转载请注明出处<http://blog.csdn.net/qianqin_2014/article/details/51452126>
预备知识:
C/C++把常量字符串放到单独的一个内存区域。当几个
指针赋值给相同的常量字符串时,它们实际上会指向相同的内存地址。但是用常量内存
初始化数组,情况却不相同。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char *ch1 = "ABCD";
char *ch2 = "ABCD";
if (ch1 == ch2)
cout << "same" << endl;
else
cout << "no same" << endl;
char ch3[] = "ABCD";
char ch4[] = "ABCD";
if (ch3 == ch4)
cout << "same" << endl;
else
cout << "no same" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:
same
no same
请按任意键继续. . .
- ch1和ch2是两个指针,我们无需为它们分配内存以存储字符串内容,而只需要把它们指向“ABCD”在内存中的地址就可以了。由于“ABCD”是常量字符串,它在内存中只有一个拷贝,因此ch1和ch2指向的是同一个地址。
- ch3和ch4是两个字符串数组,我们会为它们分别分配两个长度为5个字节的空间,并把“ABCD”的内容分别复制到数组中去,这是两个初始地址不同的数组,因此ch1和ch2的值也不相同。
题目:
请实现一个函数,把字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如输入“We are happy.”,则输出“We%20are%20happy.”。
思路一:
利用string
源代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::find;
using std::string;
int main()
{
string str = "We are happy.";
size_t pos = str.find(" ");
while (pos < str.size())//不包括'\n'
{
str.replace(pos, 1, "%20");//在pos位置上删除一个字符,并插入"%20"
size_t temp = str.find(" ", pos);//在pos位置之后查找" "
pos = temp;
}
cout << str << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}We%20are%20happy.
请按任意键继续. . .
思路二:
遍历字符串,没找到一个空格,将空格替换为“%20”,并将后边的字符向后移动两个位置。
思路三:
先统计字符串中空格的数目并计算替换之后字符串的总长度,每替换一个空格,字符长度增加2,因此替换之后的长度等于原始长度+空格数*2.
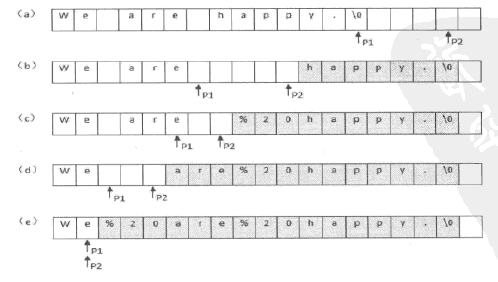
(a)把第一个指针指向字符串的末尾,把第二个指针指向替换之后的字符串的末尾
(b)依次赋值字符串中的内容,直至第一个指针碰到第一个空格
(c)把第一个空格替换成“%20”,把第一个指针向前移动1格,把第二个指针向前移动3格
(d)依次向前赋值字符串中的字符,直至碰到空格
(e)替换字符串中的倒数第二个空格,把第一个指针向前移动1格,把第二个指针向前移动3格
源代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>//malloc
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void Replace(char *ch)
{
if (ch == NULL)
return;
int len = strlen(ch)+1;//字符串的长度,包括'\n'
int count = 0;//记录空格的数目
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)//统计空格的数目
{
if (ch[i] == ' ')
count++;
}
char *temp = (char *)malloc((len + count * 2)*sizeof(char));//分配新的空间
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)//将ch中的内容复制到新分配的空间
temp[i] = ch[i];
char *p1 = temp + len - 1;//指向ch的最后一个字符'\n'
char *p2 = temp + len + count * 2 - 1;//指向新分配空间的最后一个字符空间
while (p1 != p2)
{
if (*p1 != ' ')
{
*(p2--) = *(p1--);
}
else
{
*(p2--) = '0';
*(p2--) = '2';
*(p2--) = '%';
--p1;
}
}
cout << temp << endl;
}
int main()
{
char *ch = "We are happy.";
cout << ch << endl;
Replace(ch);
<span style="white-space:pre"> char *ch2 = " ";
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Replace(ch2);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>char *ch3 = " We ";
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Replace(ch3);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>char *ch4 = NULL;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Replace(ch4);</span>
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:
We are happy.
We%20are%20happy.
%20
%20%20We%20%20
请按任意键继续. . .
官方源代码:
// ReplaceBlank.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
// 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码
// 著作权所有者:何海涛
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
/*length 为字符数组string的总容量*/
void ReplaceBlank(char string[], int length)
{
if (string == NULL && length <= 0)
return;
/*originalLength 为字符串string的实际长度*/
int originalLength = 0;
int numberOfBlank = 0;
int i = 0;
while (string[i] != '\0')
{
++originalLength;
if (string[i] == ' ')
++numberOfBlank;
++i;
}
/*newLength 为把空格替换成'%20'之后的长度*/
int newLength = originalLength + numberOfBlank * 2;
if (newLength > length)
return;
int indexOfOriginal = originalLength;
int indexOfNew = newLength;
while (indexOfOriginal >= 0 && indexOfNew > indexOfOriginal)
{
if (string[indexOfOriginal] == ' ')
{
string[indexOfNew--] = '0';
string[indexOfNew--] = '2';
string[indexOfNew--] = '%';
}
else
{
string[indexOfNew--] = string[indexOfOriginal];
}
--indexOfOriginal;
}
}
void Test(char* testName, char string[], int length, char expected[])
{
if (testName != NULL)
printf("%s begins: ", testName);
ReplaceBlank(string, length);
if (expected == NULL && string == NULL)
printf("passed.\n");
else if (expected == NULL && string != NULL)
printf("failed.\n");
else if (strcmp(string, expected) == 0)
printf("passed.\n");
else
printf("failed.\n");
}
// 空格在句子中间
void Test1()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = "hello world";
Test("Test1", string, length, "hello%20world");
}
// 空格在句子开头
void Test2()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = " helloworld";
Test("Test2", string, length, "%20helloworld");
}
// 空格在句子末尾
void Test3()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = "helloworld ";
Test("Test3", string, length, "helloworld%20");
}
// 连续有两个空格
void Test4()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = "hello world";
Test("Test4", string, length, "hello%20%20world");
}
// 传入NULL
void Test5()
{
Test("Test5", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
// 传入内容为空的字符串
void Test6()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = "";
Test("Test6", string, length, "");
}
//传入内容为一个空格的字符串
void Test7()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = " ";
Test("Test7", string, length, "%20");
}
// 传入的字符串没有空格
void Test8()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = "helloworld";
Test("Test8", string, length, "helloworld");
}
// 传入的字符串全是空格
void Test9()
{
const int length = 100;
char string[length] = " ";
Test("Test9", string, length, "%20%20%20");
}
int main3()
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
Test4();
Test5();
Test6();
Test7();
Test8();
Test9();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
测试用例:
输入的字符串包含空格(空格位于字符串最前面,空格位于字符串的最后面,空格位于字符串中间,字符串中有连续多个空格)
输入的字符串中没有空格
特殊输入测试(字符串中十个NULL指针、字符串十个空字符串、字符串中只有一个空格字符,字符串中只有连续多个空格)






















 342
342

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








