SpringMVC的原理:(自己通过程序理解的)
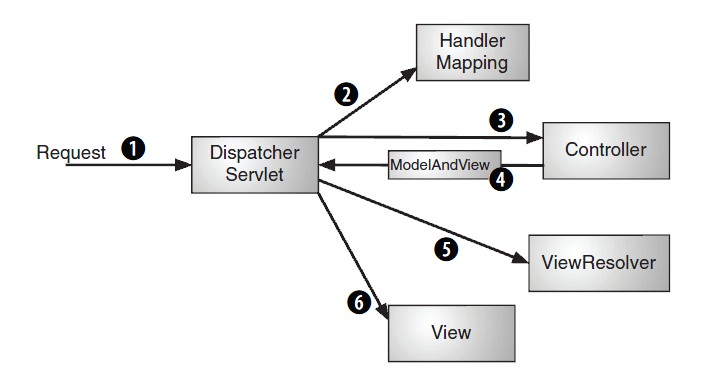
当请求到达时会被web.xml中的所配置的DispatcherServlet这个中央控制器所拦截,中央控制器通过HandlerMapping映射到指定的controller上,controller进行业务逻辑处理,返回ModelAndView对象,DispatcherServlet通过ViewResolver(视图解析器)进行视图解析渲染相应的view。
配上一个图:
SpringMVC的开发步骤:
1、导入需要的jar包
2、在web.xml中配置DispatcherServlet中央控制器
配置方式有两种:
<!--这个表示配置文件的名称一定要是springmvc-servlet.xml-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--这里是拦截哪些请求(如果要拦截所有请求则url-pattern里面写/)-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping><!--这个表示配置文件的名称可以通过init-param来进行配置-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:config/springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<!--这里是拦截哪些请求(如果要拦截所有请求则url-pattern里面写/)-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>3、写配置文件
配置文件中主要包括:
1、
所需要配置的bean(一般只包括controller层,当然也可以全部包括)方法有两种:
- 非注解的方式:
<bean name="helloCtroller" id="/hello.action" class="springmvc1.controller.HelloController"/>- 注解的方式:
<!--扫描注解驱动 @RequestMapping来代替,映射bean的做法-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!--采用扫描器-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.suyin.*.controller"/>2、HandlerMapping(当用了非注解的方式装配bean的时候使用)
<!--默认的映射方式 根据Bean的name属性来进行映射
http://localhost:8080/springmvc1/hello.action
-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/>
<!--自己配置-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<!-- http://localhost:8080/springmvc1/test1.action -->
<prop key="/test1.action">helloController</prop>
<!-- localhost:8080/springmvc1/test2.action -->
<prop key="/test2.action">helloController</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<
<!-- http://localhost:8080/springmvc1/helloController.action 根据id进行映射的-->class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping"/>3、视图解析器:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>4、上传文件解析器
<!--一定要有id,且id名称只能是multipartResolver-->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="20971520"></property>
<bean>
<!--在实际的jsp和controller中的实际应用(貌似在开发中,现在还没有使用到过,都是使用的是一些jQuery的插件,解析后将图片地址传过去的)-->
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/change/upload.action" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
名字:<input type="text" name="name"/><br/>
上传文件:<input type="file" name="upload"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
<!--controller中写入-->
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/change")
public class UploadController{
@RequestMapping(value="{"/upload.action"},method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String upload(HttpServletRequest request,String name)throws Exception{
MultipartHttpServletRequest mhr=(MultipartHttpServletRequest)request;
CommonMultipartFile fileUpload=(CommonMultipartFile )mhr.getFile("upload");
String fileName=fileUpload.getOriginalFilename();
String prefix=fileName.substring(0,fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
String suffix=fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//获得需要上传文件的
<!--getRealPath理解:得到工程目录:
request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("")
参数可具体到包名。
结果:E:\Tomcat\webapps\TEST -->
String path=request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File file=new File(path);
if(!file.exists()){
file.mkdirs():
}
File filePath=new File(file,fileName1+"_"+System.currentTimeMillis()+suffix);
byte[] bytes=fileUpload.getBytes();
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(filePath);
os.write(bytes);
stream.flush();
os.close();
return "index/sc";
}5、拦截器设置(自定义和系统自带的)
自定义的拦截器一般是用来比如用户查看某个资源的时候判断用户是否登录
代码如下:
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.suyin.system.interceptor.VerificationHandlerInterceptor"/
>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
<!--这个是我常看见的一种拦截(关于用户以及访问资源的拦截)-->
public class VerificationHandlerInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter{
//获取登录的用户
SysUser user = (SysUser) request.getSession().getAttribute("user");
//获取该用户可以访问的资源列表
List<SystemResource> list = (List<SystemResource>)request.getSession().getAttribute("resourceUrls");
//获取请求的URI也就是得到相对地址:request.getRequestURI()
//结果:/TEST/test
String url = request.getRequestURI();
String path = request.getServletPath();
boolean flag = false;
if (-1 != path.indexOf("login") || (-1 != path.indexOf("layout")&&user!=null) || -1 != path.indexOf("getPerMenuList")//获取不需要拦截资源链接
|| -1 != path.indexOf("resources") || -1 != path.indexOf("regist") || -1 != path.indexOf("querySkuList")
||-1!=path.indexOf("outImages")||-1!=path.indexOf("/uploadFile")
|| -1 != path.indexOf("queryRegion")|| -1 != path.indexOf("send") || -1 != path.indexOf("doReg") || -1!=path.indexOf("member")
)
{
return true;
}
else if (null == user)//用户有没有登录
{
response.setHeader("sessionstatus", "timeout");
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/login");
return false;
}
else
{
if (request.getHeader("x-requested-with") != null)//只有发送ajax请求才会有x-requested-with头部的信息
{
return true;
}
else
{
if(null != list)
{
for (SystemResource systemResource : list)
{
String resourceUrl = systemResource.getResourceUrl();
if("".equals(resourceUrl))
{
continue;
}
else
{
if (url.indexOf(resourceUrl) != -1 || url.indexOf("report") != -1)
{
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
if(flag)
{
return true;
}
else
{
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/login");
return false;
}
}
}
}假如不想拦截就用:
<!-- springMVC静态资源不拦截 -->
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/WEB-INF/resources/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/outImages/**" location="/outImages/" />6、@ResponseBody注解的文件配置(json与xml之间的转换)
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<property name="messageConverters">
<list>
<bean
class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>text/html; charset=UTF-8</value>
<value>application/json;charset=UTF-8</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>text/html; charset=UTF-8</value>
<value>application/json;charset=UTF-8</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>补充:
我在公司做的时候发现公司框架中将@responseBody的配置文件的写法和视图解析器一块儿写了
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver">
<property name="mediaTypes">
<map>
<!-- <entry key="atom" value="application/atom+xml" /> -->
<entry key="json" value="application/json" />
<entry key="html" value="text/html" />
</map>
</property>
<property name="viewResolvers">
<list>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.BeanNameViewResolver" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>关于SpringMVC的小知识点的理解:
1、spring mvc功能组件:
DispatcherServlet:中央控制器,把请求给转发到具体的控制类
Controller:具体处理请求的控制器
handlerMapping:映射处理器,负责映射中央处理器转发给controller时的映射策略
ModelAndView:服务层返回的数据和视图层的封装类
ViewResolver & View:视图解析器,解析具体的视图
3、如何实现在controller层之间的跳转(重定向)
public class RedirectController {
//重定向,地址栏会变得
/*controller内部重定向,redirect:加上同一个controller中的
requestMapping的值;
*/
@RequestMapping("/redirectSelef.action")
public String redir(){
return "redirect:hello.action";
} //redirect:/这个斜杠表示从根路径开始
/*controller之间的重定向:必须要指定好controller的命名空间
(change)再指定requestMapping的值(param1.action),
redirect:后必须要加/,是从根目录开始*/
@RequestMapping("/redirectOther.action")
public String redir2(){
return "redirect:/change/param1.action";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello.action")
public String hello(){
System.out.println("测试");
return "/index/sc";
}2、关于@ResponseBody(@ResponseEntity也是一样的)的使用,
假如发现返回值并没有以json数据串返回,那么可以使用
produces=MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE
@RequestMapping(value = { "/menu" }, method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public @ResponseEntity<List<Order>> getOrder(){
return List<Order>;
} 3、注解方式的好处:controller不必继承任何接口,它仅是一个简单的POJO,开发人员对controller的代码实现变得更加灵活。
4、@InitBinder的使用(对于从jsp传过来的date类型的数据在赋值的时候一定要使用InitBinder)
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(ServletRequestDataBinder binder){
System.out.println("initBinder");
binder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, new CustomDateEditor(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"),true));
} 5、对于返回值是void的方法,一定要用response返回一定的数据否则会出错
//不建议使用
@RequestMapping(value={"/ajaxdemo1.action"})
public void ajax1(String name,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException{
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setContentType("application/json");
PrintWriter out=response.getWriter();
System.out.println(name);
out.write("{\"name\":\"chj\"}");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
//建议使用
@RequestMapping(value={"/ajaxdemo2.action"})
public void ajax1(String name,PrintWriter out) throws IOException{
System.out.println(name);
out.write("{\"name\":\"chj\"}");
out.flush();
out.close();
}RESTful:
restful是什么?restful是一种软件架构风格,只是提供了一组设计原则和约束条件,满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序设计就是restful
常用的HTTP动词有下面五个(括号里是对应的SQL命令)。
GET(SELECT):从服务器取出资源(一项或多项)。
POST(CREATE):在服务器新建一个资源。
PUT(UPDATE):在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变后的完整资源)。
PATCH(UPDATE):在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变的属性)。
DELETE(DELETE):从服务器删除资源。
Spring对RESTful的支持
- Spring MVC 对 RESTful应用提供了以下支持
- 利用@RequestMapping 指定要处理请求的URI模板和HTTP请求的动作类型
- 利用@PathVariable将URI请求模板中的变量映射到处理方法参数上
- 利用Ajax,在客户端发出PUT、DELETE动作的请求(更新和删除)
例如:localhost:8080/test/1
1是id
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String toUpdate(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Model model) {}
RequestMapping的一般应用格式。
//获取数据
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
//增加数据
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.POST)
//删除数据
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
//更新数据
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








