一、静态
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"/>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment_static"
class="fragment.FragmentStatic"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
v=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_static,container, false);
return v;
}
1、activity传数据到fragment:
获取对应得fragment: FragmentManager fm=getFragmentManager();
FragmentStatic f=(FragmentStatic) fm.findFragmentById(R.id.fragment_static);
发送数据:fragment.setArguments(Bundle bundle);
在fragment里接收数据:this.getArguments();//Bundle
二、动态
Bundle bundle1=new Bundle();
bundle1.putString("toDynamicFragment1", "toDynamicFragment1");
FragmentDynamic1 f1=new FragmentDynamic1();
f1.setArguments(bundle1);
FragmentManager fm=getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction ft=fm.beginTransaction();
ft.replace(R.id.ll_main_fragment_dynamic, f1);
ft.commit();
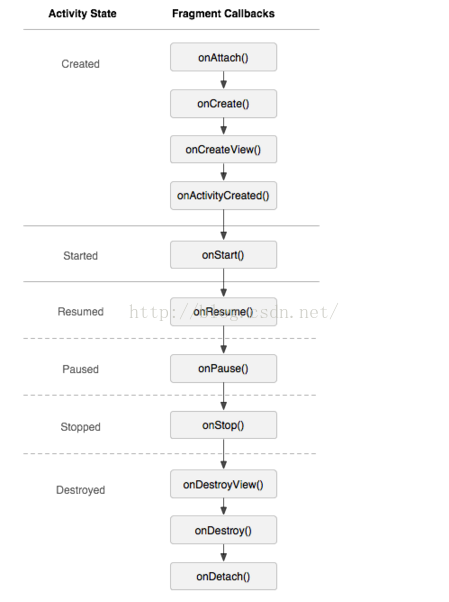
三、生命周期






















 6万+
6万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








