操作手机支持文件系统,在应用程序中读取本地存储的文件也是必须要掌握的知识。这一篇我做个简单的示例,从手机存储上读取图片。
由于是通过模拟器来显示图片,所以模拟器下的目录为root1/photos/,我会在这个目录底下放几张图片。
需要注意一点的是,root1/photos/目录不一定在wtk的目录下,虽然在wtk目录下我能找到,C:/WTK2.5.2/j2mewtk_template/appdb/DefaultColorPhone/filesystem/root1/photos/目录,但是实验证明如果文件放在这个目录下,我无法读取到。
模拟器中使用的root1/photos/目录在用户文件夹下:C:/Users/Sunny/j2mewtk/2.5.2/appdb/DefaultColorPhone/filesystem/root1/photos(Sunny是我的用户名)
还是先上效果图来的直接: 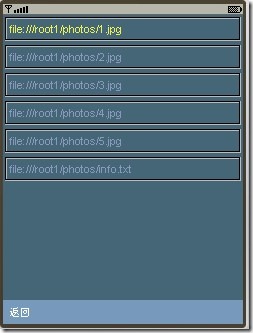

在FileSystem类中声明readImage方法,从文件系统读取图片,返回byte[]数组(代码全部采用LWUIT框架,可以自行改造为MIDP的代码)
/** * 读取图片 * @param path * @return */ public byte[] readImage(String path) { FileConnection fc = null; try { fc = (FileConnection) Connector.open(path, Connector.READ); InputStream is = fc.openInputStream(); byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos); while ((len = is.read(b)) != -1) { dos.write(b, 0, len); } byte[] data = baos.toByteArray(); fc.close(); return data; } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } return null; }
在root1/photos/下放5张图片,点击按钮读取图片,fs是FileSystem类的实例,可以参照前两节。
public void testReadImageFromEmulator() { String directory = "file:///root1/photos/"; Vector fileVector = fs.getFiles(directory); for (int i = 0; i < fileVector.size(); i++) { String name = fileVector.elementAt(i).toString(); Button b = new Button(directory + name); addComponent(b); b.addActionListener(new ButtonActionListener()); } } class ButtonActionListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) { Button b = (Button) evt.getSource(); Form f = new Form(); f.setLayout(new BorderLayout()); Image img = getImage(fs.readImage(b.getText())); f.addComponent(BorderLayout.CENTER, new Button(img)); f.addCommand(new Command("返回") { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionevent) { new Favorites(); } }); f.show(); } } public Image getImage(byte[] bytes) { return Image.createImage(bytes, 0, bytes.length); }






















 2587
2587

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








