该算法的实现,需要注意的是:
1,yi 参数与Q 参数的大小是一致的,
2,cost 函数求参数的梯度不能用于参数的更新,会导致验证指标不断增加,程序运行出错。
3,建议通篇理解隐式反馈以及现有的隐式反馈的推理,深入理解模型中的
公式的原理由来, 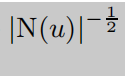
参数不是经验值,是约束集合N(u) 的不断增大。
参数的更新参照原文
Factorization Meets the Neighborhood: a Multifaceted
Collaborative Filtering Model
有关隐式反馈增加一篇文章
Scalable Collaborative Filtering with Jointly Derived Neighborhood
Interpolation Weights
以上两篇文章多看几遍
def calculate_yi(y_matrix, y_i):
rows, cols = np.nonzero(y_matrix != None)
userids = sort(list(set(rows)))
dicts = dict()
for userid in userids:
item_indexs = np.nonzero(y_matrix[userid] != None)
N = len(item_indexs[0])
sum_yj = np.sum(y_i[:, item_indexs[0]])
sqrt_ni = sum_yj / np.sqrt(N)
dicts[userid] = [N, sum_yj, sqrt_ni, item_indexs[0]]
return dicts
def getSetItems():
'''
about the parameter of R(u) in svd++ model, is for calculating the contraction factor. and the result math formula
is 1/sqrt(R(u)). this is empirical formula. hece , we need to fetch this parameter before pre-train and update model
parameters.
Returns: this function return a dict, the key is a userid and the value is the number of items that the user has al-
readly viewed.
'''
[data, userno, videono] = onloaddata()
userids = Counter(np.int32(np.array(data)[:, 0]))
return [dict(userids), data, userno, videono]
def init_P_Q_B_matrix_apend2(user_disms=[3, 3], item_disms=[3, 3], init_method='quadrature'):
'''
this is a function to create two matrix for sgd training.
we via quadrature distribution function.
Args:
user_disms: user matrix shape.
item_disms: item matrix shape
init_method: generating matrix approach.
Returns: return four matrix, B matrix as the bias matrix. P,Q is the lower dismisional matrix to fit original score-matrix.
y_subscript(i) named the bias value about products that users like.
attention: the y_i matrix as big as Q. in fact we to build this matrix based on loss function.
'''
if str(init_method) == str('quadrature'):
P = random.randn(user_disms[0], user_disms[1])
Q = random.randn(item_disms[1], item_disms[0])
B_i = random.randn(user_disms[0], 1)
B_j = random.randn(item_disms[0], 1)
y_i = random.randn(item_disms[1], item_disms[0])
return [P, Q, B_i, B_j, y_i]
return
def cal_mean_rating_apend2(y_matirx):
'''
calculate the mean score as the parameter uf u.
Returns: return a float number-type.
'''
shape = y_matirx.shape
rows, cols = np.nonzero(y_matirx != None)
u = np.sum(y_matirx[rows, cols]) / (shape[0] * shape[1])
return u
def gradient_apend2(u, a1, a2, B_i, B_j, y_i, y_matrix, P, Q, R_u, dics):
'''
via min(f(x)) to calculate the gradient about four parameters, named pi,qj,bi,bj.
Returns:
'''
# =================================================================================================
rows, cols = np.nonzero(y_matrix != None)
increment_P = np.zeros(P.shape)
for index in range(0, P.shape[0]):
increment_P[index] = P[index]
for userid in dics:
increment_P[userid, :] = P[userid, :] + dics[userid][2]
# res = np.array_equiv(increment_P, P)
R = np.sum(increment_P[rows] * Q.T[cols], axis=1)
error = list((y_matrix[rows, cols] - np.array(R)) - B_i[rows, 0] - B_j[cols, 0] - u)
error = np.array([i for i in error]).reshape(len(rows), 1)
if not isinstance(error, np.ndarray):
error = np.array(error).around(decimals=4)
gradient_p_i = error * Q[:, cols].T - a1 * P[rows, :]
gradient_b_i = error - a2 * B_i[rows]
gradient_b_j = error - a2 * B_j[cols]
#
# # here, follow two parameters-calculating need to update formula.
Q_VALUE = np.array(np.sum(Q[:, cols].T, axis=1)).reshape(len(rows), 1)
gradient_q_j = error * increment_P[rows,
:] - a1 * Q_VALUE # as step1. the operation is complete. hence, 0 steaded
user_item_set = []
regular_y_i = []
for row in rows:
user_item_set.append(np.sqrt(dics[row][0]))
regular_y_i.append(dics[row][1])
user_item_set = np.array(user_item_set).reshape(len(user_item_set), 1)
regular_y_i = np.array(regular_y_i).reshape(len(regular_y_i), 1)
gradient_y_i = error / user_item_set * Q[:, cols].T - a1 * regular_y_i
return [error, gradient_p_i, gradient_q_j, gradient_b_i, gradient_b_j, gradient_y_i]
def apend2_svd():
'''
in order to think about some low rating-defined factors, named bias.
eg: some item defined unrelated to user about rating may reduce
the user's rating. detail defined as user-bias and item bias.
Returns: cost, and iters count.
'''
[R_u, o_data, userno, videono] = getSetItems()
learning_rate = 0.01
iters = 1000
a1 = 0.01
a2 = 0.02
cost_arr = []
count = 0
[P, Q, B_i, B_j, y_i] = init_P_Q_B_matrix_apend2(user_disms=[userno, 2], item_disms=[videono, 2],
init_method='quadrature')
y_matirx = build_score_matrix_R(o_data, userno, videono)
if not isinstance(P, np.ndarray):
P = np.array(P).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(Q, np.ndarray):
Q = np.array(Q).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(y_matirx, np.ndarray):
y_matirx = np.array(y_matirx).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(y_matirx, np.ndarray):
B_i = np.array(B_i).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(y_matirx, np.ndarray):
B_j = np.array(B_j).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(y_i, np.ndarray):
y_i = np.array(y_i).round(decimals=4)
u = cal_mean_rating_apend2(y_matirx)
# to fetch the position(index) about score matrix element.
rows, cols = np.nonzero(y_matirx != None)
dic = calculate_yi(y_matirx, y_i)
bar = progressbar
for i in bar.progressbar(range(iters)):
[error, gradient_p_i, gradient_q_j, gradient_b_i, gradient_b_j, gradient_y_i] = gradient_apend2(u, a1, a2, B_i,
B_j, y_i,
y_matirx, P, Q,
R_u, dic)
P[rows, :] += learning_rate * gradient_p_i
Q[:, cols] += learning_rate * gradient_q_j.T
B_i[rows] += learning_rate * gradient_b_i
B_j[cols] += learning_rate * gradient_b_j
y_i[:, cols] += learning_rate * gradient_y_i.T
cost = np.sum(np.square(error))
cost_arr.append(cost)
count += 1
# print(cost)
return cost_arr, count
cost_arr, count = apend2_svd()
fig, axes = plt.subplots()
axes.plot(np.arange(count), np.round(cost_arr, 4), 'r')
axes.set_xlabel('Epoch')
axes.set_ylabel('loss')
axes.set_title('avg_cost vs. Epoch')
fig.savefig('p2.png')
公共函数请参照上一篇博客或者上上篇博客。























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








