下面翻译下field的基本属性
1.analyzer
对字段使用分词器,注意一般如果要使用分词器,字段的type一般是text。对于查询来说,也要指定相同的分词器,这样能保证查询和存储使用相同的格式。
分词器可以应用到field,index和查询中。es在存储时,分词器使用的优先级是:
- field最高
- index的次之
standard分词器
es在查询时,分词器优先级是:full-text query使用的分词器- 定义在field上的
search_analyzer分词器,是指term查询 - 定在在field上的
analyzer分词器 - 索引上的
default_search分词器 - 索引上的
default分词器 standard分词器
最简单的方式是直接在field定义分词器,不用向上去找其他定义的分词器,下面是一个例子,title使用默认的standard分词器,address使用english分词器
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
}
}
我们可以使用_analyze查看一个文本是怎么分词的
例如
GET my_index/_analyze
{
"field": "title",
"text": "The quick Brown Foxes."
}
对应的分词结果是:
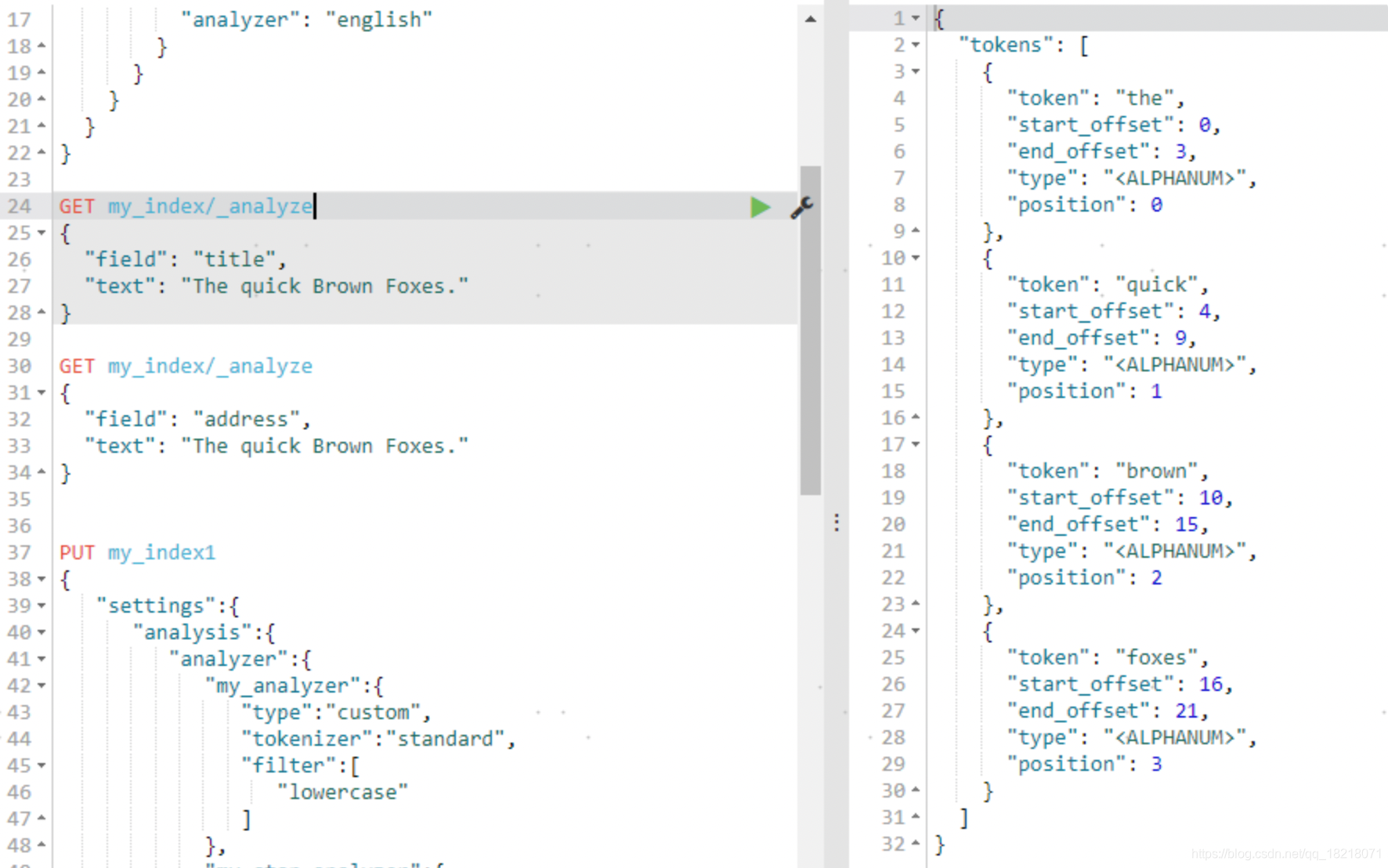
- search_quote_analyzer 短语查询分词
用于确定用引号的句子查询,对句子使用的分词方式,我们之所以使用带有引号的短语作为查询,一般都是想精确查询,这时候该功能就有用了,下面是例子,定义两个分词器:my_analyzer不会去除停顿词,my_stop_analyzer:去除停顿词。并放入两个文档。
PUT my_index
{
"settings":{
"analysis":{
"analyzer":{
"my_analyzer":{
"type":"custom",
"tokenizer":"standard",
"filter":[
"lowercase"
]
},
"my_stop_analyzer":{
"type":"custom",
"tokenizer":"standard",
"filter":[
"lowercase",
"english_stop"
]
}
},
"filter":{
"english_stop":{
"type":"stop",
"stopwords":"_english_"
}
}
}
},
"mappings":{
"my_type":{
"properties":{
"title": {
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"my_analyzer",
"search_analyzer":"my_stop_analyzer",
"search_quote_analyzer":"my_analyzer"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT my_index/my_type/1
{
"title":"The Quick Brown Fox"
}
PUT my_index/my_type/2
{
"title":"A Quick Brown Fox"
}
如果我们的查询条件是下面情况,则会返回两条数据,因为使用是my_stop_analyzer,去除查询中的停顿词。
GET my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query":{
"":{
"query":"the quick brown fox"
}
}
}
如果我们的查询条件是下面情况,则会返回第二条数据,因为使用是my_analyzer,不会去除the,精确查询。
GET my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query":{
"":{
"query":"\“the quick brown fox"\"
}
}
}
2.normalizer
对field设置为标准,例如把字段中的所有的大写转为小写等,下面是具体的例子
PUT index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"normalizer": {
"my_normalizer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": [],
"filter": ["lowercase", "asciifolding"]
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"type": {
"properties": {
"foo": {
"type": "keyword",
"normalizer": "my_normalizer"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT index/type/1
{
"foo": "BÀR"
}
PUT index/type/2
{
"foo": "bar"
}
PUT index/type/3
{
"foo": "baz"
}
GET index/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"foo": "BAR"
}
}
}
返回的结果是两个,因为在查询和索引的时候会把BAR都转为小写,其实文档1和2具有相同的含义。同样上面的情况在聚合也是一样的,1和2是同样的。
3.boost
提高field的得分权重,不建议使用。
4.coerce
是否可以使用强制转换,例如“5”可以放入integer的字段中。如果设置为false,则不可以使用该功能。可以在索引上设置默认的值 "index.mapping.coerce": true
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"number_one": {
"type": "integer"
},
"number_two": {
"type": "integer",
"coerce": false
}
}
}
}
}
可以正确的添加
PUT my_index/my_type/1
{
"number_one": "10"
}
失败:字符串不可以转成整型。
PUT my_index/my_type/2
{
"number_two": "10"
}
5.copy_to
把值拷贝到另一个字段中。一般是索引的_all设置为false,用于自定义新的组合字段。
6.doc_values
一般都是设置为true,支持除了text的字段所有的字段类型。排序、聚合、脚本等方式必须要设置为true。如果确定不使用字段聚合、排序、脚本查询等功能,可以设置为false,例如地址信息等,会节约磁盘空间,但是数据仍然会在_source中展示出来。
doc_values设置为false,对于查询仍然是可以用的,只是不能用于排序和聚合操作。
"session_id": {
"type": "keyword",
"doc_values": false
}
7.dynamic
设置索引新加字段field是否可以动态添加到索引mapping中。有三种值可以使用
true:新监听到的字段可以动态添加到mapping中false:新监听到字段会被忽略,不可以索引,也不可以被搜索到,但是会在_source中展示出来,(必须显示添加字段到mapping)strict:新监听到字段会抛出异常,必须显示添加字段到mapping
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type" : {
"dynamic": false,
"properties": {
"name" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"date" :{
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
},
"session_info" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"doc_values" : false
}
}
}
}
}
设置为false,添加数据如下,添加一个不存在的addr字段
POST my_index/my_type/1111
{
"name" : "zhangsan",
"age" : 19,
"addr" : "shanghai",
"session_info" : "one"
}
可以用其他字段查询

但是直接用addr查询,则查询不到

当设置为strict,则添加数据的时候,直接报错。
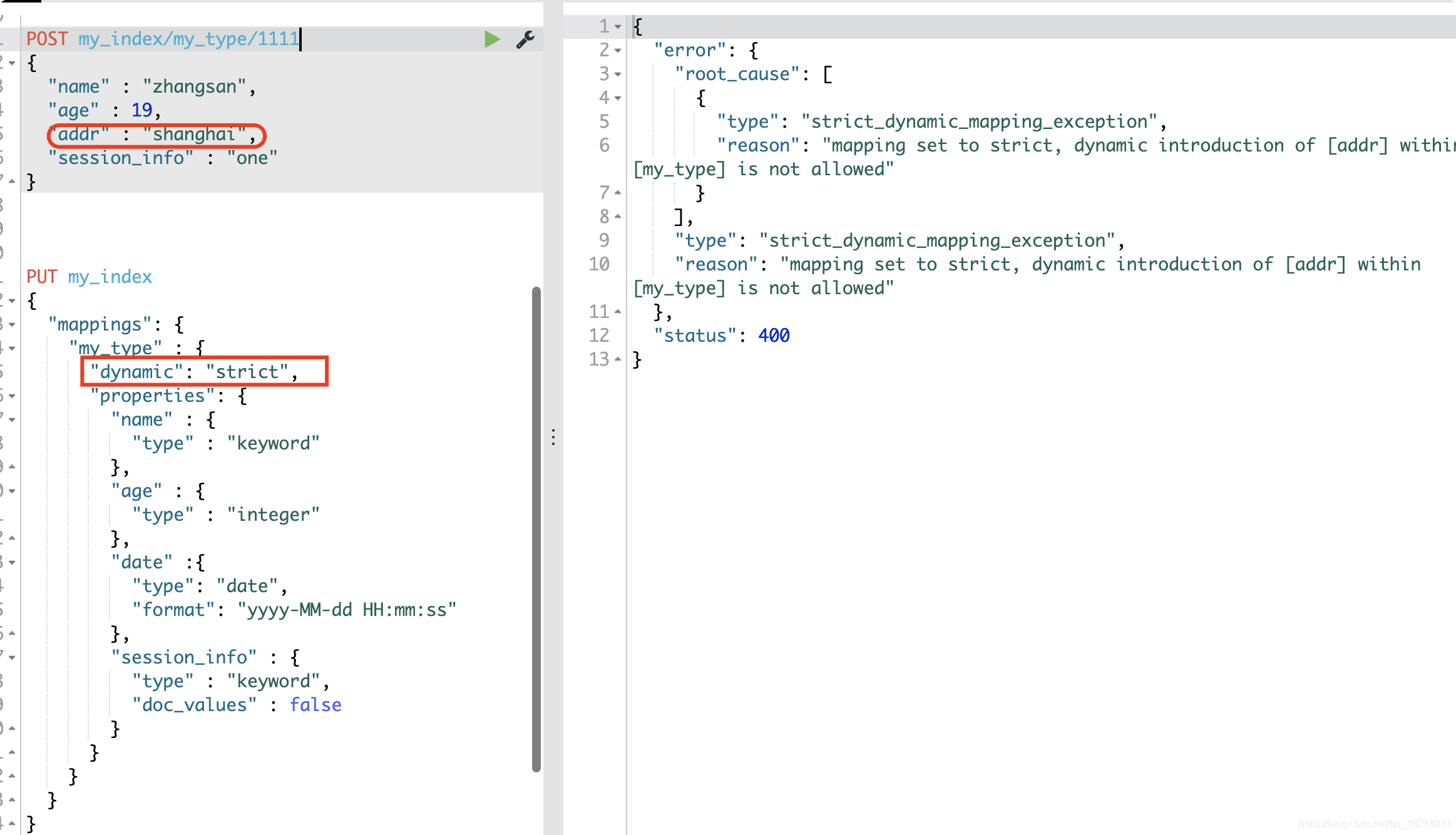
8.enabled
字段或者索引是否可以被检索,但是数据会存储下来,只是不能被查询。通常用于记录数据,例如用户反馈问题的正文,内容较大,只是存储展示,但是不需要检索。该字段可以放入任何样式的数据,因为es不会对其进行分析。
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type" : {
"properties": {
"name" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"session_info" : {
"enabled" : false
}
}
}
}
}
POST my_index/my_type/1111
{
"name" : "zhangsan",
"age" : 19,
"session_info" : "one"
}
也可以对整个索引设置为false,只是这时候只是用于存储数据,不能用任何字段检索,一般比较少用
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"session": {
"enabled": false
}
}
}
设置为false,只有一个作用就是记录数据,查询、排序、聚合等都不可用
9.fielddata
解决text类型字段不能用于排序、聚合的问题,但是该属性,默认值是false,因为会大大加大内存的压力,不鼓励使用。
"addr": {
"type": "text",
"fielddata":true
}
如果非要使用排序、聚合,建议使用下面方式,用addr.keyword进行聚合,排序。
"addr": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
10.format
定义日期时间格式,详细见 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18218071/article/details/113471974
11.ignore_above
对于字段内容过长的字段,超过指定的长度,该文档的字段将不可以被检索或者存储,一般该值设置为 256
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type" : {
"properties": {
"name" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above": 10
},
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"session_info" : {
"enabled" : false
}
}
}
}
}
插入两条数据
POST my_index/my_type/1111
{
"name" : "zhangsan",
"age" : 19,
"session_info" : "one"
}
POST my_index/my_type/2222
{
"name" : "zhangsan124578082432",
"age" : 19,
"session_info" : "one"
}
执行下面查询将不会有结果。
GET my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name": {
"value": "zhangsan124578082432"
}
}
}
}
注意该字段可以用于查询、排序或者聚合,因为有的文档并没有超过范围,只是对超过范围的文档不在存在作用
比如下图:排序的结果,数据作为null检索处理
12.ignore_malformed
允许当值插入字段时,因为字段类型配置不对,导致插入异常时,可以把该值设置为true,这时候就不会抛出异常,只是该字段不能被索引,其他字段可以正常插入。
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"number_one": {
"type": "integer",
"ignore_malformed": true
},
"number_two": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
}
可以正常插入,但是不能用foo检索
PUT my_index/my_type/1
{
"text": "Some text value",
"number_one": "foo"
}
抛出异常,整个文档都不可以插入
PUT my_index/my_type/2
{
"text": "Some text value",
"number_two": "foo"
}
在索引级别设置
“settings”: {
“index.mapping.ignore_malformed”: true
}
13.include_in_all
字段是否作为_all其中的一部分
14.index
设置字段是否索引,默认是true,如果是false则该字段不能被查询
15.fields
实现一个字段多种数据类型,例如下例name是全文检索的,但是我们也可以对其进行排序或者聚合等,其中kyname可以理解为附加名,如果不设置,默认是keyword。
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"number_one": {
"type": "integer"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"kyname" : {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
下面是查询方式:
GET my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name.kyname": {
"value": "ma yun"
}
}
}
}
16.null_value
给null设置默认值,name 的默认值是 "is null"
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"number_one": {
"type": "integer"
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword",
"null_value": "is null"
}
}
}
}
}
查询结果如下:

17.search_analyzer
显示指定搜索时分词器,默认是和索引是同一个,保证分词的一致性。
18.similarity
指定text检索相似性的算法
- BM25 默认算法
- classic TF/IDF算法
- boolean
19.store
对于es默认字段是可以索引的,但是不能store的,也就是字段可以被查询,但是不能检索原始值。(我也没理解),但是通常这是无所谓的,因为他们都会存在_source中,数据都是拿到的。但是对于大字段,我们不需要检索,那么我们就可以不store,节省磁盘空间。
该属性只要是设置_source的enabled为false时,其他字段可以被存储。
20.总结:
index:不可以搜索,但可以排序、聚合
enabled:不可以搜索,排序、聚合
doc_values:可以搜索,但不可以排序、聚合
store:可以搜索、排序、聚合
fielddata:是解决text字段不能排序、聚合的问题。
最后补充点:_source只是记录写入es中数据的原始数据,至于字段是否能搜索、排序、聚合和_source没有任何关系。因为是否被搜索、排序、聚合是由倒排索引决定的,也就是文档的词项是否存在倒排索引中。例如source中是name的值是 Quick star,当我们用标准分词器standard分词后,其实在倒排索引中是 quick 和 star词项,也就是你直接使用Quick查询,就查不到该文档了。使用quick可以查到。所以_source只是记录你写入es的数据的原始数据。至于es认识不认识你的查询,是看倒排索引中是否有你查询的词项的。

























 2695
2695

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








