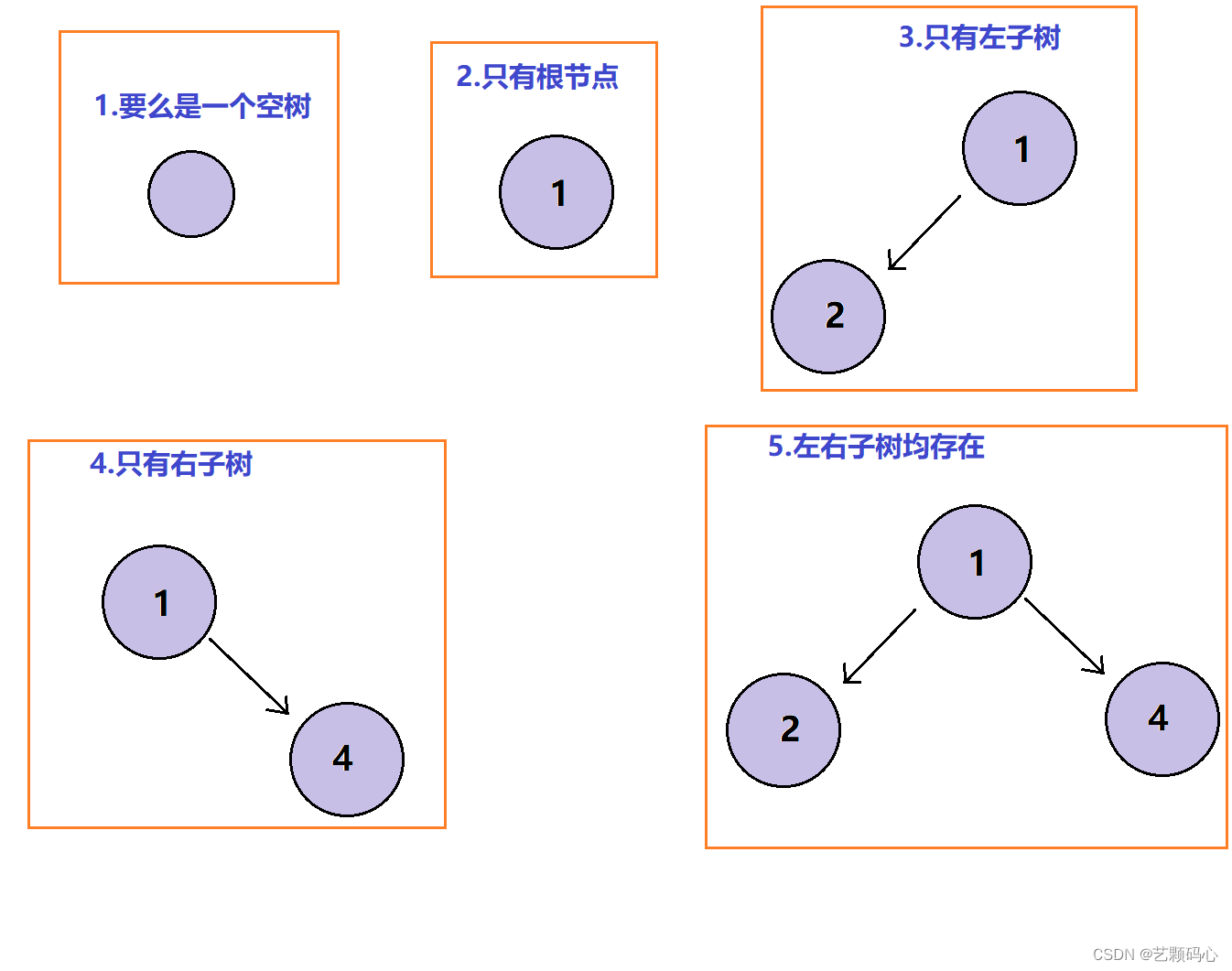
注意 : 对于任意二叉树都是由以下几种情况复合而成的 :
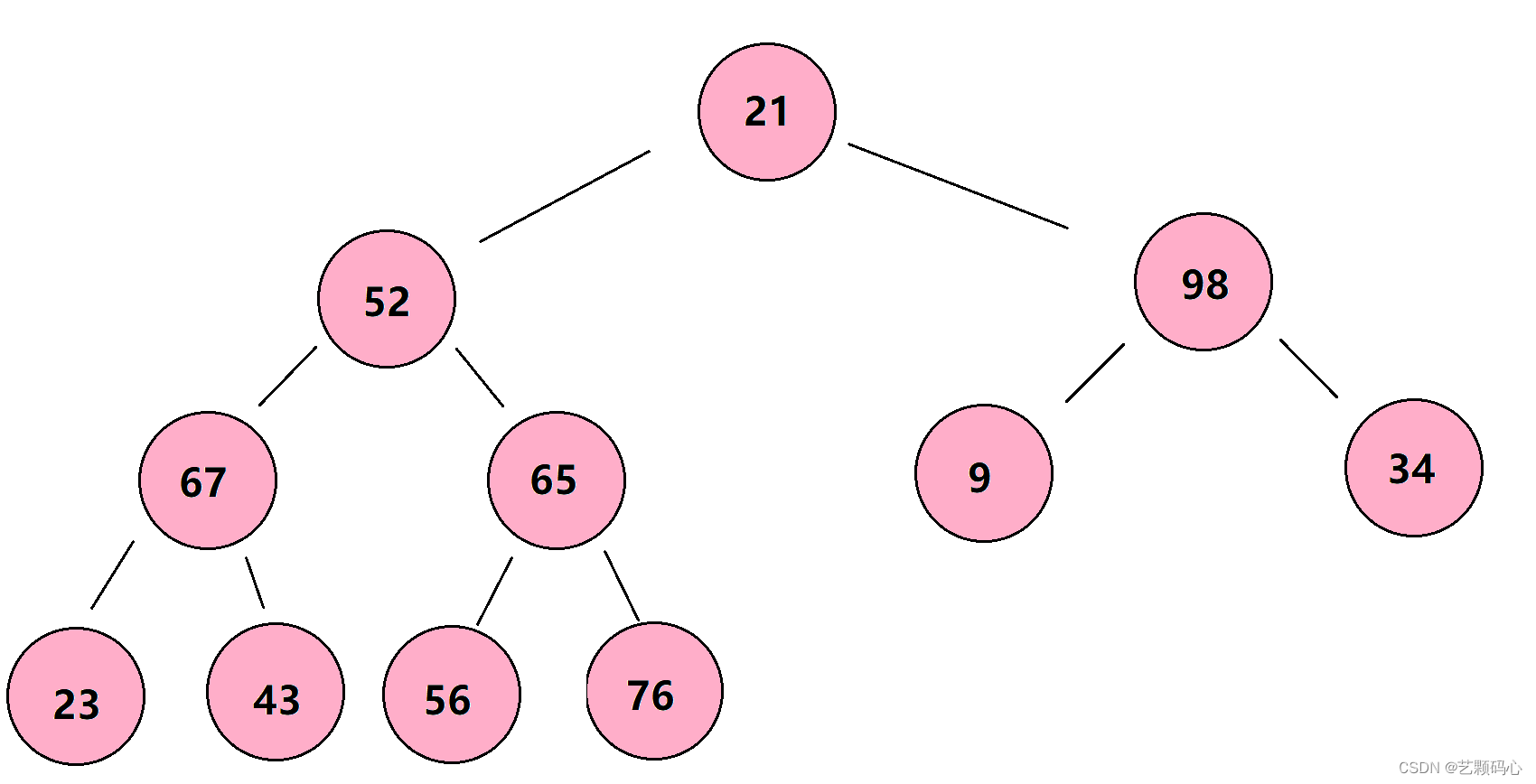
2. 两种特殊的二叉树

3. 二叉树的性质
5. 对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从左至右的顺序对所有节点从0开始编号,则对于序号为i的结点有:
4. 二叉树的存储
二叉树的遍历
1. 前序遍历
首先我们先用穷举的办法来建一个二叉树 :
为了方便操作 我们定义一个成员变量root
public class TreeNode {
static class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
Node root = null;
//创建树
public void createTree() {
Node n1 = new Node(11);
Node n2 = new Node(21);
Node n3 = new Node(31);
Node n4 = new Node(41);
Node n5 = new Node(51);
Node n6 = new Node(61);
n1.left = n2;
n1.right = n3;
n2.left = n4;
n2.right = n5;
n3.right = n6;
this.root = n1;
}
}将上面的代码 图形化 :

前序遍历 : 根 左 右 依次去遍历

对于二叉树的遍历,使用递归是最好的办法
package demo1;
public class TreeNode {
static class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
Node root = null;
//创建树
public Node createTree() {
Node n1 = new Node(11);
Node n2 = new Node(21);
Node n3 = new Node(31);
Node n4 = new Node(41);
Node n5 = new Node(51);
Node n6 = new Node(61);
n1.left = n2;
n1.right = n3;
n2.left = n4;
n2.right = n5;
n3.right = n6;
return n1;
}
public void preorder(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
}
package demo1;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode();
TreeNode.Node root = treeNode.createTree();
treeNode.preorder(root);
}
}
接下来我们来看一下OJ上这道前序遍历的题 : 144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(Leetcode)
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
}它的返回值类型是List<Integer>
解决的思路有两种 :
1. 遍历思路
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(Node root) {
pre(root);
return list;
}
public void pre(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
pre(root.left);
pre(root.right);
}2. 子问题思路
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
list.add(root.val);
List<Integer> left = preorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(left);
List<Integer> right = preorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(right);
return list;
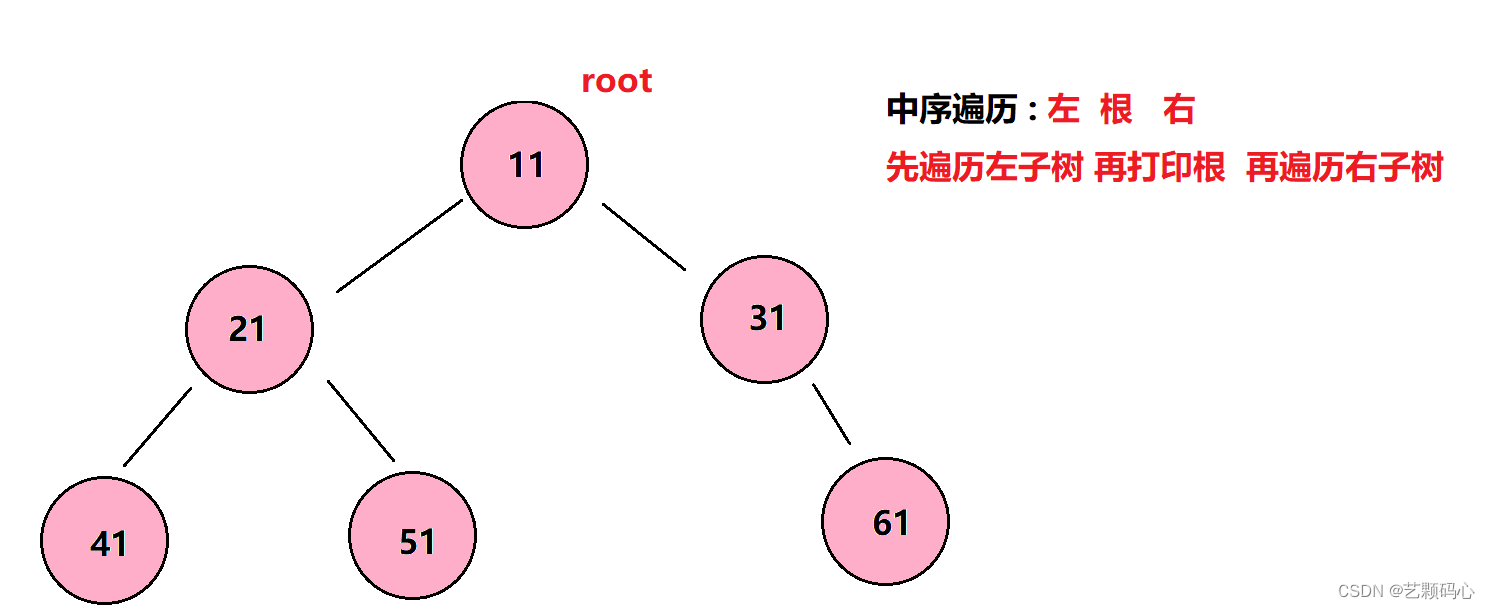
}2. 中序遍历
1. 遍历思路解决
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(Node root) {
inorder(root);
return list;
}
public void inorder(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right);
}2. 子问题思路解决
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
List<Integer> left = inorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(left);
list.add(root.val);
List<Integer> right = inorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(right);
return list;
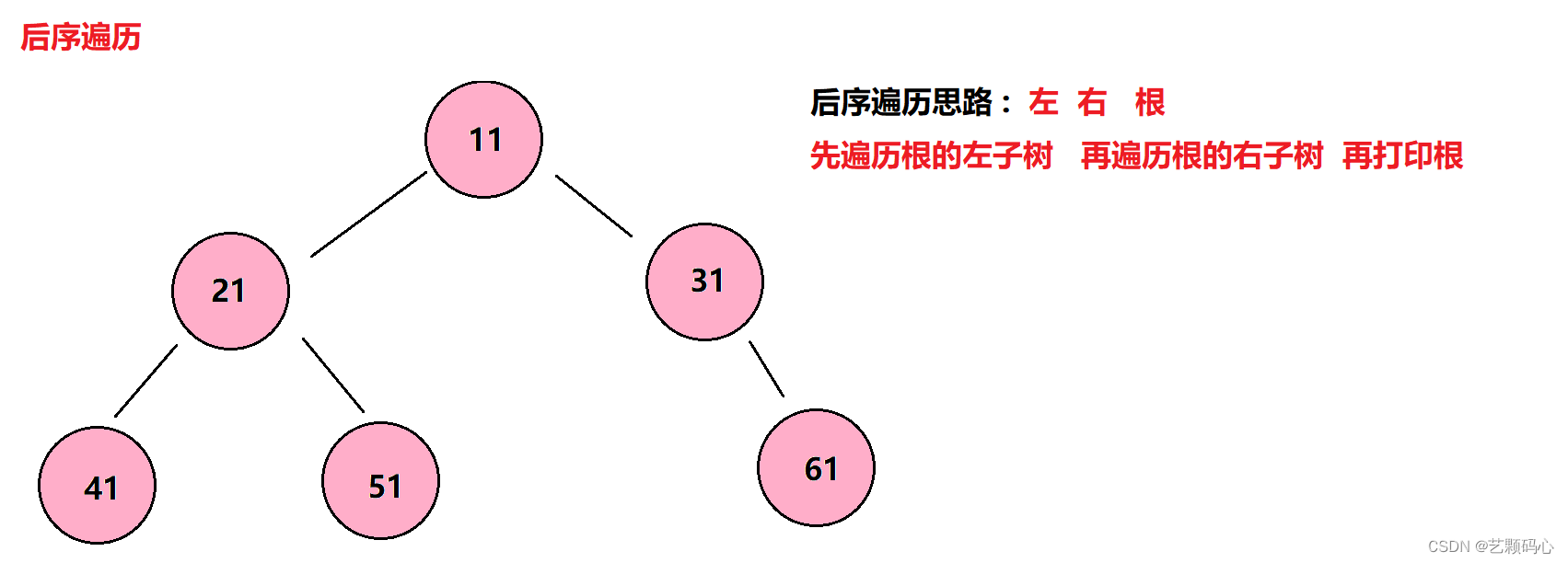
}3 . 后序遍历
遍历思路 : 左 右 根
1. 遍历思路
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
postorder(root);
return list;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
list.add(root.val);
}2. 子问题思路
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
List<Integer> left = postorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(left);
List<Integer> right = postorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(right);
list.add(root.val);
return list;
}二叉树的基本操作
package demo2;
public class BinaryTree {
static class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
Node root = null;
//创建树
public Node createTree() {
Node n1 = new Node(11);
Node n2 = new Node(21);
Node n3 = new Node(31);
Node n4 = new Node(41);
Node n5 = new Node(51);
Node n6 = new Node(61);
n1.left = n2;
n1.right = n3;
n2.left = n4;
n2.right = n5;
n3.right = n6;
return n1;
}
int count = 0;
// 获取树中节点的个数
int size(Node root) {
preorder(root);
return count;
}
public void preorder(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
count++;
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
// 获取叶子节点的个数
// 子问题思路-求叶子结点个数
int getLeafNodeCount(Node root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
return getLeafNodeCount(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
}
// 获取第K层节点的个数
int getKLevelNodeCount(Node root,int k) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (k == 1) {
return 1;
}
return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k - 1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k - 1);
}
// 获取二叉树的高度
int getHeight(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.left);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在
Node find(Node root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val == val) {
return root;
}
Node left = find(root.left,val);
if (left != null) {
return left;
}
Node right = find(root.right,val);
if (right != null) {
return right;
}
return null;
}
}
package demo2;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree.Node root = binaryTree.createTree();
System.out.print("树的节点个数 : ");
System.out.println(binaryTree.size(root));
System.out.print("树的叶子节点个数 : ");
System.out.println(binaryTree.getLeafNodeCount(root));
System.out.print("第3层的节点个数 : ");
System.out.println(binaryTree.getKLevelNodeCount(root,3));
System.out.print("树的高度 : ");
System.out.println(binaryTree.getHeight(root));
System.out.println("找到21这个节点 : ");
BinaryTree.Node node = binaryTree.find(root,21);
System.out.println(node.val);
}
}

层序遍历
思路 : 从上往下 从左往右 依次遍历
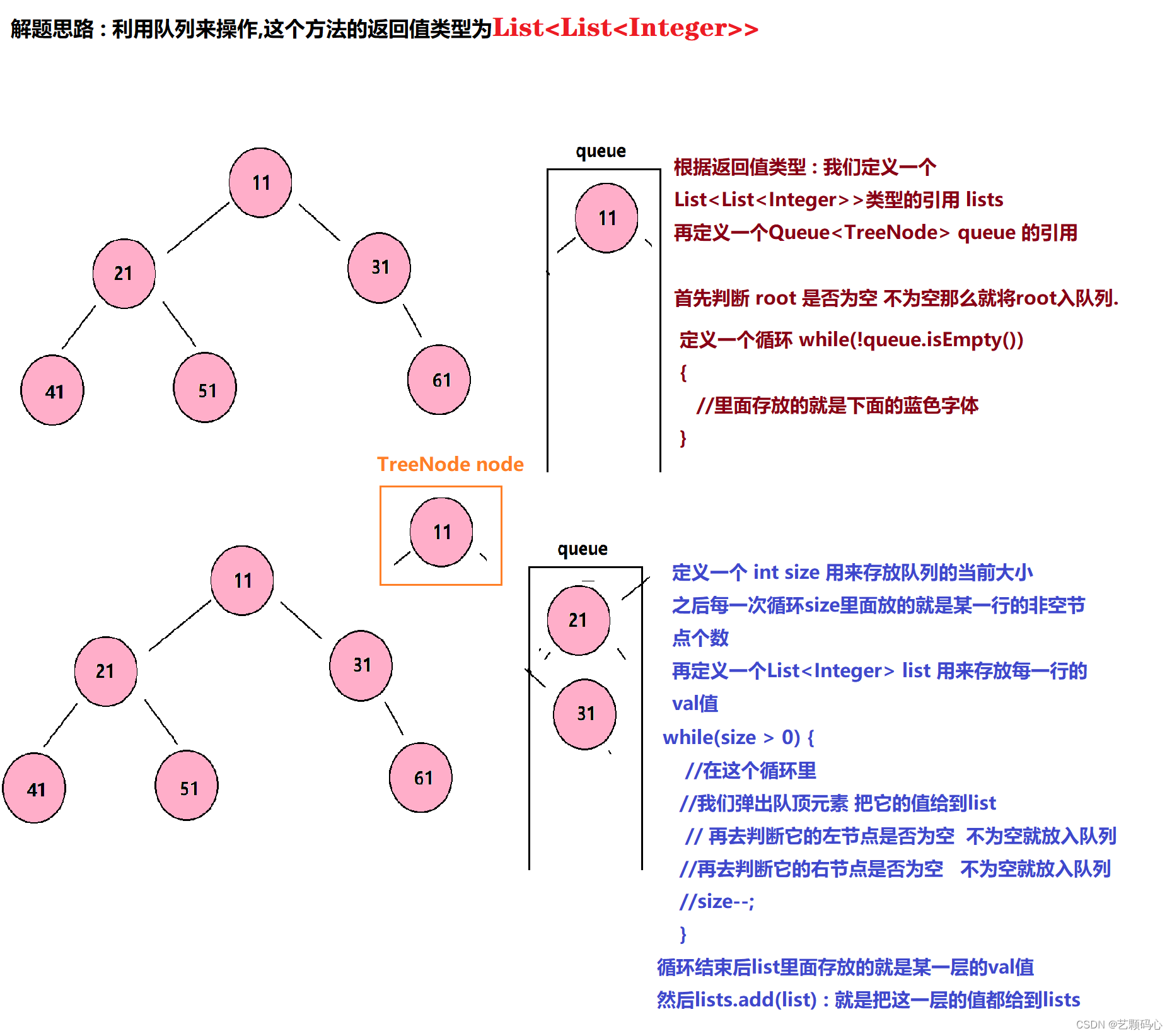
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
lists.add(list);
}
return lists;
}判断完全二叉树
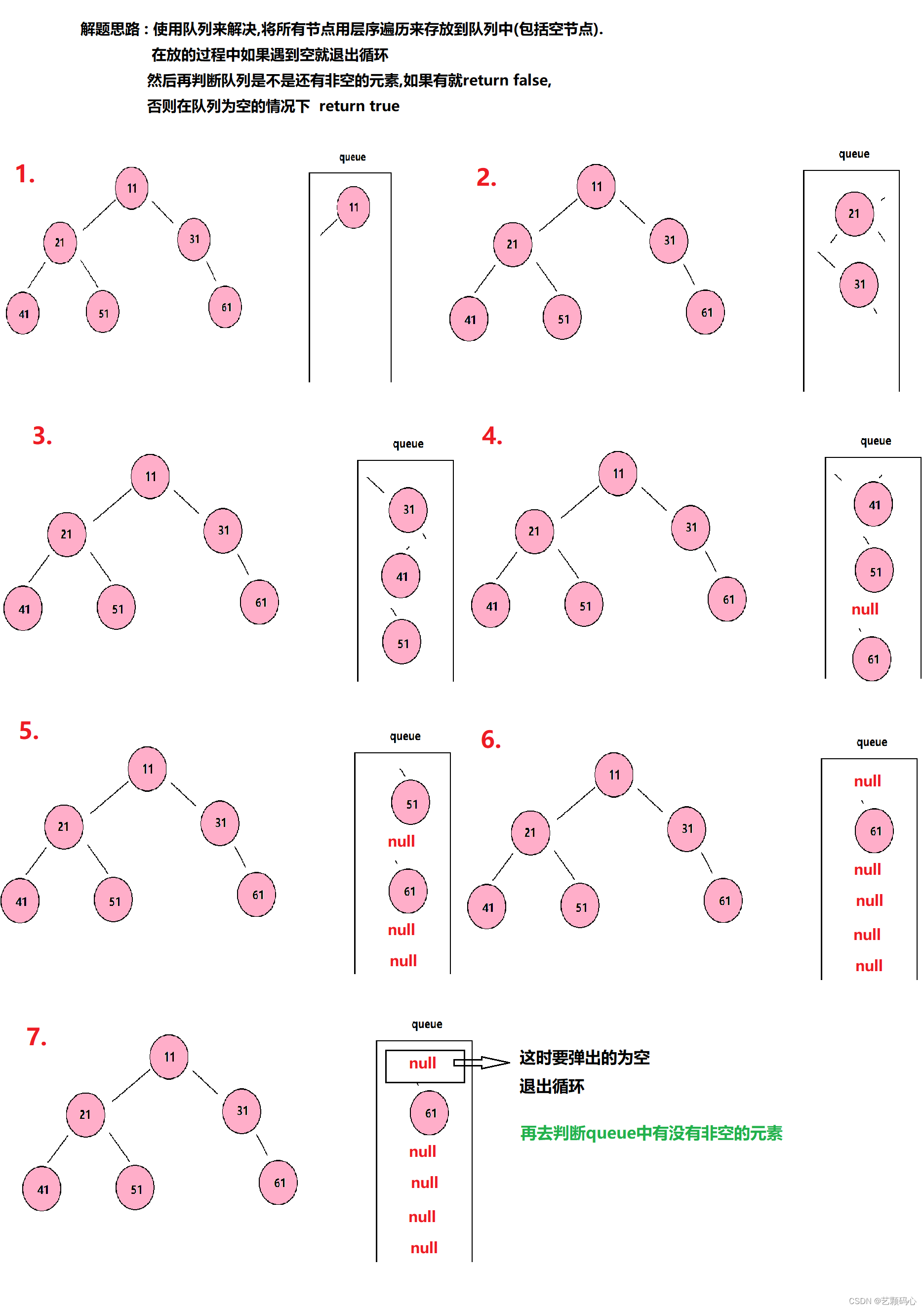
// 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
boolean isCompleteTree(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTree.Node node = queue.poll();
if (node == null) {
break;
}
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
if (queue.poll() != null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}希望可以帮到大家~~~~~






















 241
241











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








