目录
1. HashMap要点
1) hashMap利用指针数组来存储键值对,键由key通过hash操作获得
2) 通过链来存储多个hash值相同的数据
3) 初始时需要确定size,即桶数,将hash值对size进行求余操作即得到存储位置
hashmap.h (实现简单的增、删、插入操作)
#ifndef HASHMAP_H_
#define HASHMAP_H_
template<class Key, class Value>
class HashNode
{
private:
/* data */
public:
Key _key;
Value _value;
HashNode *next;
HashNode(Key key, Value value){
_key = key;
_value = value;
next = NULL;
}
~HashNode(){};
HashNode& operator = (const HashNode& node){
_key = node._key;
_value = node._value;
next = node.next;
return *this;
}
};
template <class Key, class Value, class HashFun, class EqualKey>
class HashMap
{
public:
HashMap(int size);
~HashMap();
bool insert(const Key& key, const Value& value);
bool del(const Key& key);
Value& find(const Key& key);
Value& operator[] (const Key& key);
private:
HashFun hash;
EqualKey equal;
HashNode<Key, Value> **table;
unsigned int _size;
Value ValueNULL;
};
template <class Key, class Value, class HashFun, class EqualKey>
HashMap<Key, Value, HashFun, EqualKey>::HashMap(int size):_size(size),hash(),equal()
{
table = new HashNode<Key, Value>*[_size];
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
table[i] = NULL;
}
}
template <class Key, class Value, class HashFun, class EqualKey>
HashMap<Key, Value, HashFun, EqualKey>::~HashMap()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
HashNode<Key, Value> *currentNode = table[i];
while (currentNode)
{
HashNode<Key, Value> *temp = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode->next;
delete temp;
}
}
delete table;
}
template <class Key, class Value, class HashFun, class EqualKey>
bool HashMap<Key, Value, HashFun, EqualKey>::insert(const Key& key, const Value& value)
{
int index = hash(key)%_size;
HashNode<Key, Value>* node = new HashNode<Key, Value>(key, value);
node->next = table[index];
table[index] = node;
return true;
}
template <class Key, class Value, class HashFun, class EqualKey>
bool HashMap<Key, Value, HashFun, EqualKey>::del(const Key& key)
{
int index = hash(key)%_size;
HashNode<Key, Value> *node = table[index];
HashNode<Key, Value> *pre = NULL;
while (node)
{
if (node->_key == key)
{
if (pre == NULL)
{
table[index] = node->next;
}else
{
pre->next = node->next;
/* code */
}
delete node;
return true;
}
pre = node;
node = node->next;
}
}
template <class Key, class Value, class HashFun, class EqualKey>
Value& HashMap<Key, Value, HashFun, EqualKey>::find(const Key& key)
{
int index = hash(key)%_size;
if (table[index] == NULL)
{
return ValueNULL;
}else
{
HashNode<Key, Value> *node = table[index];
while (node)
{
if (node->_key == key)
{
return node->_value;
}
node = node->next;
}
}
}
template <class Key, class Value, class HashFun, class EqualKey>
Value& HashMap<Key, Value, HashFun, EqualKey>::operator[](const Key& key)
{
return find(key);
}
#endif // !HASHMAP_H_测试代码
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include "hashMap.h"
using namespace std;
class HashFunc
{
public:
int operator()(const string &key)
{
int hash = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < key.length(); i++)
{
hash = (hash << 7 ^ key[i]);
}
return 1;
//return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
};
class EqualKey
{
public:
bool operator()(const string& A, const string& B)
{
if(A.compare(B) == 0){
return true;
}else
{
return false;
}
return false;
}
};
int main()
{
HashMap<string,string,HashFunc,EqualKey> hashmap(100);
hashmap.insert("hello","world");
hashmap.insert("why","dream");
hashmap.insert("hello","qican");
hashmap.insert("nihao","china");
std::cout<<"after insert"<<endl;
cout<<hashmap.find("hello")<<endl;
cout<<hashmap["nihao"]<<endl;
if (hashmap.del("hello"))
{
cout<<"remove is ok"<<endl;
}
cout<<hashmap.find("hello")<<endl;
hashmap["why" ] = "love";
cout<<hashmap["why"]<<endl;
return 0;
}
2. Hash冲突的解决
2.1 开放定址法
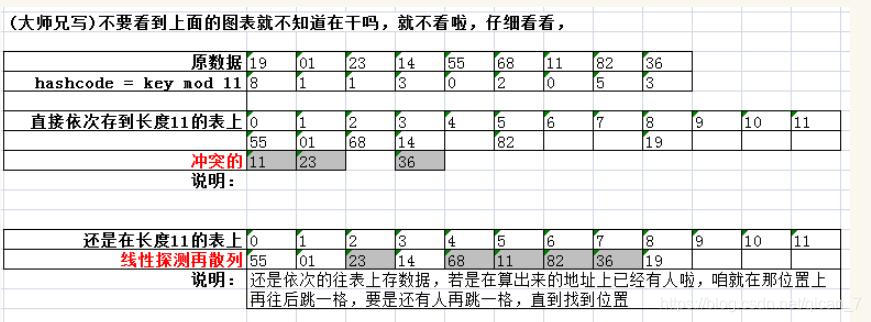
- 简单线性再散列
当关键字key的哈希地址p=H(key)出现冲突时,依次向后查找,直到找到一个空闲的位置。
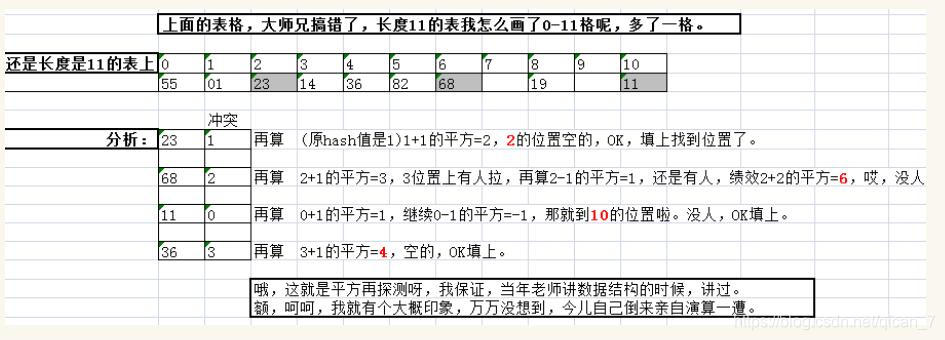
- 二次探测再散列
当关键字key的哈希地址p=H(key)出现冲突时,在表的左右进行跳跃式探测,比较灵活,规则为

- 伪随机探测再散列
首先生成伪随机码,如{2,3,5,9.....},当发生冲突时,将哈希地址加上伪随机码进行探测,直到找到空闲的地址。
2.2 链地址法
将所有哈希地址为i的相同元素构成一个称为同义词链的单链表,并将单链表的头指针存在哈希表的第i个单元里,因而查找、插入和删除主要在同义词链中进行。链地址法适合经常进行插入和删除的情况。
2.3 再哈希法
构造多种不同的哈希函数,当出现冲突时,依次使用后面的哈希函数。
2.4 建立公共溢出区
将哈希表分为基本表和溢出表两部分,凡是和基本表发生冲突的元素全部放入到溢出表中。
2.5 开放散列法和封闭散列法的优缺点
- 开放散列/拉链法 (针对桶链结构)
优点
1)对于记录总数频繁可变的情况,处理的比较好,避免了动态调整的开销。
2)由于记录存储在节点中,而节点是动态分配的,不会造成内存的浪费。(另一种思路,没有存储数据的地方会造成内存的浪费)
3)删除记录时比较方便,直接通过指针操作即可。
缺点
1)存储的记录是随机存储在内存中的,查询记录时,哈希表的跳转回带来额外的时间开销,(相对于数组存储来说)
2)如果所有的key-value提前可知,可以认为创建一个不会产生冲突的完美hash函数,这样封闭散列比开放散列的性能更高。
3)由于使用指针,记录不容易序列化操作。
- 封闭散列/开放定址法
优点
1)如果记录总数提前可知,可以创建完美hash函数,此时可以高效地处理数据。
2)记录更容易进行序列化操作。
缺点
1)存储记录的数目不能超过桶数组的长度,如果超过就需要扩容,而扩容会导致某次操作的时间成本飙升,这在实时或者交互式应用中会是一个严重的缺陷。
2)使用探测序列,有可能其计算的成本过高,导致哈希表的处理性能降低。
3)由于记录存放在桶数组中,而桶数组必然存在空槽,但记录本身尺寸很大并且记录总数规模很大时,空槽占用的空间会导致明显的内存浪费。
4)删除记录时,比较麻烦。(数组存储,空槽设置删除标记或后面的记录往前补,需要额外的空间和操作)
3. 参考文献
1) https://www.cnblogs.com/myd620/p/6349552.html?utm_source=itdadao&utm_medium=referral (c++ 实现hashmap)
2) https://www.cnblogs.com/novalist/p/6396410.html (hash冲突的四种办法)
3) https://www.cnblogs.com/wuchaodzxx/p/7396599.html (解决hash冲突的三个方法)






















 2884
2884











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








