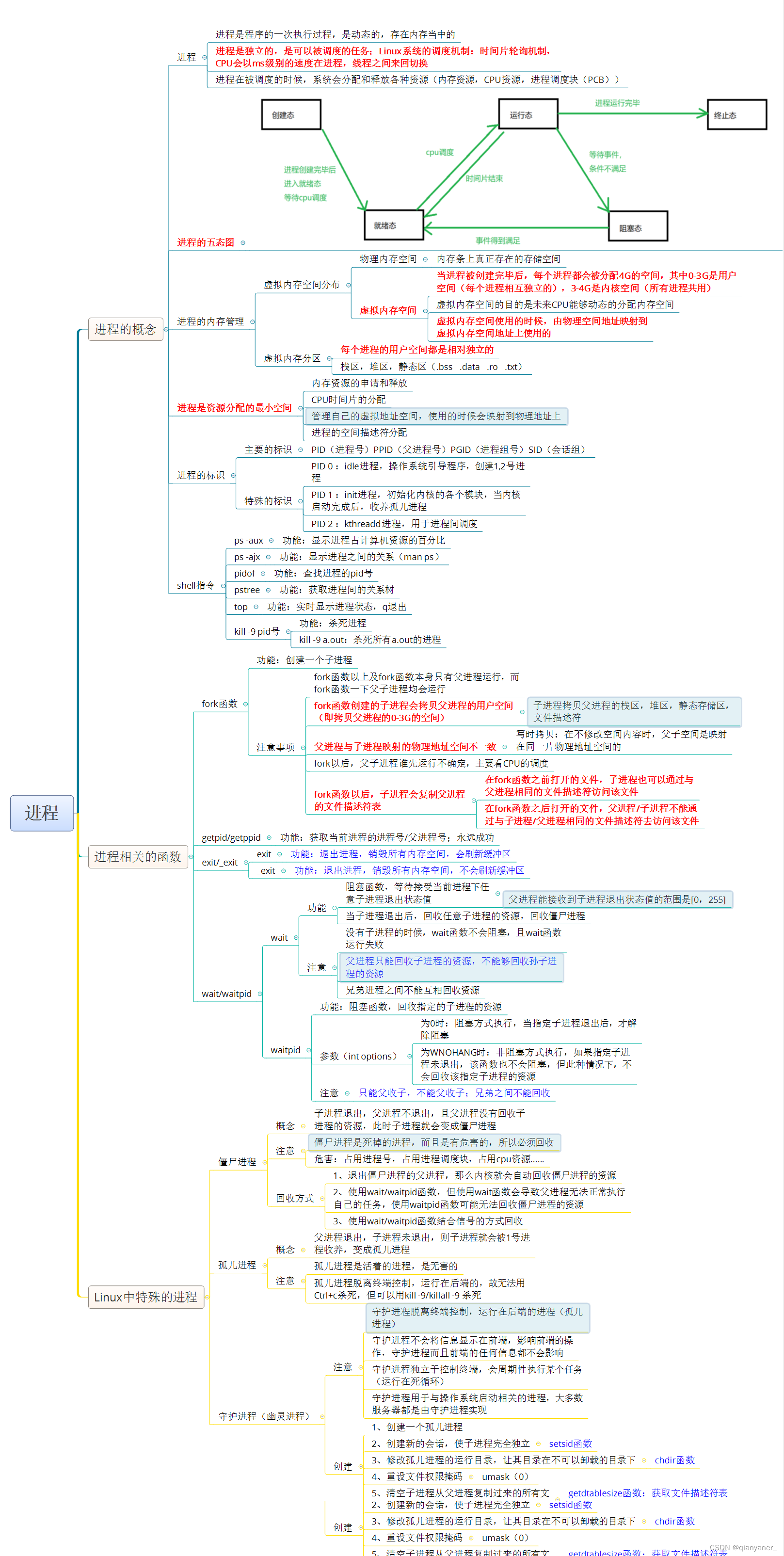
僵尸进程
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,const char *argv[])
{
pid_t cpid = fork();
if(0 == cpid){
printf("child was killed\n");
exit(0);
//子进程未被父进程回收资源,变成僵尸进程
}
while(1)
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
孤儿进程
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,const char *argv[])
{
pid_t cpid = fork();
if(cpid == 0){
//child
printf("this is child\n");
//父进程结束而子进程为结束,则子进程变成孤儿进程
while(1){
printf("this is a orphan %d\n",getpid());
sleep(1);
}
}
printf("parent is die\n");
return 0;
}
守护进程(幽灵进程)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main(int argc,const char *argv[])
{
//1、创建孤儿进程
if(0 == fork()){
//2、创建新的会话组
if(setsid() == -1){
perror("setsid");
return -1;
}
//3、使孤儿进程运行在不可以被删除的目录下
if(chdir("/") == -1){
perror("chdir");
return -1;
}
//4、重设文件权限掩码
umask(0);
//5、关闭所有从父进程复制过来的文件描述符,用时再使用open打开
for(int i=0;i<getdtablesize();i++){
close(i);
}
while(1){
//守护进程(幽灵进程)运行代码
sleep(1);
}
}
return 0;
}





















 315
315











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








