一、引言
MathJax引擎是一个开源的JavaScript库,它允许Web开发者在网页中嵌入高质量的数学公式。通过利用Web的最新技术,MathJax引擎可以解析LaTeX、MathML和AsciiMath等数学标记语言,并将其渲染为可视化的数学公式,这些公式可以在各种浏览器和操作系统上流畅地显示。
使用MathJax引擎,网页作者可以轻松地编写包含数学内容的文档,而无需担心用户的浏览器或操作系统是否能够正确显示这些数学公式。因为MathJax引擎会自动处理这些兼容性问题,确保用户能够以清晰、准确的方式查看数学内容。
MathJax引擎的特点包括:
- 跨平台兼容性:它支持多种浏览器和操作系统,确保数学公式能够在各种设备上正确显示。
- 高质量的排版:MathJax引擎使用先进的排版算法,确保数学公式能够以清晰、准确的方式呈现。
- 易于使用:通过简单的标记语言,如LaTeX,用户可以轻松地编写数学公式,并将其嵌入到网页中。
- 高度可定制性:MathJax引擎提供了丰富的配置选项,允许用户根据自己的需求进行定制,以满足特定的排版和显示要求。
总的来说,MathJax引擎是一个功能强大、易于使用的工具,它为Web上的数学内容显示提供了高质量的解决方案。无论是科学论文、教育资料还是技术文档,都可以利用MathJax引擎来呈现复杂的数学公式,提升网页的可读性和专业性。
二、使用
1、安装依赖
pnpm i mathjax2、配置
MathJax = {
tex: {
packages: ['base'], // extensions to use
inlineMath: [ // start/end delimiter pairs for in-line math
['\\(', '\\)']
],
displayMath: [ // start/end delimiter pairs for display math
['$$', '$$'],
['\\[', '\\]']
],
processEscapes: true, // use \$ to produce a literal dollar sign
processEnvironments: true, // process \begin{xxx}...\end{xxx} outside math mode
processRefs: true, // process \ref{...} outside of math mode
digits: /^(?:[0-9]+(?:\{,\}[0-9]{3})*(?:\.[0-9]*)?|\.[0-9]+)/,
// pattern for recognizing numbers
tags: 'none', // or 'ams' or 'all'
tagSide: 'right', // side for \tag macros
tagIndent: '0.8em', // amount to indent tags
useLabelIds: true, // use label name rather than tag for ids
maxMacros: 10000, // maximum number of macro substitutions per expression
maxBuffer: 5 * 1024, // maximum size for the internal TeX string (5K)
baseURL: // URL for use with links to tags (when there is a <base> tag in effect)
(document.getElementsByTagName('base').length === 0) ?
'' : String(document.location).replace(/#.*$/, '')),
formatError: // function called when TeX syntax errors occur
(jax, err) => jax.formatError(err)
},
options: {
skipHtmlTags: [ // HTML tags that won't be searched for math
'script', 'noscript', 'style', 'textarea', 'pre',
'code', 'annotation', 'annotation-xml'
],
includeHtmlTags: { // HTML tags that can appear within math
br: '\n', wbr: '', '#comment': ''
},
ignoreHtmlClass: 'tex2jax_ignore', // class that marks tags not to search
processHtmlClass: 'tex2jax_process', // class that marks tags that should be searched
compileError: function (doc, math, err) {doc.compileError(math, err)},
typesetError: function (doc, math, err) {doc.typesetError(math, err)},
renderActions: {...}
},
startup: {
elements: null, // The elements to typeset (default is document body)
typeset: true, // Perform initial typeset?
ready: Startup.defaultReady.bind(Startup), // Called when components are loaded
pageReady: Startup.defaultPageReady.bind(Startup), // Called when MathJax and page are ready
document: document, // The document (or fragment or string) to work in
invalidOption: 'warn', // Are invalid options fatal or produce an error?
optionError: OPTIONS.optionError, // Function used to report invalid options
input: [], // The names of the input jax to use from among those loaded
output: null, // The name for the output jax to use from among those loaded
handler: null, // The name of the handler to register from among those loaded
adaptor: null // The name for the DOM adaptor to use from among those loaded
},
svg: {
scale: 1, // global scaling factor for all expressions
minScale: .5, // smallest scaling factor to use
mtextInheritFont: false, // true to make mtext elements use surrounding font
merrorInheritFont: true, // true to make merror text use surrounding font
mathmlSpacing: false, // true for MathML spacing rules, false for TeX rules
skipAttributes: {}, // RFDa and other attributes NOT to copy to the output
exFactor: .5, // default size of ex in em units
displayAlign: 'center', // default for indentalign when set to 'auto'
displayIndent: '0', // default for indentshift when set to 'auto'
fontCache: 'local', // or 'global' or 'none'
localID: null, // ID to use for local font cache (for single equation processing)
internalSpeechTitles: true, // insert <title> tags with speech content
titleID: 0 // initial id number to use for aria-labeledby titles
}
};tex配置:https://docs.mathjax.org/en/latest/options/input/tex.html#the-configuration-block
startup配置: https://docs.mathjax.org/en/latest/options/startup/startup.html#startup-options
options配置:https://docs.mathjax.org/en/latest/options/document.html#the-configuration-block
svg配置: https://docs.mathjax.org/en/latest/options/output/svg.html#the-configuration-block
🌰:
$$x = {-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac} \over 2a}.$$
$x = {-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac} \over 2a}.$
$$P_{价格} =\frac {1/a}{1/a+1/b+1/c}*P_A+\frac{1/b}{1/a+1/b+1/c}*P_B+\frac{1/c}{1/a+1/b+1/c}*P_C$$
 3、基本的LaTeX公式输入
3、基本的LaTeX公式输入
四则运算
加减:
a+b-c乘法:
a\times b (注意\times和b之间要有空格)分数:
\frac{a}{b}使用例:
\frac{(a+b)\times c}{(d+e)\times f} 一个小技巧:对含分式的式子两边加括号
(\frac{a}{b}), \left( \frac{a}{b} \right)
(使用右边的方法效果会更好,可把小括号换成中括号)比较运算
小于、大于、小于等于、大于等于: <,>,≤,≥
<, >, \leq, \geq (\leq,\geq的记忆:Less,Greater)等于,不等于: =,≠
=, \not= (实际上,\not 就是那一杠,可运用于其它符号)恒等于(同余): ≡
\equiv 幂运算与下标
,但是注意
和
的区别:
x^a, x^{ab}, x^ab (多个字符时,要用花括号代替,不过单个字符时有无花括号是等价的)下标: ,但是注意
和
的区别:
a_n, a_{nm}, a_nm (花括号原理同上)根号与多次方根:
\sqrt a, \sqrt[n]a, \sqrt[nm]{ab}使用例:
a_i^2, a^2_i 集合间的运算
一对花括号(表示集合):
\left\{
x_1,x_2
\right\} (不能直接打花括号,必须要有\left\,\right\)
(可以写成一行,这样仅为了方便查看)属于、包含与真包含: ∈,∉,⊂,⊆,⊃,⊇
\in, \notin, \subset, \subseteq, \supset,\supseteq交,并,补:
\cap, \cup, C_UA, \complement_UA省略号:
\cdot, \cdots (一个点与三个点)描述法: ∣
\mid使用例:
\left\{ x_1,x_2,\cdots,x_n \right\},
A\cap C_{A\cup B}B=A常用特殊函数
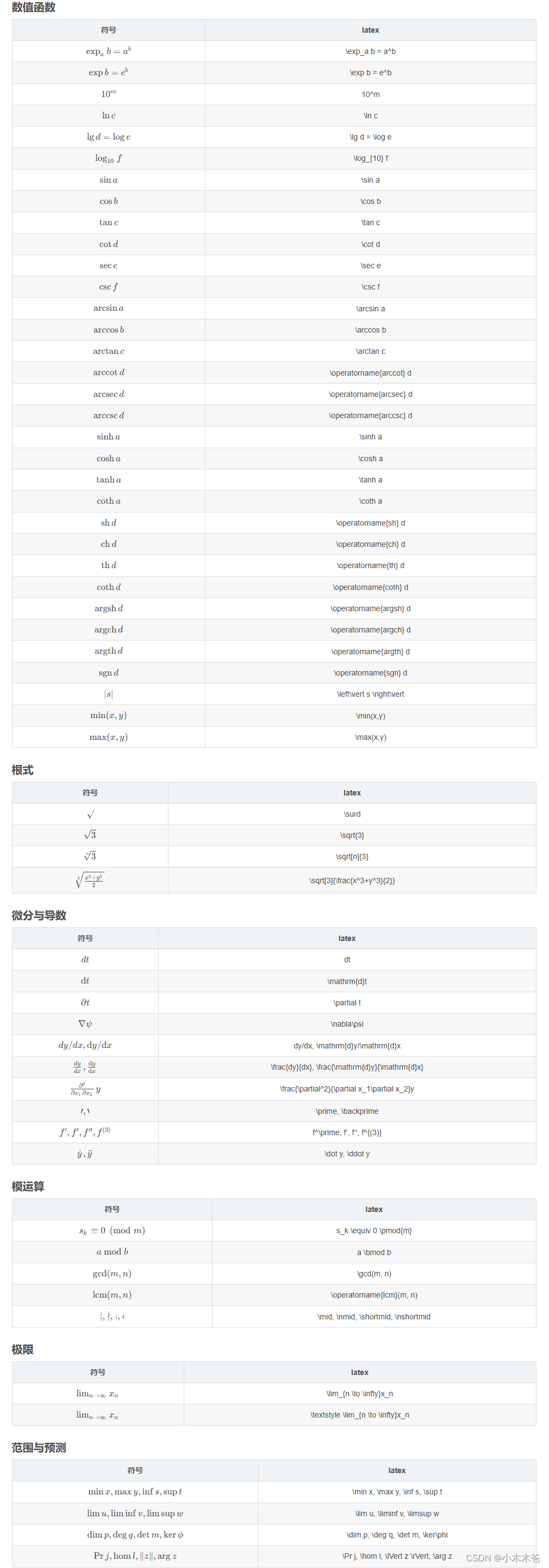
三角函数:
\sin x, \cos x, \tan x, \cot x (注意中间的空格)反三角函数:
\arcsin x, \arccos x, \arctan x (事实上许多特殊函数都可以在前面加'\')双曲函数:
\sinh x, \cosh x, \tanh x, \coth x对数:
\log_ax, \ln x, \lg x用希腊字母表示的函数见下方“常用希腊字母”。
常用特殊符号
求和:
\sum, \sum_{i=1}^n, \sum_{i=1}^na_i, \sum_{i=1}^{na_i}无穷: ∞,+∞,−∞
\infty, +\infty, -\infty箭头: →,←,↑,↓
\rightarrow, \leftarrow, \uparrow, \downarrow极限:
\lim, \lim_{x\rightarrow 0}, \lim_{x\rightarrow \infty}定积分与不定积分:
\int, \int_a^b, \int_{ab}^{cd}二重积分:
\iint, \iint_D三重积分:
\iiint, \iiint_D (以此类推,超过四重的积分不可用)定积分使用例:
\int_a^b \left( -\frac{1}{x^2} \right) dx = \frac{1}{x}|_a^b = \frac{1}{b} - \frac{1}{a}偏导: ∂
\partial梯度(Gradient): ∇
\nabla常用希腊字母
阿尔法,贝塔,伽马:
\alpha, \beta, \gammaGamma函数: Γ
\Gamma变化量: Δ
\Deltaepsilon:
\epsilon (但是总感觉平时好像用的是\xi?)Zeta函数:
\zeta机械效率:
\eta常数lambda:
\lambda数学期望,摩擦系数mu:
\mu圆周率pi:
\pi极径:
\rho标准差、方差sigma:
\sigma力矩,逆序数:
\tau欧拉函数phi:
\phi, \Phi卡方分布:
\chi (卡方分布的英文名是Chi-Square Distribution)电阻,欧米茄:
\omega, \Omega多行公式
换行:
a \\ b, c \\ d ('\\'是换行)对齐:
\begin{aligned}
[(n+1)!+k]\operatorname{mod}k &=(n+1)!\operatorname{mod}k+k\operatorname{mod}k
\\ &=0+0
\\ &=0
\end{aligned}
('&'是对齐)方程组:
\begin{cases}
x_1+x_2=2
\\ x_1-x_2=0
\end{cases}空格:
a \ b ('\ '表示一空格)矩阵与行列式:
\left(
\begin{matrix}
a &b
\\c &d
\end{matrix}
\right)
,
\left|
\begin{matrix}
a &b
\\c &d
\end{matrix}
\right|
(\left,\right后的符号可替换) 








 本文介绍了MathJax引擎,一个开源的JavaScript库,支持LaTeX、MathML和AsciiMath,提供跨平台兼容性、高质量排版和易于使用的数学公式插入。文章详细讲解了如何安装配置MathJax及其在网页中的应用,适合科学论文、教育资料和技术文档的数学表达增强。
本文介绍了MathJax引擎,一个开源的JavaScript库,支持LaTeX、MathML和AsciiMath,提供跨平台兼容性、高质量排版和易于使用的数学公式插入。文章详细讲解了如何安装配置MathJax及其在网页中的应用,适合科学论文、教育资料和技术文档的数学表达增强。
















 3780
3780

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








